34273-10-4
| Name | Saralasin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Saralasin
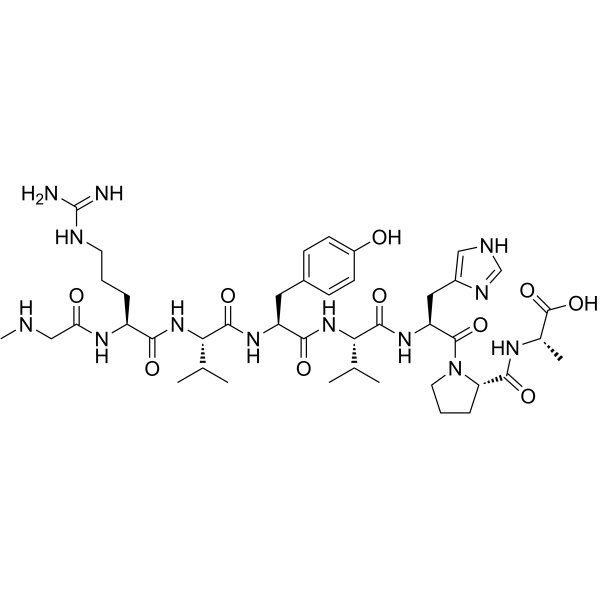
1-(N-Methylglycine)-5-L-valine-8-L-alanineangiotensin II Sar-Arg-Val-Tyr-Val-His-Pro-Ala H-Sar-Arg-Val-Tyr-Val-His-Pro-Ala-OH 1-Sar-8-ala-angiotensin II M.W. 912.05 C42H65N13O10 N-Methylglycyl-N-(diaminomethylene)-L-ornithyl-L-valyl-L-tyrosyl-L-valyl-L-histidyl-L-prolyl-L-alanine Sar-L-Arg-L-Val-L-Tyr-L-Val-L-His-L-Pro-L-Ala-OH N-[1-[N-[N-[N-[N-[N2-(N-methylglycyl)-L-arginyl]-L-valyl]-L-tyrosyl]-L-valyl]-L-histidyl]-L-prolyl]-L-alanine Sar-RVYVHPA SAR-ARG-VAL-TYR-VAL-HIS-PRO-ALA-OH MFCD00133980 [Sar1,Val5, Ala8] Angiotensin II SAR-ARG-VAL-TYR-VAL-HIS-PRO-ALA: SAR-RVYVHPA (Sar1,Val5,Ala8)-Angiotensin II |
| Description | Saralasin ([Sar1,Ala8] Angiotensin II) is an octapeptide analog of angiotensin II. Saralasin is a competitive angiotensin II receptor antagonist with a Ki value of 0.32 nM for 74% of the binding sites, and has partial agonist activity as well. Saralasin can be used for the research of renovascular hypertension, renin-dependent (angiotensinogenic) hypertension[1][3][6]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.32 nM (Angiotensin II receptor)[3] |
| In Vitro | Saralasin (1 nM, 48 or 72 h) inhibits cell growth in 3T3 and SV3T3 cells[1]. Saralasin (5 μM, 2h) restores Ito, fast (Fast-Inactivating Transient Outward K+ Current in Mouse Ventricle) and I K, slow (Slow-Inactivating Transient Outward K+ Current in Mouse Ventricl) to control levels in myocytes[2]. Saralasin (0.1-10 nM, 40 min) inhibits binding of FITC-Ang II to rat liver membrane preparation (used as the source of angiotensin receptors) with a Ki value of 0.32 nM for 74% of the binding sites and 2.7 nM for the remaining binding sites[3]. Saralasin (1 μM, perfused rat ovary in vitro) inhibits the ovulation rate versus control and reduces prostaglandin E2 and 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α levels[4]. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: 3T3 and SV3T3 cells Concentration: 1 nM Incubation Time: 48 h, 72 h Result: Inhibited cell growth in 3T3 and SV3T3 cells and caused an increase of cellular renin concentration. |
| In Vivo | Saralasin (intravenous injection, 5-50 μg/kg, a single dose) ameliorates the oxidative stress and tissue injury in cerulein-induced pancreatitis[5]. Saralasin (subcutaneous injection, 10 and 30 mg/kg, a single dose) increases serum renin activity (SRA) in normal, conscious rats, without markedly altering blood pressure or heart rate[6]. Animal Model: Cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis rats model[5] Dosage: 5, 10, 20, and 50 μg/kg, a single dose. Administration: Intravenous injection Result: Restored the pancreatic morphological characteristics to the control level. Reduced pancreatic injury and suppressed the glutathione depletion induced by cerulean. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats[6] Dosage: 10 and 30 mg/kg, a single dose. Administration: Subcutaneous injection Result: Stimulated renin release without altering blood pressure or heart rate at the time of measuring serum renin levels 20 minutes after injection. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C42H65N13O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 912.047 |
| Exact Mass | 911.497742 |
| PSA | 355.05000 |
| LogP | -0.27 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.654 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|