114568-26-2
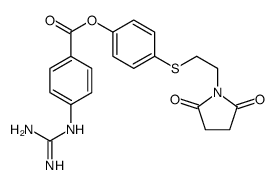
| Name | [4-[2-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)ethylsulfanyl]phenyl] 4-(diaminomethylideneamino)benzoate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Patamostat
p-((2-Succinimidoethyl)thio)phenyl p-guanidinobenzoate Benzoic acid,4-((aminoiminomethyl)amino)-,4-((2-(2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl)thio)phenyl ester Patamostat [INN] E 3123 4-(2-succinimidoethylthio)phenyl 4-guanidinobenzoate UNII-2T7W4EA51W |
| Description | Patamostat (E-3123) is a potent protease inhibitor. Patamostat potently inhibits trypsin, plasmin and thrombin with IC50s of 39 nM, 950 nM and 1.9 μM, respectively. E-3123 may possess suppressing effects on pathogenesis and development of acute pancreatitis[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 39 nM (trypsin), 950 nM (plasmin) and 1.9 μM (thrombin)[1] |
| In Vivo | Intravenous infusion of Patamostat (E-3123) at 0.03-0.3 mg/kg in rats or at 0.3-3.0 mg/kg in rabbits reduced mortality after the induction of pancreatitis in a dose-dependent manner. In dogs with pancreatitis, increases in serum trypsin and lipase activities were significantly reduced by infusion of Patamostat at 1.0 and 3.0 mg/kg[1]. Patamostat (E3123; continuous infusion in a dose of 2 mg/kg per h) improves almost all parameters, including mortality rate, serum and ascitic fluid amylase levels, plasma endotoxin and serum FDP levels, and distribution of lysosomal enzyme in male Wistar rats[2]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats weighing about 350 g[2] Dosage: 2 mg/kg Administration: Continuous infusion per h for 1 h Result: Significantly improved the survival rate. |
| References |
| Density | 1.41g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 701.5ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H20N4O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 412.46200 |
| Flash Point | 378.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 412.12100 |
| PSA | 150.88000 |
| LogP | 3.26320 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.58E-19mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.678 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~% 
114568-26-2 |
| Literature: Nochi; Shimomura; Hattori; Sato; Miyake; Tanizawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1989 , vol. 37, # 10 p. 2855 - 2857 |