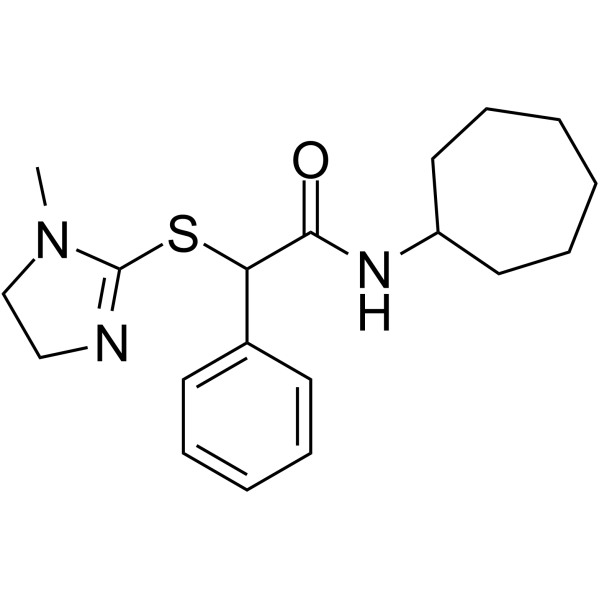
| Description |
Apostatin-1 (Apt-1) is a potent TRADD inhibitor. Apostatin-1 can bind with TRADD-N (KD=2.17 μM), disrupting its binding to both TRADD-C and TRAF2. Apostatin-1 modulates the ubiquitination of RIPK1 and beclin 1. Apostatin-1 blocks apoptosis and restores cellular homeostasis by activating autophagy in cells with accumulated mutant tau, α-synuclein, or huntingtin[1].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Apostatin-1 inhibits Velcade (bortezomib)-induced apoptosis and RIPK1-dependent apoptosis (RDA) and necroptosis, with an IC50 of 0.97 μM[1]. Apostatin-1 (10 μM, 6 h) effectively induces autophagy and the degradation of long-lived proteins[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: SH-SY5Y, HeLa, HT-29, and Jurkat cells Concentration: 10 μM Incubation Time: 6 h Result: Effectively induced autophagy by LC3 II induction and p62 reduction.
|
| In Vivo |
Apostatin-1 (20 mg/kg, IP, once) inhibits inflammatory responses, and increases survival of systemic inflammation mouse model[1]. Animal Model: Wild-type mice (n = 10, male, 8 weeks of age, systemic inflammation mouse model)[1] Dosage: 20 mg/kg Administration: IP, once Result: Reduced expression of the TNF-induced inflammatory target gene products, NOS and COXII27, and of inflammatory cytokines in cells stimulated with pathogen-associated molecular patterns, including interferon γ (IFNγ), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), Pam3CSK4 (a synthetic bacterial lipopeptide), and muramyl dipeptide (MDP). Showed increased survival following intravenous delivery of TNF, a mouse model of systemic inflammation.
|
| References |
[1]. Xu D, et al. Modulating TRADD to restore cellular homeostasis and inhibit apoptosis. Nature. 2020 Nov;587(7832):133-138.
|