158966-92-8
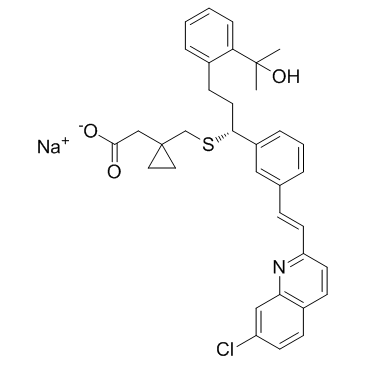
| Name | montelukast |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
[3H]-Montelukast
Brondilat (TN) Montelukast (1-{1-{3(R)-[2-(7-chloro-quinolin-2-yl)-vinyl]-phenyl}-3-[2-(1-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethyl)-phenyl]-propylsulfanylmethyl}-cyclopropyl)-acetic acid {1-[({(1R)-1-{3-[(E)-2-(7-Chloroquinolin-2-yl)vinyl]phenyl}-3-[2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]propyl}sulfanyl)methyl]cyclopropyl}acetic acid Montair 2-[1-[[(1R)-1-[3-[(E)-2-(7-chloroquinolin-2-yl)ethenyl]phenyl]-3-[2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]propyl]sulfanylmethyl]cyclopropyl]acetic acid Singular [R-(E)]-1-[[[1-[3-[2-(7-Chloro-2-quinolinyl)ethenyl]phenyl]-3-[2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)phenyl]propyl]thio]methyl]cyclopropaneacetic Acid {1-[({(1R)-1-{3-[(E)-2-(7-Chloro-2-quinolinyl)vinyl]phenyl}-3-[2-(2-hydroxy-2-propanyl)phenyl]propyl}sulfanyl)methyl]cyclopropyl}acetic acid Montelukast [INN:BAN] MFCD05662278 Montelukast (INN) {1-[({(1R)-1-{3-[(E)-2-(7-chloroquinolin-2-yl)ethenyl]phenyl}-3-[2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)phenyl]propyl}sulfanyl)methyl]cyclopropyl}acetic acid [14C]-Montelukast UNII-MHM278SD3E |
| Description | Montelukast is a potent, selective and orally active antagonist of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (CysLT1). Montelukast can be used for the reseach of asthma and liver injury. Montelukast also has an antioxidant effect in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury, and could reduce cardiac damage[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CysLT1 |
| In Vitro | Montelukast (5 μM; 1 h) inhibits APAP-induced cell damage[1]. |
| In Vivo | Montelukast (3 mg/kg; oral gavage) protects against APAP-induced hepatotoxicity in mice[1]. Montelukast (1 mg/kg; miniosmotic pump administration) reduces the airway remodeling changes observed in OVA-treated mice and blocks the actions of cysteinyl leukotrienes (LT) C4, D4, and E4 mediated by the CysLT1 receptor[2]. Montelukast (1 mg/kg; miniosmotic pump administration) reduces the elevated levels of IL-4 and IL-13 found in the BAL fluid of OVA-treated mice[2]. Animal Model: C57BL/6J mice (8-week-old; 22-25 g) are induced acute hepatic injury[1] Dosage: 3 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage 1 h after saline or APAP administration Result: Decreased serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alleviated liver damage. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 750.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C35H36ClNO3S |
| Molecular Weight | 586.183 |
| Flash Point | 407.7±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 585.210449 |
| PSA | 95.72000 |
| LogP | 7.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.678 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
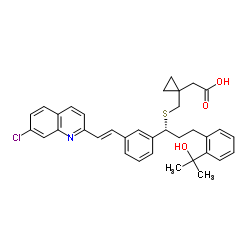
![(1-{1-(R)-(3-bromophenyl)-3-[2-(1-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethyl)-phenyl]-propylsulfanylmethyl}-cyclopropyl)-acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/276/1015076-80-8.png)
![(1S)-1-{3-[(E)-2-(7-Chloro-2-quinolinyl)vinyl]phenyl}-3-[2-(2-hyd roxy-2-propanyl)phenyl]-1-propanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/477/287930-77-2.png)
![2-[1-(Mercaptomethyl)cyclopropyl]acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/092/162515-68-6.png)