123931-40-8
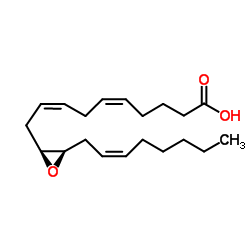
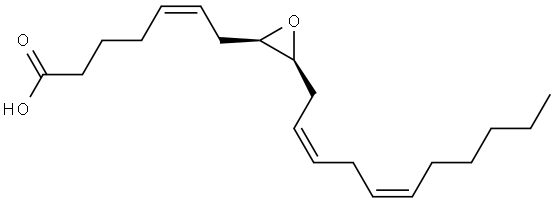
| Name | 11,12-Epoxy-(5Z,8Z,14Z)-eicosatrienoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(5Z,8Z)-10-{(2S,3R)-3-[(2Z)-2-Octen-1-yl]-2-oxiranyl}-5,8-decadienoic acid
(11S,12R)-EET (5Z,8Z)-10-{(2S,3R)-3-[(2Z)-oct-2-en-1-yl]oxiran-2-yl}deca-5,8-dienoic acid (5Z,8Z)-10-{(2S,3R)-3-[(2Z)-2-Octen-1-yl]-2-oxiranyl}-5,8-decadie noic acid |
| Description | (±)11(12)-EET is a NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor. (±)11(12)-EET can be used for the research of anti-inflammatory, angiogenic and cardioprotective[1][2][3][4][6]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NLRP3 inflammasome |
| In Vitro | (±)11(12)-EET (5 μM; 10 mimutes; macrophages) depresses NLRP3 protein expression, dramatically decreases the expression of pro-IL-1β in cells and the supernatant and reduces the intracellular ROS[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Macrophages Concentration: 5 μM Incubation Time: 10 mimutes Result: Depresses NLRP3 protein expression. Immunofluorescence[1] Cell Line: Macrophages Concentration: 5 μM Incubation Time: 10 mimutes Result: Reduced the intracellular ROS. |
| In Vivo | (±)11(12)-EET increases adhesion of isolated peripheral blood leukocytes in a chamber coated with P-selectin and ICAM-1 in 50 µg/kg[5]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 461.8±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H32O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 320.466 |
| Flash Point | 154.6±18.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 320.235138 |
| PSA | 49.83000 |
| LogP | 6.30 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.501 |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| RIDADR | UN1170 - class 3 - PG 2 - Ethanol, solution |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |