4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid

4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid structure
|
Common Name | 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104-01-8 | Molecular Weight | 166.174 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 306.0±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 | Melting Point | 84-86 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 124.3±14.4 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)acetic acid is a plasma metabolite, with high sensitivity and specificity value as a biomarker for discriminating between NSCLC and healthy controls. |
| Name | 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)acetic acid is a plasma metabolite, with high sensitivity and specificity value as a biomarker for discriminating between NSCLC and healthy controls. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | 2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)acetic acid (4-methoxyphenylacetic acid) is a plasma metabolite, with high sensitivity and specificity values as a biomarker for discriminating between NSCLC and healthy controls. 2-(4-Methoxyphenyl)acetic acid may play a protective role to prevent the development of lung cancer[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 306.0±17.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 84-86 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 166.174 |
| Flash Point | 124.3±14.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 166.062988 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 1.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.538 |
| InChIKey | NRPFNQUDKRYCNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1ccc(CC(=O)O)cc1 |
| Water Solubility | 6 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AI8960000 |
| HS Code | 29189090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2918990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918990090. other carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
A metabolite profiling approach to identify biomarkers of flavonoid intake in humans.
J. Nucl. Med. 139 , 2309-14, (2009) Flavonoids are phytochemicals that are widespread in the human diet. Despite limitations in their bioavailability, experimental and epidemiological data suggest health benefits of flavonoid consumptio... |
|
|
Mass spectrometric behavior of phenolic acids standards and their analysis in the plant samples with LC/ESI/MS system.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 967 , 21-7, (2014) Liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (MS) with electrospray ionization (ESI) is one of analytical techniques to obtain accurate results of low molecular weight aromatic compounds in biol... |
|
|
High-performance liquid chromatographic method for screening disorders of aromatic acid metabolism using a multi-detection system.
J. Chromatogr. A. 310(2) , 273-81, (1984) This paper describes the use of a high-performance liquid chromatograph equipped with an ultraviolet multi-detection system for the analysis of aromatic acids to help establish a high-risk screening s... |
| 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid |
| Benzeneacetic acid, 4-methoxy- |
| 4-Methoxyphenylacetic acid |
| EINECS 203-166-4 |
| (4-Methoxyphenyl)acetic acid |
| QV1R DO1 |
| Homoanisic Acid |
| MFCD00004345 |
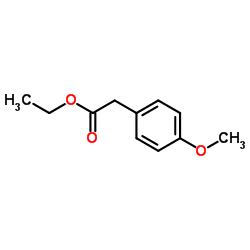 CAS#:14062-18-1
CAS#:14062-18-1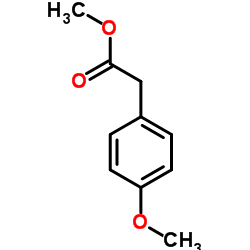 CAS#:23786-14-3
CAS#:23786-14-3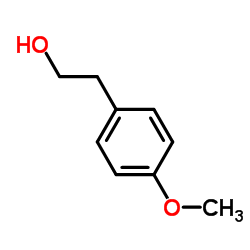 CAS#:702-23-8
CAS#:702-23-8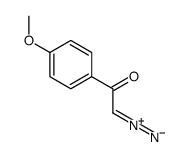 CAS#:6832-17-3
CAS#:6832-17-3 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:824-94-2
CAS#:824-94-2 CAS#:14337-31-6
CAS#:14337-31-6 CAS#:60512-57-4
CAS#:60512-57-4 CAS#:104-47-2
CAS#:104-47-2 CAS#:10499-17-9
CAS#:10499-17-9 CAS#:110005-81-7
CAS#:110005-81-7 CAS#:4091-50-3
CAS#:4091-50-3 CAS#:3722-56-3
CAS#:3722-56-3 CAS#:491-80-5
CAS#:491-80-5 CAS#:34837-88-2
CAS#:34837-88-2 CAS#:57676-49-0
CAS#:57676-49-0 CAS#:123-11-5
CAS#:123-11-5 CAS#:100-09-4
CAS#:100-09-4![(S)-4-Benzyl-3-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)acetyl]-2-oxazolidinone structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/123/143589-97-3.png) CAS#:143589-97-3
CAS#:143589-97-3
