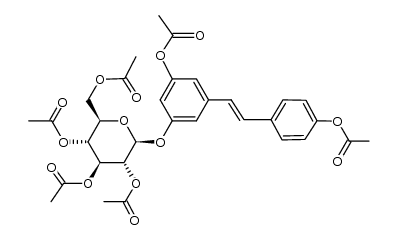
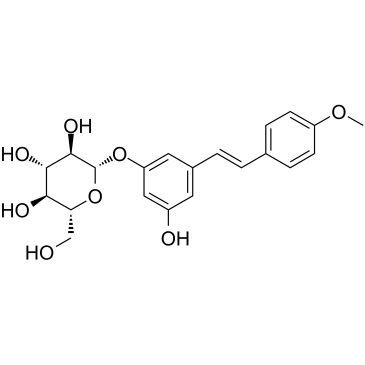
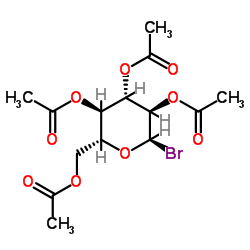
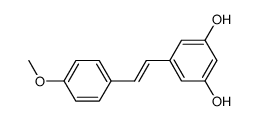
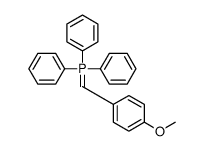
27208-80-6
| Name | trans-piceid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Resveratrol 3-O-glucoside
3-Hydroxy-5-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenyl-b-D-glucopyranoside β-D-Glucopyranoside, 3-hydroxy-5-(2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl)phenyl trans-polydatin 3-Hydroxy-5-(p-hydroxystyryl)phenyl Glucoside β-D-Glucopyranoside, 3-hydroxy-5-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenyl MFCD00210592 3-hydroxy-5-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside Piceid trans-Piceid Resveratrol 3-Glucoside Polydotin peceid Pieceid Plydatin 4',5-Dihydroxystilben-3-yl β-D-Glucopyranoside Resveratrol-3-b-mono-D-glucoside 3,4',5-Trihydroxystilbene-3-b-glucoside 3-Hydroxy-5-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)vinyl]phenyl β-D-glucopyranoside RESVERATROL GLUCOSIDE Polydatin |
| Description | Polydatin (Piceid), extracted from the roots of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb, a widely used traditional Chinese remedies, possesses anti-inflammatory activity in several experimental models. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NF-κB, Autophagy |
| In Vitro | Polydatin protects cerebral cells from ischemic damages via improvement of microcirculation and inhibition of platelet aggregation. In addition, polydatin inhibits ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells stimulated by lipopolysaccharide; it also attenuates adhesion between white blood cells and endothelial cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | Polydatin could significantly increase the activity of SOD and the heart rate, attenuate myocardial pathological damage, decrease MDA content, slightly increase arterial pressure and GSH-Px activity, reduce intervals of QRS, QT and ST, and lower FFA content[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The effect of polydatin on mMEC viability is evaluated with an MTT assay. mMECs are incubated in the presence or absence of various concentrations of polydatin (25, 50 and 100 μg/mL) and DEX (100 μg/mL) for 24 h. Next, 20 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL) is added to each well and incubated for 4 h. After the supernatants are removed and the formazan is dis¬solved with 150 μL of DMSO in each well, the optical density (OD) value is measured at 570 nm on a microplate reader[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Rats are divided into six groups by random assignment and treated as follows: in normal group and polydatin control group: rats are administrated with CMC-Na and polydatin (200 μmol/kg) by gavage respectively, and given normal saline (NS) by tail intravenous (iv) injection with the same volume; in DOX group: rats are injected with DOX by cauda vein for 4 weeks (3 mg/kg per week), the cumulative dosage is 12 mg/kg similar to that in the research of Chang et al[2]. Mice: Polydatin is dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM). Sixty adult female postpartum and lactating BALB/c mice (6–8 weeks old, weighing 35–40 g) are obtained. Control group (CG): The mice are treated with 100 μL of PBS as a vehicle control. Polydatin groups: 24h after S aureus infection, the mouse model of S aureus mastitis is intraperitoneally administered polydatin at 15, 30 and 45 mg/kg[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 707.7±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 223-226ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C20H22O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 390.384 |
| Flash Point | 381.8±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 390.131470 |
| PSA | 139.84000 |
| LogP | 1.00 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.737 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |


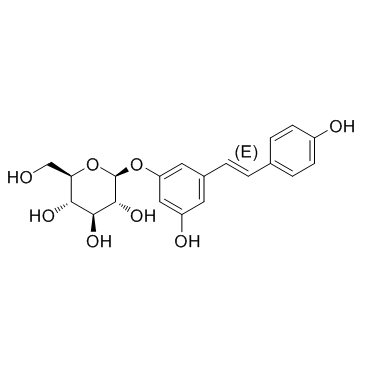
![(E)-1-[3-{[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy}-5-(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-benzoyl-β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)phenyl]-2-(4-{[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy}phenyl)ethene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/109/892402-77-6.png)