Complement factor D-IN-1
Modify Date: 2024-01-11 09:43:16
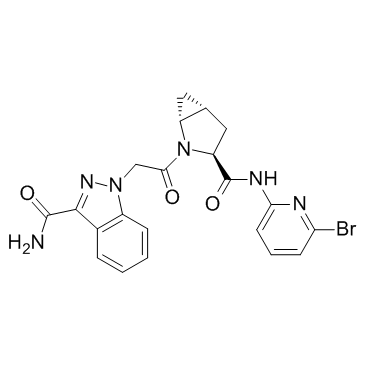
Complement factor D-IN-1 structure
|
Common Name | Complement factor D-IN-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1386455-76-0 | Molecular Weight | 483.32 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H19BrN6O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Complement factor D-IN-1Complement factor D-IN-1 is a potent and selective small-molecule reversible factor d inhibitor, with IC50s of 0.006 and 0.05 μM in FD Thioesterolytic Fluorescent Assay and a MAC Deposition Assay, respectively. |
| Name | ComplementfactorD-IN-1 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Complement factor D-IN-1 is a potent and selective small-molecule reversible factor d inhibitor, with IC50s of 0.006 and 0.05 μM in FD Thioesterolytic Fluorescent Assay and a MAC Deposition Assay, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.006 μM (FD), 0.05 μM (MAC)[1] |
| In Vitro | The highly specific S1 serine protease factor D (FD) plays a central role in the amplification of the complement alternative pathway (AP) of the innate immune system. Complement factor D-IN-1 (compound 2) shows similar potency against human and monkey FD (IC50s in FD thioesterolytic assays of 0.005 μM and in 50% serum MAC deposition assays of 0.011 μM for both human and monkey)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Complement factor D-IN-1 displays an excellent oral PK profile in Sprague–Dawley rats and, following an oral dose (10 mg/kg) in Brown Norway rats, demonstrates a good distribution and sustained exposure in ocular tissues including the neural retina and the posterior eye cup (PEC), which comprises the sclera, retinal pigmented epithelium, and choroid. Mean exposure levels in plasma, the PEC, and the retina at 6 h after dosing are 0.36, 0.43, and 0.09 μM, respectively[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Complement factor D-IN-1 is tested at 30 mg/kg in the human factor D knock-in mouse pharmacodynamic model. Groups of mice (n=4, female human FD knock-in) are treated either with Complement factor D-IN-1 or dosing vehicle by oral gavage at 24, 16, 12, 8, 6, and 4 h, respectively, prior to the termination of the study. All animals are given intraperitoneal LPS to activate complement 7.5 h prior to study termination. Baseline complement levels are obtained from mice that received oral dosing vehicle and intraperitoneal saline (indicated by PBS line on graph). The positive control group receives oral dosing vehicle and intraperitoneal LPS[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C21H19BrN6O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 483.32 |
| Complement factor D-IN-1 |