14930-96-2
| Name | cytochalasin B |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EINECS 239-000-2
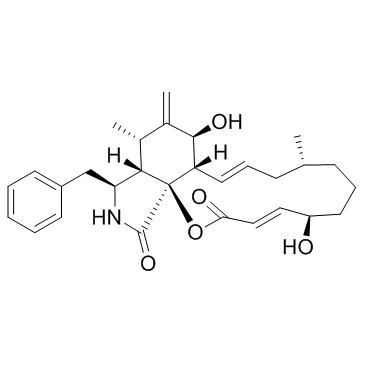
(3E,5R,9R,11E,12aS,13S,15S,15aS,16S,18aS)-16-Benzyl-5,13-dihydroxy-9,15-dimethyl-14-methylene-6,7,8,9,10,12a,13,14,15,15a,16,17-dodecahydro-2H-oxacyclotetradecino[2,3-d]isoindole-2,18(5H)-dione Phomin (3E,5R,9R,11E,12aS,13S,15S,15aS,16S,18aS)-16-benzyl-5,13-dihydroxy-9,15-dimethyl-14-methylidene-6,7,8,9,10,12a,13,14,15,15a,16,17-dodecahydro-2H-oxacyclotetradecino[2,3-d]isoindole-2,18(5H)-dione Cytochalasin B MFCD00077704 |
| Description | Cytochalasin B is a cell-permeable mycotoxin binding to the barbed end of actin filaments, disrupting the formation of actin polymers, with Kd value of 1.4-2.2 nM for F-actin. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 2.2 nM (F-actin, with Mg2+), 1.4 nM (F-actin, with Mg2+/K+)[1] |
| In Vitro | Cytochalasin B is a cell-permeable mycotoxin binding to the barbed end of actin filaments, inhibits the enlongation and shortening of actin filaments, with Kds of 2.2 nM and 1.4 nM for F-actin in the presence of MgCl2 (2 mM) or MgCl2 (2 mM) plus KCl, respectively[1]. Cytochalasin B (0.1-10 μM) shows inhibitory effect on multiple murine cancer cell lines, with IC50s of 2.56 μM (M109c), 10.46 μM (B16BL6), 105.5 μM (P388/ADR), 51.9 μM (P388/S) and IC80s of 12.23 μM (M109c), 44.86 μM (B16BL6), 188.4 μM (P388/ADR), 84.1 μM (P388/S) after treatment for 3 h, with IC50s of 0.25 μM (M109c), 0.37 μM (B16F10), 0.87 μM (B16BL6), and IC80s of 0.75 μM (M109c), 1.21 μM (B16F10), 10.41 μM (B16BL6) after treatment for 4 days[2]. Cytochalasin B (6 μM) increases the myofibrillar fragmentation index (MFI), which is attributed to the intensely breaking of myofibrillar proteins into short segments. Cytochalasin B also accelerates the disruption of actin filaments. In addition, Cytochalasin B accelerates the transformation from F-actin to G-actin, lowering the content of F-actin and significantly increasing G-actin bands during postmortem conditioning[3]. |
| In Vivo | Cytochalasin B (10, 25, 50 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently increases the life expectancy of Balb/c mice bearing with P388/ADR leukemias. Cytochalasin B at 50 mg/kg produces 10 % long-term survival in the multidrug resistant P388/ADR cohort, and 40 % long-term survival in the drug sensitive P388/S cohort[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The attached cell lines M109c, B16BL6, and B16F10 are seeded at 1 to 4 × 104 cells/mL in 2 mL volumes in 24-well culture plates 1 day prior to treatment with Cytochalasin B. The suspension culture of P388/ADR cells is seeded at 5 × 104 cells/mL and allowed to grow overnight before Cytochalasin B treatment. Cells are treated with Cytochalasin B for 3 h, as well as 2, 3, or 4 days. In the case of continuous exposure for 2, 3, or 4 days, attached cells are trypsinized and counted with a hemacytometer. Leukemia cell suspensions are counted with a Coulter Counter. In the case of short-term exposure, cells are washed twice with fresh medium, then trypsinized (except for P388/ADR cells), reseeded, and allowed to regrow for 3 days, at which time they are counted. Growth results are calculated as the number of cells generated above the seeding density compared to the untreated control cells and graphically presented as percent of control increase[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] For chemotherapy testing, Balb/c mice under isoflurane anesthesia are challenged with 2 × 105 trypan blue negative P388/S or P388/ADR cells subcutaneously (s.c.) in a volume of 200 μL. Untreated mice are kept in order to determine the lethality of the challenge without chemotherapeutic intervention. Long-term survival is defined as challenged mice that survive the duration of the observation period. Cytochalasins B and D are prepared in suspension form in 2 % carboxymethyl cellulose 1 % tween 20 (CMC/Tw) for intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration. The congeners or the vehicle are administered to leukemia-challenged mice on Days 1-8 following the initial challenge[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 740.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 218-223ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C29H37NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 479.608 |
