CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
-
RTECS NUMBER :
-
LZ5250000
-
CAS REGISTRY NUMBER :
-
7054-25-3
-
LAST UPDATED :
-
199506
-
DATA ITEMS CITED :
-
5
-
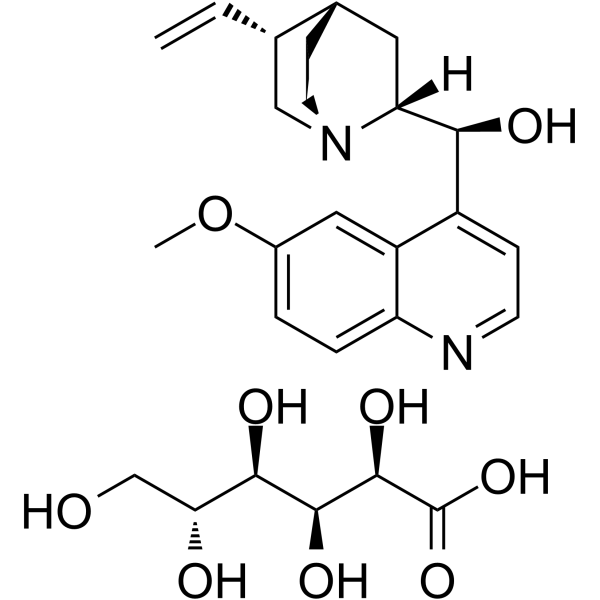
MOLECULAR FORMULA :
-
C20-H24-N2-O2.C6-H12-O7
-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT :
-
520.64
-
WISWESSER LINE NOTATION :
-
T66 BNJ HO1 EYQ- DT66 A B CNTJ A1U1 &QVYQYQYQYQ1Q
HEALTH HAZARD DATA
ACUTE TOXICITY DATA
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - man
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
7609 mg/kg/78W-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Skin and Appendages - dermatitis, allergic (after systemic exposure)
-
REFERENCE :
-
AIMDAP Archives of Internal Medicine. (AMA, 535 N. Dearborn St., Chicago, IL 60610) V.1- 1908- Volume(issue)/page/year: 145,446,1985
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
TDLo - Lowest published toxic dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Oral
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Human - woman
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
337 mg/kg/17D-I
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Blood - changes in cell count (unspecified) Nutritional and Gross Metabolic - body temperature increase
-
REFERENCE :
-
AJMEAZ American Journal of Medicine. (Technical Pub., 875 Third Ave., New York, NY 10022) V.1- 1946- Volume(issue)/page/year: 77,345,1984
-
TYPE OF TEST :
-
LDLo - Lowest published lethal dose
-
ROUTE OF EXPOSURE :
-
Intraperitoneal
-
SPECIES OBSERVED :
-
Rodent - mouse
-
DOSE/DURATION :
-
150 mg/kg
-
TOXIC EFFECTS :
-
Details of toxic effects not reported other than lethal dose value
-
REFERENCE :
-
TXAPA9 Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. (Academic Press, Inc., 1 E. First St., Duluth, MN 55802) V.1- 1959- Volume(issue)/page/year: 23,288,1972 *** NIOSH STANDARDS DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE DATA *** NIOSH OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE SURVEY DATA : NOHS - National Occupational Hazard Survey (1974) NOHS Hazard Code - 83945 No. of Facilities: 33 (estimated) No. of Industries: 1 No. of Occupations: 1 No. of Employees: 66 (estimated) NOES - National Occupational Exposure Survey (1983) NOES Hazard Code - 83945 No. of Facilities: 63 (estimated) No. of Industries: 1 No. of Occupations: 3 No. of Employees: 9094 (estimated) No. of Female Employees: 8028 (estimated)
|