87-08-1
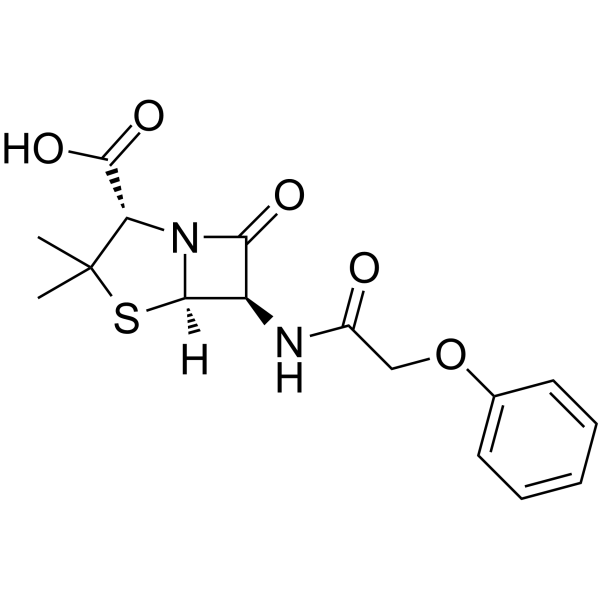
| Name | phenoxymethylpenicillin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
penicillin-V
Oracillin Pen-vee-oral Fenospen (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid Penicillin phenoxymethyl (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid PenicillinV Phenocillin Beromycin (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-{[(phenyloxy)acetyl]amino}-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid Phenopenicillin Acipen-V Phenomycilline Phenospen V-Cillin [2S-(2a,5a,6b)]-3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenoxy acetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid Orocillin penicillin V 6-phenoxyacetamidopenicillanic acid dowpen v-k penicillin VK Phenoxymethylpenicillin |
| Description | Penicillin V (Phenoxymethylpenicillin) is a potent and orally active antibiotic. Penicillin V shows antibacterial activity for Streptococci, Clostridium difficile and staphylococcus aureus. Penicillin V has the potential for the research of otitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis and tonsillitis[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Penicillin V (0.002-8.0 mg/L) inhibits the growth of Streptococci, with the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 0.004-0.008 mg/L[2]. Penicillin V (0.002-8.0 mg/L) shows antibacterial activity for Clostridium difficile with an MIC50 value of 4.0 mg/L and an MIC90 value of 8.0 mg/L[3]. Penicillin V (0.004-0.063 mg/L; 18 h) inhibits the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, with an MIC value of 0.016 mg/L[4]. |
| In Vivo | Penicillin V (0.063-0.25 mg/kg; s.c.) inhibits the outgrowth of S. aureus in mice thigh muscle[4]. Penicillin V (2 mg/kg; s.c.) exhibits the plasma half-life (61 min) and mean AUC (0.47 mg/L·h)[4]. Penicillin V (100 mg/kg; p.o. once daily for 5 d) avoids the fulminant infection of acute purulent otitis media (AOM) in rats[5]. Animal Model: Specific pathogen free (SPF) male Swiss mice (20-25 g) are inoculated S. aureus[4] Dosage: 0.063, 0.13, 0.25 mg/kg Administration: S.c. Result: Decreased the number of CFU (1.34×107 counts/mL) compared to controls (3.5×107 counts/mL) at the dose of 0.25 mg/kg. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 681.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 120 - 128ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C16H18N2O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 350.389 |
| Flash Point | 365.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 350.093628 |
| PSA | 121.24000 |
| LogP | 1.88 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.651 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | RY4025000 |
| HS Code | 3003101300 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 3003101300 |
|---|
![2-bromoethyl (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/479/65538-78-5.png)

![(4S)-2t-[(R)-tert-butoxycarbonyl-(2-phenoxy-acetylamino)-methyl]-5,5-dimethyl-thiazolidine-4r-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/415/1057-37-0.png)

![2-[(1,3-dioxoisoindol-2-yl)-tert-butoxycarbonyl-methyl]-5,5-dimethyl-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/053/59168-65-9.png)
![methyl 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenoxyacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/137/2315-05-1.png)