59-43-8
| Name | thiamine(1+) chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
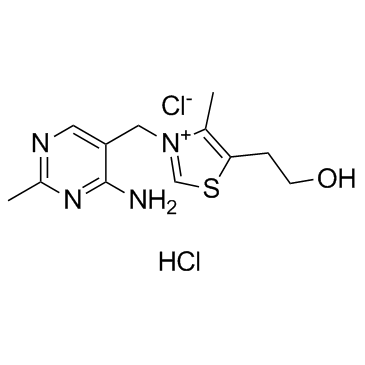
3-[(4-Amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium chloride
Vitamin B1 thiamine hydrochloride MFCD00044586 3-((4-Amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl)-5-(2- hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazolium chloride Aneurin thiazolium, 3-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-, chloride 2-[3-[(4-amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium-5-yl]ethanol,chloride Thiamine chloride 5-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-3-[(6-imino-2-methyl-1,6-dihydro-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-3-ium chloride EINECS 200-425-3 Thiaminium chloride Thiazolium, 3-[(1,6-dihydro-6-imino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-, chloride (1:1) Thiamine Thiamine monochloride |
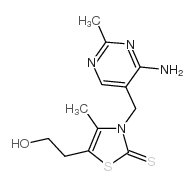
| Description | Thiamine monochloride (Vitamin B1) is an essential vitamin that plays an important role in cellular production of energy from ingested food and enhances normal neuronal actives. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Vitamin[1] |
| In Vitro | Thiamine levels in the blood of homozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet are decreased to 0.058±0.051 and 0.126±0.092 μM, respectively, at 7 weeks compared to WT mice (0.796±0.259 μM). When WT and homozygous KO and KI mice are fed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food), blood thiamine concentration at 5 and 14 days is markedly decreased to 0.010±0.009 and 0.010±0.006 μM, respectively, compared to WT mice (0.609±0.288 μM). Thiamine concentration in brain homogenate of WT mice fed a conventional diet is 3.81±2.18 nmol/g wet weight, and that of KO and KI is 1.33±0.96 and 2.16±1.55 nmol/g wet weight, respectively. Notably, thiamine concentration in brain homogenate decreased steadily in KO and KI mice fed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food) for 5 days (0.95±0.72 nmol/g wet weight) and 14 days (1.11±0.24 nmol/g wet weight), respectively, compared to WT (3.65±1.02 nmol/g wet weight), before the mice presented an phenotype of disease[2]. |
| In Vivo | WT, homozygous, and heterozygous KO and KI mice feed a conventional diet (thiamine: 1.71 mg/100 g) survive for over 6 months without any phenotype of disease. Homozygous KO and KI mice feed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg/100 g food) showe paralysis, weight loss, and immobility, and die within 12 and 30 days, respectively. Similarly, homozygous KO and KI mice feed a thiamine-restricted diet with an even lower percentage of thiamine (thiamine: 0.27 mg/100 g food) die within 14 and 18 days, respectively. However, WT and heterozygous KO and KI mice feed a thiamine-restricted diet (thiamine: 0.60 mg or 0.27 mg/100g food) survive for over 6 months without any phenotype of disease[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Slc19a3 E314Q KI mice are maintained routinely with conventional diet, which has a thiamine concentration (thiamine hydrochloride, MW=337.3) of 1.71 mg/100 g food. two types of thiamine-restricted food based on “purified diets for laboratory rodents” are prepared, in which thiamine concentration is 0.60 mg/100 g food (35% thiamine of conventional food) or 0.27 mg/100 g food (16% thiamine of conventional food). A high-thiamine-containing food is also prepared from AIN-93M, in which thiamine concentration is five times that of CE-2 (thiamine: 8.50 mg/100 g food). Thiamine concentration is determined at Japan Food Research Laboratories[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 6 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 125 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C12H17ClN4OS |
| Molecular Weight | 300.808 |
| Exact Mass | 300.081146 |
| PSA | 104.15000 |
| LogP | 1.99090 |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S22 |
| HS Code | 3004500000 |
|
~97% 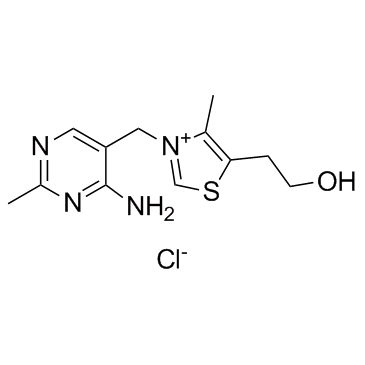
59-43-8 |
| Literature: Karimian, Khashayar; Mohanazadeh, Farajollah Synthesis, 1986 , # 12 p. 1065 - 1067 |
|
~% 
59-43-8 |
| Literature: Chemical and pharmaceutical bulletin, , vol. 15, # 4 p. 448 - 453 |
|
~% 
59-43-8 |
| Literature: Chemical and pharmaceutical bulletin, , vol. 15, # 4 p. 448 - 453 |
|
~% 
59-43-8 |
| Literature: Chemical and pharmaceutical bulletin, , vol. 17, # 2 p. 343 - 347 |
|
~% 
59-43-8 |
| Literature: J. Appl. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 34, p. 229 - 232,219 - 221 |
|
~% 
59-43-8 |
| Literature: Russian Journal of General Chemistry, , vol. 64, # 6.2 p. 937 - 940 Zhurnal Obshchei Khimii, , vol. 64, # 6 p. 1037 - 1040 |
|
~% 
59-43-8 |
| Literature: J. Gen. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), , vol. 60, # 8.2. p. 1867 - 1871,1669 - 1672 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 3004500000 |
|---|




![furan-2-yl-[5-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-4-methyl-thiazol-2-yl]-methanone structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/114/28168-46-9.png)