Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH
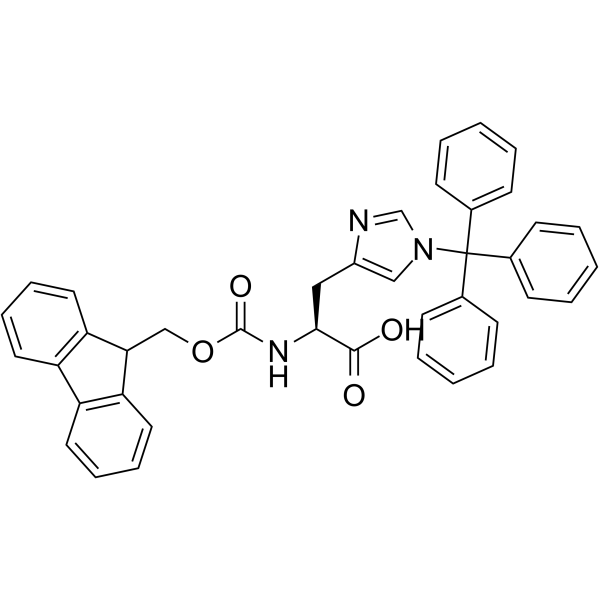
Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH structure
|
Common Name | Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 109425-51-6 | Molecular Weight | 619.708 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 811.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C40H33N3O4 | Melting Point | 150-155 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 444.7±34.3 °C | |
Use of Fmoc-His(Trt)-OHFmoc-His(Trt)-OH has trityl (Trt) group to protect the side-chain of His. Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH has Fmoc group to protect -αNH2. Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH can be used for solid phase synthesis of peptides, providing protection against racemization and by-product formation[1]. |
| Name | N-Fmoc-N'-trityl-L-histidine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH has trityl (Trt) group to protect the side-chain of His. Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH has Fmoc group to protect -αNH2. Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH can be used for solid phase synthesis of peptides, providing protection against racemization and by-product formation[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 811.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 150-155 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C40H33N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 619.708 |
| Flash Point | 444.7±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 619.247131 |
| PSA | 93.45000 |
| LogP | 8.03 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.657 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~56% 
Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH CAS#:109425-51-6 |
| Literature: Nowshuddin, Shaik; Rao; Reddy, A. Ram Synthetic Communications, 2009 , vol. 39, # 11 p. 2022 - 2031 |
|
~73% 
Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH CAS#:109425-51-6 |
| Literature: Barlos, Kleomenis; Mamos, Petros; Papaioannou, Dionysios; Patrianakou, Stella; Sanida, Chariklia; Schaefer, Wolfram Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1987 , p. 1025 - 1030 |
|
Chemical synthesis of a polypeptide backbone derived from the primary sequence of the cancer protein NY-ESO-1 enabled by kinetically controlled ligation and pseudoprolines.
Biopolymers 104 , 116-27, (2015) The cancer protein NY-ESO-1 has been shown to be one of the most promising vaccine candidates although little is known about its cellular function. Using a chemical protein strategy, the 180 amino aci... |
|
|
New amphiphilic N-phosphoryl oligopeptides designed for gene delivery.
Int. J. Pharm. 468(1-2) , 83-90, (2014) Gene therapy is a potent tool for the treatment of cancer and other gene defect diseases, which involves using DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic gene to replace a mutated gene. However, the D... |
| MFCD00043332 |
| N-Fmoc-N'-Trityl-L-Histidine |
| N-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-1-trityl-L-histidine |
| N-alpha-FMOC-N-Trityl-L-histidine |
| EINECS 439-640-4 |
| Nα-Fmoc-N(im)-trityl-L-histidine |
| Na-Fmoc-Nim-trityl-L-histidine |
| Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH |
| Nα-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylMethoxy)carbonyl]-tele-(triphenylMethyl)-L-histidine |
| N-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-1-(triphenylmethyl)-L-histidine, |
| (2S)-2-(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonylamino)-3-(1-tritylimidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid |
| L-Histidine, N-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-1-(triphenylmethyl)- |
| Nα-Fmoc-τ-trityl-L-histidine |
| Nα-[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-τ-(triphenylmethyl)-L-histidine |
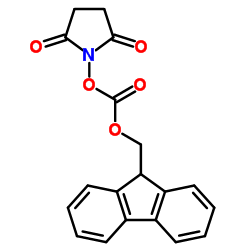
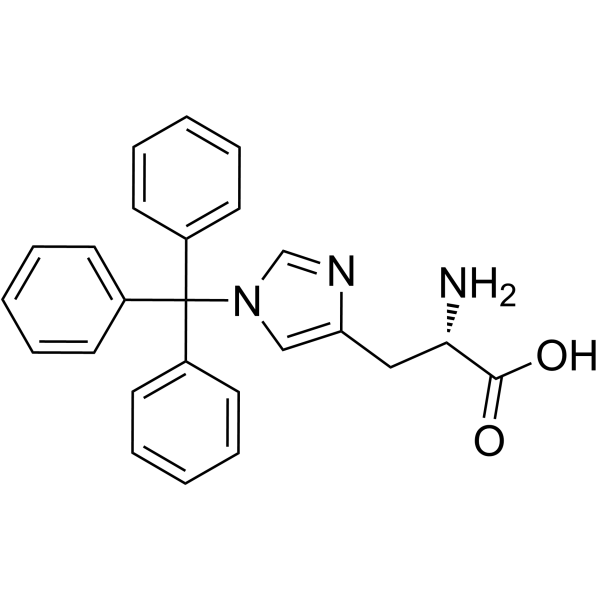
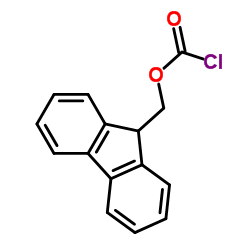
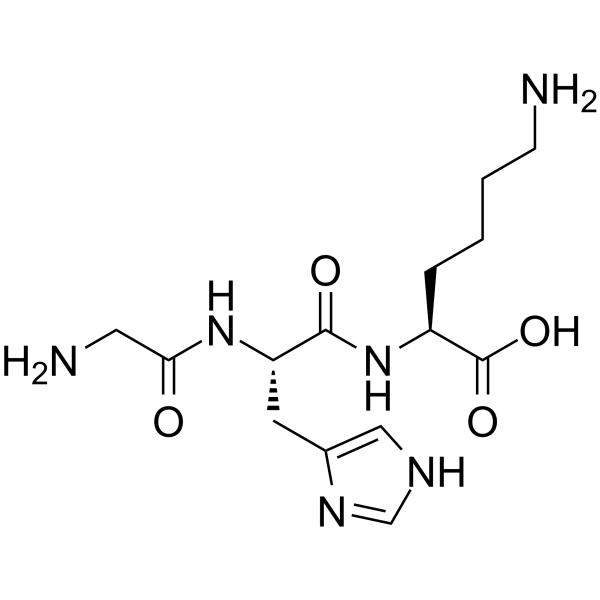 CAS#:49557-75-7
CAS#:49557-75-7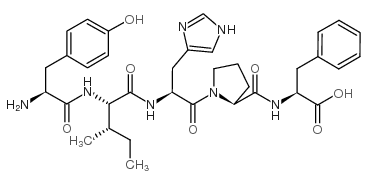 CAS#:52530-60-6
CAS#:52530-60-6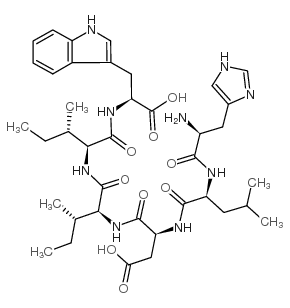 CAS#:121377-67-1
CAS#:121377-67-1
