Dicloxacillin sodium
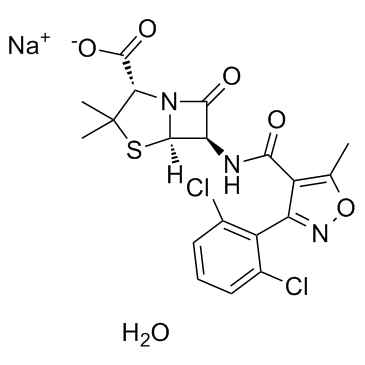
Dicloxacillin sodium structure
|
Common Name | Dicloxacillin sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 13412-64-1 | Molecular Weight | 510.323 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 692.4ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18Cl2N3NaO6S | Melting Point | 222-225°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 372.5ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Dicloxacillin sodiumDicloxacillin NaOH is a narrow-spectrum β-Lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class, is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria, active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus. |
| Name | dicloxacillin sodium monohydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dicloxacillin NaOH is a narrow-spectrum β-Lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class, is used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria, active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Boiling Point | 692.4ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 222-225°C |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18Cl2N3NaO6S |
| Molecular Weight | 510.323 |
| Flash Point | 372.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 509.019104 |
| PSA | 150.10000 |
| LogP | 2.13190 |
| InChIKey | QBFCIKYALGTFHK-VICXVTCVSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1onc(-c2c(Cl)cccc2Cl)c1C(=O)NC1C(=O)N2C1SC(C)(C)C2C(=O)O.O.[Na] |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H334-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P284-P304 + P340-P305 + P351 + P338-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S26-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | XH8925000 |
| HS Code | 2941109900 |
| HS Code | 2941109900 |
|---|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
|
|
Gingival pain: an unusual side effect of ziprasidone.
BMJ Case Rep. 2013 , doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-007577, (2013) The patient is a 52-year-old man with schizophrenia who developed severe, unremitting gingival pain after his ziprasidone dosage was increased from 80 to 120 mg. His physical examination and laborator... |
| 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-(3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, monosodium salt, monohydrate |
| Dicloxacillin sodium salt monohydrate |
| Dicloxacillin sodium |
| MFCD00210902 |
| Sodium 6-({[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate hydrate (1:1:1) |
| 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-[[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, sodium salt, hydrate (1:1:1) |
| EINECS 206-444-3 |
| Dicloxacillin (Sodium hydrate) |