oleic acid

oleic acid structure
|
Common Name | oleic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 112-80-1 | Molecular Weight | 282.461 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 360.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H34O2 | Melting Point | 13-14 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 270.1±14.4 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of oleic acidOleic acid is an abundant monounsaturated fatty acid. |
| Name | oleic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Oleic acid is an abundant monounsaturated fatty acid. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Oleic acid is the most common monounsaturated fatty acids (FA) in human adipocytes and other tissues. Oleic acid prompts cell proliferation and migration in high metastatic cancer cells via enhancing β-oxidation mediated by AMPK activation. Oleic acid inhibits cancer cell growth and survival in low metastatic carcinoma cells, such as gastric carcinoma SGC7901 and breast carcinoma MCF-7 cell lines[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 360.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 13-14 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C18H34O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 282.461 |
| Flash Point | 270.1±14.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 282.255890 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 7.70 |
| Vapour density | 1.03 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.467 |
| InChIKey | ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, aluminium. |
| Water Solubility | negligible |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37-S37/39-S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 1198 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | LP8925000 |
| HS Code | 2916150000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916150000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916150000 oleic, linoleic or linolenic acids, their salts and esters。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Differential expression of efflux pump genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in response to varied subinhibitory concentrations of antituberculosis agents.
Tuberculosis (Edinb.) 95(2) , 155-61, (2015) Several reports have elaborated on the role of efflux pumps in drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis by analysing the mRNA expression profiles. However, there is no uniformity in the subinhibi... |
|
|
Decreased lipogenesis in white adipose tissue contributes to the resistance to high fat diet-induced obesity in phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase-deficient mice.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1851(2) , 152-62, (2015) Mice lacking phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT, Pemt(-/-) mice) are resistant to high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity (DIO) but develop non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PEMT expression i... |
|
|
Exploring the impact of drug properties on the extent of intestinal lymphatic transport - in vitro and in vivo studies.
Pharm. Res. 32(5) , 1817-29, (2015) Intestinal lymphatic transport of specific lipophilic drugs offers therapeutic advantages and maximises oral bioavailability. The aims of this study were; to compare intestinal lymphatic transport of ... |
| oleicacidamide-heptaglycolether |
| Oleic Acid |
| adogen73 |
| Amide O |
| OLEAMID |
| Armid O |
| Slip-eze |
| AMD-O |
| octadec-9-enoic acid |
| MFCD00003274 |
| EINECS 200-001-8 |
| cis-9-octadecenamide |
| cis-oleamide |
| cis-9-Octadecenoic acid |
 CAS#:112-77-6
CAS#:112-77-6 CAS#:112-62-9
CAS#:112-62-9 CAS#:122-32-7
CAS#:122-32-7 CAS#:111-62-6
CAS#:111-62-6![[(E)-octadec-9-enoyl] (E)-octadec-9-enoate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/181/6085-36-5.png) CAS#:6085-36-5
CAS#:6085-36-5 CAS#:114119-34-5
CAS#:114119-34-5 CAS#:506-24-1
CAS#:506-24-1 CAS#:112-91-4
CAS#:112-91-4![9-Octadecenamide,N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-, (9Z)- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/088/109-28-4.png) CAS#:109-28-4
CAS#:109-28-4 CAS#:107743-37-3
CAS#:107743-37-3 CAS#:104855-14-3
CAS#:104855-14-3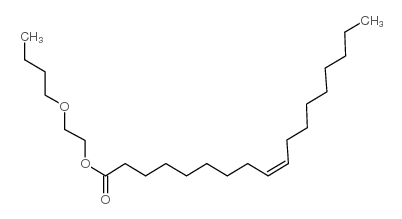 CAS#:109-39-7
CAS#:109-39-7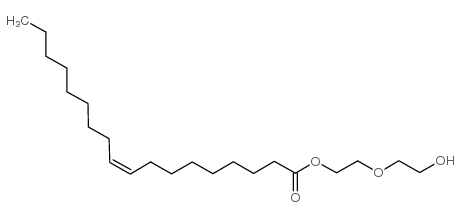 CAS#:106-12-7
CAS#:106-12-7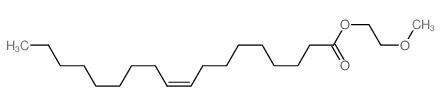 CAS#:111-10-4
CAS#:111-10-4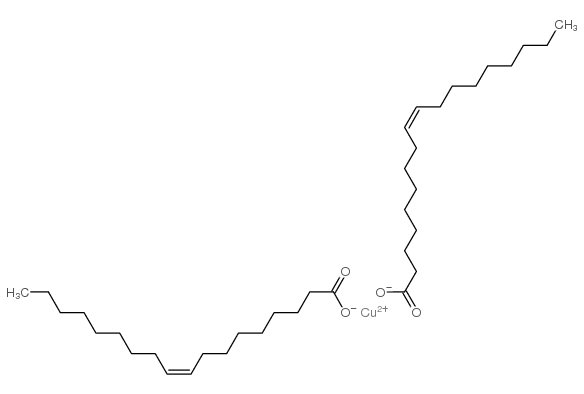 CAS#:1120-44-1
CAS#:1120-44-1 CAS#:10468-30-1
CAS#:10468-30-1![[R-(Z)]-4-Hydroxy-N,N,N-triMethyl-9-oxo-7-[(triphenylmethoxy)Methyl]-3,5,8-trioxa-4-phosphahexacos-17-en-1-aminium 4-Oxide Inner Salt structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/262/103634-10-2.png) CAS#:103634-10-2
CAS#:103634-10-2 CAS#:109-36-4
CAS#:109-36-4
