113558-15-9
| Name | icariside II |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Icariside II
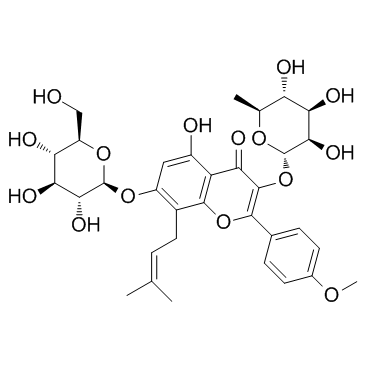
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranoside 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-deoxy-α-L-mannopyranoside 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-4'-methoxyl-8-prenylflavone-3-O-rhamnopyranoside Baohuoside I icarisid II 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one 2h44 |
| Description | Baohuoside I, a flavonoid isolated from Epimedium koreanum Nakai, acts as an inhibitor of CXCR4, downregulates CXCR4 expression, induces apoptosis and shows anti-tumor activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CXCR4 Apoptosis |
| In Vitro | Baohuoside I is an inhibitor of CXCR4, and downregulates CXCR4 expression at 12-25 μM. Baohuoside I (0-25 μM) suppresses NF-κB activation in a dose-dependent manner, suppresses CXCL12 induced the invasion of cervical cancer cells. Baohuoside I also inhibits invasion of breast cancer cells[1]. Baohuoside I inhibits A549 cell viability, with IC50s of 25.1 μM at 24 h, 11.5 μM and 9.6 μM at 48 h and 72 h, respectively. Baohuoside I ((25 μM) suppresses the caspase cascade in A549 cells, elevates ROS levels and activates JNK and p38MAPK signaling cascade[2]. Baohuoside I (3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25.0 and 50.0 µg/mL) significantly and dose-dependently blocks the growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca109 cells, with an IC50 of 4.8 µg/mL at 48 h[3]. |
| In Vivo | Baohuoside I (25 mg/kg) decreases β-catenin protein levels, cyclin D1 and survivin expression in nude mice[3]. |
| Cell Assay | The cytotoxicity effect of Baohuoside I on A549 cells is determined by MTT assay. Cells (1×104 cells/well) are seeded in a 96-well plate, and treated with Baohuoside I (6.25, 12.5, and 25 μM) or 1 mM NAC for 24, 48 or 72 h. After MTT containing medium is removed, the crystals that have formed are dissolved by the addition of DMSO to each well. After mixing, the absorbance of the cells is measured at 540 nm by using Multiskan Spectrum Microplate Reader[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Female Balb/c nude mice (4- to 6-weeks-old) are used in the assay. Subconfluent Eca109-Luc cells are harvested and resuspended in PBS to a final density of 2 × 107 cells/mL. Prior to injection, cells are resuspended in PBS and analyzed by 0.4% trypan blue exclusion assay (viable cells >90%). For subcutaneous injection, 1 × 107 Eca109-Luc cells in 200 µL PBS are injected into the left flank of each mouse using 27G needles. At 1 week after tumor cell injection, Baohuoside I (25 mg/kg per mouse) is injected intralesionally once a day, whereas the 10 mice intended for vehicle treatment are administered an equal volume of PBS[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 759.4±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C27H30O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 514.521 |
| Flash Point | 253.9±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 514.183899 |
| PSA | 159.05000 |
| LogP | 4.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.666 |
| HS Code | 29329990 |
|---|
|
~78% 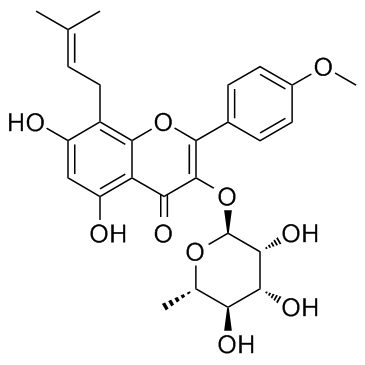
113558-15-9 |
| Literature: Journal of Natural Products, , vol. 71, # 9 p. 1513 - 1517 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |