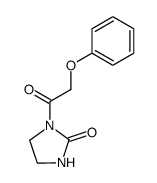
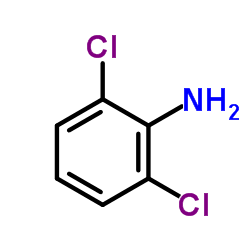
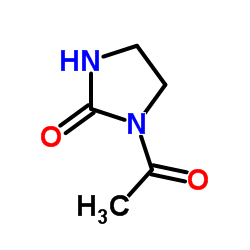
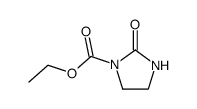
4205-91-8
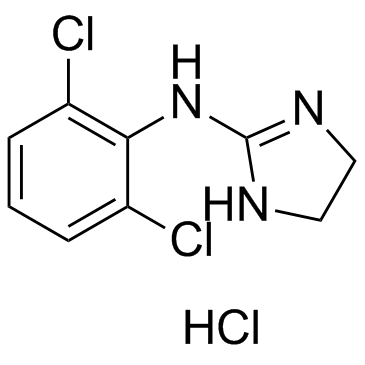
| Name | Clonidine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(2,6-dichlorophenyl)imidazolidin-2-ylidene-amine hydrochloride
ipotensium catapresan klophelin Clonidine hydrochloride Isoglaucon N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)imidazolidin-2-imine hydrochloride (1:1) dcai hemiton Dixarit MFCD00036705 Clonidine HCl Clonidine monohydrochloride capresin Neuclon 2,6-Dichloro-N-2-imidazolidinylidenebenzenamine Monohydrochloride 2,6-dichloro-N-imidazolidin-2-ylideneaniline hydrochloride clofelin clonidine hydrochloride salt Clonistada Tenso-Timelets EINECS 224-121-5 2-(2,6-Dichlorophenylamino)-2-imidazoline Hydrochloride 2,6-Dichloro-N-(imidazolidin-2-ylidene)aniline hydrochloride (1:1) atensina DURACLON haemiton (2,6-dichloro-phenyl)-imidazolidin-2-ylidene-amine,hydrogen chloride 2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)-2-iMidazoline Hydrochloride Catapressan N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-amine hydrochloride (1:1) Catapres 1H-Imidazol-2-amine, N-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-, hydrochloride (1:1) Clonidine (hydrochloride) |
| Description | Clonidine hydrochloride is an agonist of α2-adrenoceptor and potent antihypertensive agent. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Clonidine (0.01, 0.1 or 1 μM) significantly induces CGRP (α and β) mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner in endothelial cells. Clonidine treatment (1 μM) for 24 h significantly increases the NO level in endothelial cells. NO pathway modulates CGRP production induced by clonidine[2]. |
| In Vivo | Clonidine (50 μg/kg, i.p.) induces a significant decrease in body temperature of rat lasting 3 hr, with the maximum at 1 hr after administration. An intracerebroventricular pretreatment of rats with neutral doses of phentolamine 15 min before clonidine considerably antagonizes the clonidine-induced hypothermia[1]. Clonidine (0.003-0.05 mg/kg, i.p.) potently suppresses dopamine efflux in the prefrontal cortex induced by PCP. Pretreatment with the alpha-2A receptor antagonist (BRL-44408) prevents clonidine from suppressing PCP-induced dopamine overflow in the prefrontal cortex[3]. In DMSO-pretreated SO rats, clonidine (0.6 μg i.c.) has no effect on blood pressure. However, after central adenosine A1R blockade (DPCPX) in SO rats, clonidine significantly (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA) reduces blood pressure. In contrast, in DMSO-pretreated ABD rats, clonidine (0.6 μg i.c.) causes significant reduction in blood pressure; importantly, central A1R blockade (DPCPX pretreatment) does not influence (P > 0.05, one-way ANOVA) clonidine-evoked reduction in blood pressure in ABD rats. In DPCPX-pretreated SO rats and along with the appearance of the hypotensive response, clonidine causes a significant (P < 0.05) increase in the RVLM pERK1/2 level compared with basal or clonidine treatment in DMSO-pretreated SO rats. In vehicle (DMSO)-pretreated ABD rats, clonidine significantly (P < 0.05) enhances RVLM pERK1/2, and this response is not affected by DPCPX pretreatment[4]. |
| Animal Admin | On the day of the experiment, the flow rate is increased to 2 μL/min approximately 2 h before beginning the collection of baseline samples. Dialysates are collected every 20 min; after 4 baseline samples are collected, animals are pretreated with an intra-peritoneal (i.p.) injection of either 0.9% saline (the vehicle), clonidine (0.0033, 0.01 or 0.05 mg/kg) or guanfacine (0.05 or 0.5 mg/kg), before receiving an injection of PCP (2.5 mg/kg, i.p.) 20 min later. In a separate study, BRL (1.0 mg/kg) is administered 20 min prior to clonidine. In addition, for some control experiments, the animals only receive one injection of saline, clonidine (0.01 or 0.05 mg/kg), guanfacine (0.5 mg/kg) or BRL (1.0 mg/kg). |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 319.3ºC at760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 312 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10Cl3N3 |
| Molecular Weight | 266.555 |
| Flash Point | 146.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 264.994019 |
| PSA | 36.42000 |
| LogP | 3.00390 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H330 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P260-P304 + P340 + P310-P403 + P233 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+:Verytoxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25;R26 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S28-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NJ2490000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|
~% 
4205-91-8 |
| Literature: Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH Patent: US3931216 A1, 1976 ; |
|
~% 
4205-91-8 |
| Literature: Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH Patent: US3931216 A1, 1976 ; |
|
~% 
4205-91-8 |
| Literature: Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH Patent: US3931216 A1, 1976 ; |
|
~% 
4205-91-8 |
| Literature: Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH Patent: US3931216 A1, 1976 ; |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933290090. other compounds containing an unfused imidazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |