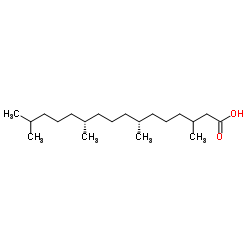
Pristanic acid
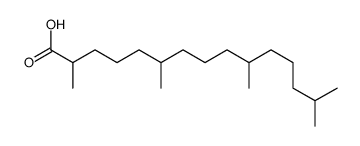
Pristanic acid structure
|
Common Name | Pristanic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1189-37-3 | Molecular Weight | 298.50400 | |
| Density | 0.882g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 408ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H38O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 14ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Pristanic acidPristanic acid is an endogenous metabolite present in Blood that can be used for the research of Alpha Methylacyl CoA Racemase Deficiency and Zellweger Syndrome[1][2][3]. |
| Name | pristanic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pristanic acid is an endogenous metabolite present in Blood that can be used for the research of Alpha Methylacyl CoA Racemase Deficiency and Zellweger Syndrome[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Endogenous metabolites is defined as those that are annotated by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes as substrates or products of the ~1900 metabolic enzymes encoded in our genome. It is clear in the body of literature that there are documented toxic properties for many of these metabolites[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 0.882g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 408ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H38O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 298.50400 |
| Flash Point | 14ºC |
| Exact Mass | 298.28700 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.14620 |
| Appearance of Characters | ethanol solution |
| Vapour Pressure | 8.48E-08mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.453 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F: Flammable; |
| Risk Phrases | R11 |
| Safety Phrases | S7 |
| RIDADR | UN 1170 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
|
~% 
Pristanic acid CAS#:1189-37-3 |
| Literature: Smith; Boyack Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1948 , vol. 70, p. 2693 |
|
~% 
Pristanic acid CAS#:1189-37-3 |
| Literature: Eldjarn,L. et al. Acta Chemica Scandinavica (1947-1973), 1966 , vol. 20, p. 2313 - 2314 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
New insights into the peroxisomal protein inventory: Acyl-CoA oxidases and -dehydrogenases are an ancient feature of peroxisomes.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853(1) , 111-25, (2014) Peroxisomes are ubiquitous organelles which participate in a variety of essential biochemical pathways. An intimate interrelationship between peroxisomes and mitochondria is emerging in mammals, where... |
|
|
Peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme deficiency.
J. Clin. Invest. 83(3) , 771-7, (1989) Peroxisomal function was evaluated in a male infant with clinical features of neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Very long chain fatty acid levels were elevated in both plasma and fibroblasts, and beta-ox... |
|
|
Branched fatty acids in dairy and beef products markedly enhance alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase expression in prostate cancer cells in vitro.
Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 12(8) , 775-83, (2003) An enzyme previously identified as alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is overexpressed in high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and in a majority (60-100%) of prostate cancers (CaPs) as co... |
| (2S,6R,10R)-2,6,10,14-tetramethylpentadecanoic acid |
| Pristaninsaeure |
| acide pristanique |
| Pristanic acid solution |
| 2,6,10,14-Tetramethyl-pentadecansaeure |
| 2,6,10,14-tetramethylpentadecanoic |
| acido pristanico |
| 2,6,10,14-Tetramethylpentadecanoic acid |
| 2,6,10,14-tetramethyl-pentadecanoic acid |
| MFCD05664739 |