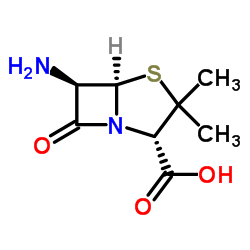
642-78-4
| Name | cloxacillin sodium |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Tegopen
4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-[[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, sodium salt, (2S,5R,6R)-, hydrate (1:1:1) Staphybiotic Sodium cloxacillin cloxacillin sodium hydrate Ankerbin Cloxapen Austrastaph (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[3-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid Sodium Salt Monohydrate Prevencilina P Cloxacillin sodium salt hydrate Sodium cloxacillin monohydrate cloxacillin sodium monohydrate Orbenin Sodium (2S,5R,6R)-6-({[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate hydrate (1:1:1) MFCD00150735 Prostaphilin A Ekvacillin [(2S,5R,6R)-6-({[3-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylato-κO]sodium hydrate (1:1) sodium, [(2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylato-κO]-, hydrate (1:1) Cloxacillin Sodium Salt EINECS 211-390-9 Gelstaph Monosodium (2S,5R,6R)-6-(3-(o-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate Monohydrate Cloxacillin Sodium |
| Description | Cloxacillin sodium exhibits antibiotic efficacy, with a MIC of 256 mg/L for Staphylococcus aureus 25923[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the study of a number of bacterial infections[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: Strains M12 and M60. Concentration: 0.5 μg/mL. Incubation Time: 4-24 h. Result: Significantly reduced the bacterial numbers. |
| In Vivo | Cloxacillin sodium (50 mg/kg, Subcutaneously) results a significant antibiotic efficacy against S. aureus[3] Animal Model: Mice[2]. Dosage: 10 mg/kg (Pharmacological Analysis). Administration: Given subcutaneously. Result: Reached a maximal concentration in plasma of 8.4 μg/mL at 10 min and had a half-life of approximately 15 min. Animal Model: Mice injected with approximately 2 × 106 CFU of bacteria in 0.1 mL saline were aseptically injected into the right thigh muscle[3]. Dosage: 0–500 mg/kg. Administration: Subcutaneously in the nuchal region at 1 h after infection. Result: Resulted in a significant decrease in the number of viable S. aureus measured 18 h thereafter. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 170ºC |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H17ClN3NaO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 475.878 |
| Exact Mass | 475.058075 |
| PSA | 140.87000 |
| LogP | 1.54280 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Refrigerate. |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38-42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S22 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | XH8920000 |
| HS Code | 2941109900 |
|
~% 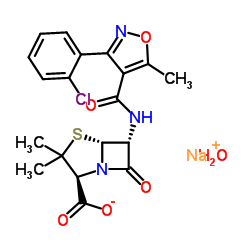
642-78-4 |
| Literature: WO2012/164355 A1, ; Page/Page column 9-10 ; |
|
~% 
642-78-4 |
| Literature: WO2012/164355 A1, ; |
|
~% 
642-78-4 |
| Literature: WO2012/164355 A1, ; |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2941109900 |
|---|