643-22-1
| Name | Erythromycin Stearate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EINECS 211-396-1
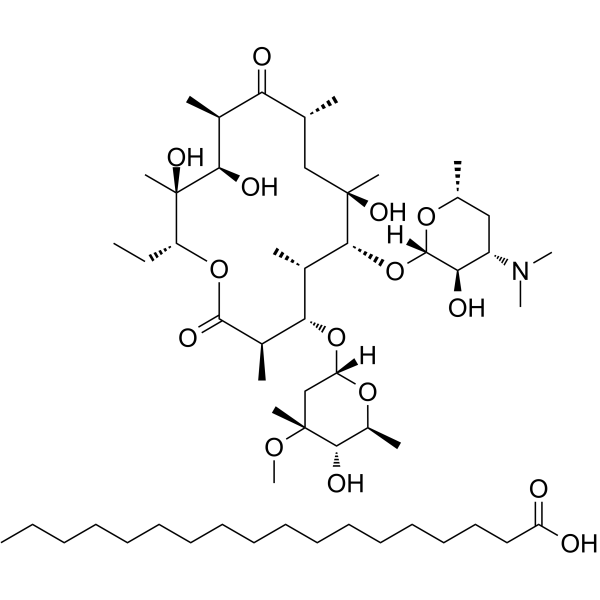
MFCD00084690 Heptadecanoic acid - (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11R,12R,13S,14R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-{[(2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione (1:1) Erythromycin stearate |
| Description | Erythromycin stearate is a macrolide antibiotic produced by actinomycete Streptomyces erythreus with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. Erythromycin stearate binds to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits and inhibits RNA-dependent protein synthesis by blockage of transpeptidation and/or translocation reactions, without affecting synthesis of nucleic acid[1][2]. Erythromycin stearate also exhibits antitumor and neuroprotective effect in different fields of research[3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial; RNA-dependent protein synthesis[1] |
| In Vitro | Erythromycin stearate inhibits growth of P. falciparum with IC50 and IC90 values of 58.2 μM and 104.0 μM, respectively[1]. Erythromycin stearate (10 μM, 100 μM; 24 h, 72 h) shows antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and suppresses the accumulation of 4-HNE (p<0.01) and 8-OHdG (p<0.01), reduces Iba-1 (p<0.01) and TNF-α (p<0.01) expression significantly[4]. Cell Viability Assay[4] Cell Line: Embryos primary cortical neuron (from the cerebral cortices of 17-day-old Sprague-Dawley rat) Concentration: 10, 100 μM Incubation Time: 24, 72 hours Result: Improved the viability of cultured neuronal cells in vitro after 3 hours oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). |
| In Vivo | Erythromycin stearate (gastric intubation; 0.1-50 mg/kg; 30-120 days) decreases tumor growth and prolong the survival time of mice from dose of 5 mg/kg in mice[3]. Erythromycin stearate (gastric intubation; 5 mg/kg) protects mice alive even at 120 days after inoculation, but shortens mean survival time in tumor-bearing mice by 4-5 days with dose of 50 mg/kg[3]. Erythromycin stearate (i.h.; single injection; 50 mg/kg) has a protective effect on the rat model with cerebral ischemia reperfusion-injury[4]. Animal Model: Female ddY mice (6-week-old) with EAC cells or CDF mice (6-week-old) with P388 cells[3] Dosage: 0.1 mg/kg; 0.5 mg/kg; 10 mg/kg; 30 mg/kg; 50 mg/kg Administration: Gastric intubation; 30-120 days Result: Decreased tumor growth and prolonged the mean survival time of mice from the dose of 5 mg/kg, however, the 50 mg/kg dosage shortened the MST in tumorbearing mice. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (8-week-old, 250-300 g)[4] Dosage: 50 mg/kg Administration: Subcutaneous single injection Result: Reduced infarct volume and edema volume, improved neurological deficit. |
| References |
[1]. Gribble MJ, et al. Erythromycin. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Jan;66(1):79-89. [3]. K Hamada, et al. Antitumor Effect of Erythromycin in Mice. Chemotherapy |
| Density | 1.112g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 77-79ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C55H103NO15 |
| Molecular Weight | 1004.377 |
| Flash Point | 523.101ºC |
| Exact Mass | 1003.717102 |
| PSA | 231.21000 |
| LogP | 8.11810 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.518 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: soluble50mg/mL, clear to very slightly hazy, colorless |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P284-P304 + P340-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | KF5785000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|