| Flash Point | 401.7±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 479.267181 |
| PSA | 95.86000 |
| LogP | 3.71 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: 20 mg/mL |
Synonym:None Known Section 2 - COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Risk Phrases: 26/27/28 40 Section 3 - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION EMERGENCY OVERVIEW
Very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect. Potential Health Effects Eye: May cause eye irritation. Skin: May cause skin irritation. Ingestion: May cause irritation of the digestive tract. May cause cardiac disturbances. May cause central nervous system depression. Inhalation: May cause respiratory tract irritation. May cause cardiac abnormalities. Inhalation at high concentrations may cause CNS depression and asphixiation. Chronic: Effects may be delayed. Adverse reproductive effects have been reported in animals. Laboratory experiments have resulted in mutagenic effects. Section 4 - FIRST AID MEASURES Eyes: Flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Get medical aid. Skin: Get medical aid. Flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing before reuse. Ingestion: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical aid. Do NOT induce vomiting. If conscious and alert, rinse mouth and drink 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Inhalation: Remove from exposure and move to fresh air immediately. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Get medical aid. Notes to Physician: Section 5 - FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES General Information: As in any fire, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus in pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent), and full protective gear. During a fire, irritating and highly toxic gases may be generated by thermal decomposition or combustion. Containers may explode when heated. Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution. Extinguishing Media: Use water spray to cool fire-exposed containers. For small fires, use dry chemical, carbon dioxide, or water spray. For large fires, use dry chemical, carbon dioxide, alcohol-resistant foam, or water spray. Section 6 - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES General Information: Use proper personal protective equipment as indicated in Section 8. Spills/Leaks: Vacuum or sweep up material and place into a suitable disposal container. Clean up spills immediately, observing precautions in the Protective Equipment section. Avoid generating dusty conditions. Provide ventilation. Section 7 - HANDLING and STORAGE Handling: Wash thoroughly after handling. Use with adequate ventilation. Minimize dust generation and accumulation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Keep container tightly closed. Avoid ingestion and inhalation. Storage: Store in a tightly closed container. Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances. Poison room locked/refrigerator. Section 8 - EXPOSURE CONTROLS, PERSONAL PROTECTION Engineering Controls: Facilities storing or utilizing this material should be equipped with an eyewash facility and a safety shower. Use adequate ventilation to keep airborne concentrations low. Exposure Limits CAS# 14930-96-2: Personal Protective Equipment Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN166. Skin: Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure. Clothing: Wear appropriate protective clothing to minimize contact with skin. Respirators: Follow the OSHA respirator regulations found in 29 CFR 1910.134 or European Standard EN 149. Use a NIOSH/MSHA or European Standard EN 149 approved respirator if exposure limits are exceeded or if irritation or other symptoms are experienced. Section 9 - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Powder Color: white Odor: None reported. pH: Not available. Vapor Pressure: Not available. Viscosity: Not available. Boiling Point: Not available. Freezing/Melting Point: 221.00 - 223.00 deg C Autoignition Temperature: Not applicable. Flash Point: Not applicable. Explosion Limits, lower: Not available. Explosion Limits, upper: Not available. Decomposition Temperature: Solubility in water: insoluble Specific Gravity/Density: Molecular Formula: C29H37NO5 Molecular Weight: 479.60 Section 10 - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Chemical Stability: Stable under normal temperatures and pressures. Conditions to Avoid: Incompatible materials, dust generation, excess heat, strong oxidants. Incompatibilities with Other Materials: Oxidizing agents. Hazardous Decomposition Products: Nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, irritating and toxic fumes and gases, carbon dioxide. Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported. Section 11 - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION RTECS#: CAS# 14930-96-2: RO0205000 LD50/LC50: Not available. Carcinogenicity: Cytochalasin B - Not listed by ACGIH, IARC, or NTP. Other: See actual entry in RTECS for complete information. Section 12 - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Section 13 - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Dispose of in a manner consistent with federal, state, and local regulations. Section 14 - TRANSPORT INFORMATION IATA Shipping Name: TOXIC SOLID, ORGANIC, N.O.S.* Hazard Class: 6.1 UN Number: 2811 Packing Group: II IMO Shipping Name: TOXIC SOLID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. Hazard Class: 6.1 UN Number: 2811 Packing Group: II RID/ADR Shipping Name: TOXIC SOLID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. Hazard Class: 6.1 UN Number: 2811 Packing group: II Section 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION European/International Regulations European Labeling in Accordance with EC Directives Hazard Symbols: T+ Risk Phrases: R 26/27/28 Very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R 40 Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect. Safety Phrases: S 1 Keep locked up. S 28A After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of water. S 37 Wear suitable gloves. S 45 In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible). WGK (Water Danger/Protection) CAS# 14930-96-2: No information available. Canada None of the chemicals in this product are listed on the DSL/NDSL list. CAS# 14930-96-2 is listed on Canada's Ingredient Disclosure List. US FEDERAL TSCA CAS# 14930-96-2 is not listed on the TSCA inventory. It is for research and development use only. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H330 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P284-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R26/27/28;R63 |
| Safety Phrases | 28-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 6 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RO0205000 |
| Packaging Group | I |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| HS Code | 29349990 |
|
~% 
14930-96-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 105, # 16 p. 5510 - 5512 |
|
~% 
14930-96-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 105, # 16 p. 5510 - 5512 |
|
~% 
14930-96-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 105, # 16 p. 5510 - 5512 |
|
~% 
14930-96-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 105, # 16 p. 5510 - 5512 |
|
~% 
14930-96-2 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 105, # 16 p. 5510 - 5512 |
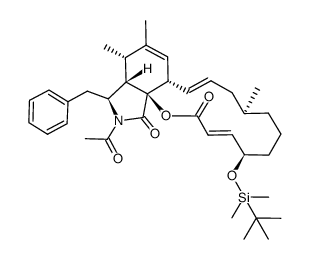
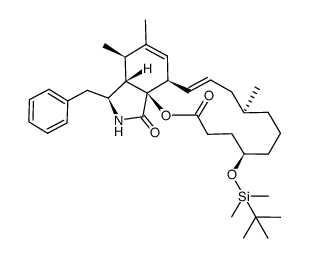
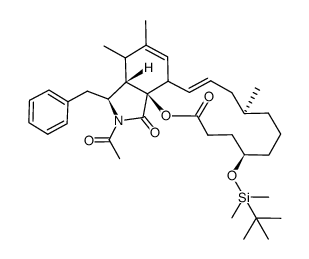
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
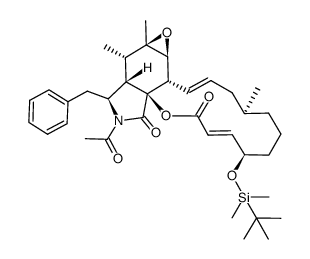
| DownStream 1 | |