Butyl levulinate
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 12:31:35
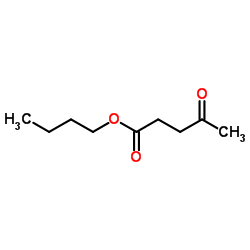
Butyl levulinate structure
|
Common Name | Butyl levulinate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2052-15-5 | Molecular Weight | 172.221 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 240.3±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H16O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 91.7±0.0 °C | |
| Name | butyl 4-oxopentanoate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 240.3±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C9H16O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 172.221 |
| Flash Point | 91.7±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 172.109940 |
| PSA | 43.37000 |
| LogP | 1.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.426 |
| InChIKey | ISBWNEKJSSLXOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCOC(=O)CCC(C)=O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2918300090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918300090 other carboxylic acids with aldehyde or ketone function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Conversion of biomass-derived levulinate and formate esters into γ-valerolactone over supported gold catalysts.
ChemSusChem 4(12) , 1838-43, (2011) The utilization of biomass has recently attracted tremendous attention as a potential alternative to petroleum for the production of liquid fuels and chemicals. We report an efficient alcohol-mediated... |
| n-Butyl laevulinate |
| Pentanoic acid, 4-oxo-, butyl ester |
| n-Butyl levulinate |
| Butyl 4-Oxovalerate |
| Butyl laevulinate |
| Laevulinsaeure-butylester |
| EINECS 218-143-4 |
| Butyl 4-oxopentanoate |
| Levulinic Acid Butyl Ester |
| MFCD00009449 |
| Butyl 4-ketovalerate |
| LEVULINIC ACID,BUTYL ESTER |
| Butyl acetylpropionate |
| butyl-4-oxopentanoate |
| Butyl levulinate |
| Pentanoic acid,4-oxo-,butyl ester |
| 4-Oxovaleric acid butyl ester |
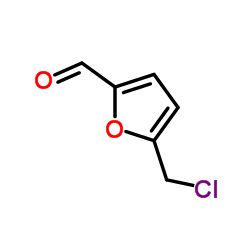 CAS#:1623-88-7
CAS#:1623-88-7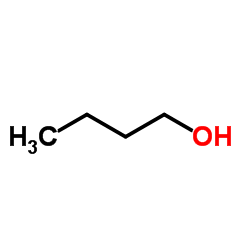 CAS#:71-36-3
CAS#:71-36-3 CAS#:79-24-3
CAS#:79-24-3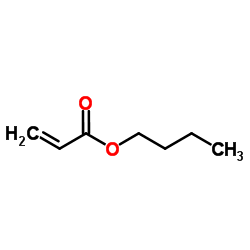 CAS#:141-32-2
CAS#:141-32-2 CAS#:98-00-0
CAS#:98-00-0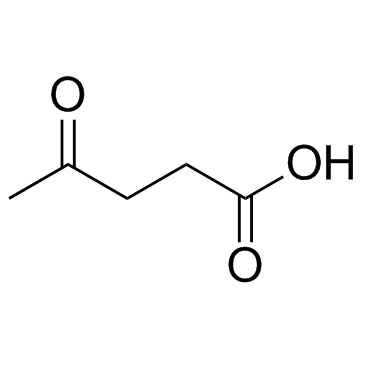 CAS#:123-76-2
CAS#:123-76-2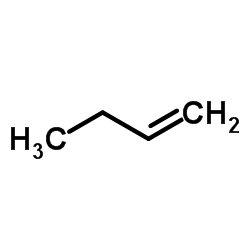 CAS#:106-98-9
CAS#:106-98-9 CAS#:64-18-6
CAS#:64-18-6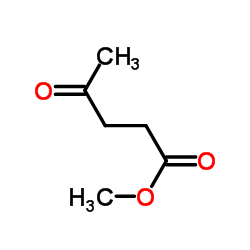 CAS#:624-45-3
CAS#:624-45-3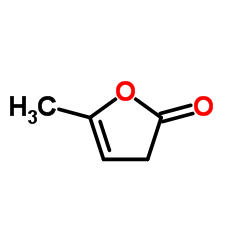 CAS#:591-12-8
CAS#:591-12-8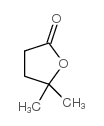 CAS#:3123-97-5
CAS#:3123-97-5 CAS#:108-29-2
CAS#:108-29-2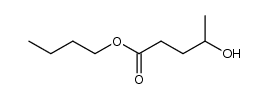 CAS#:129549-67-3
CAS#:129549-67-3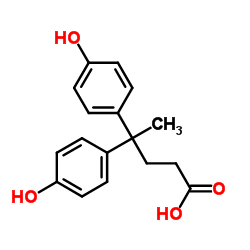 CAS#:126-00-1
CAS#:126-00-1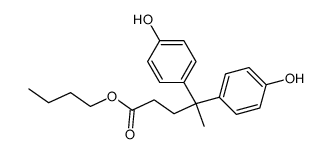 CAS#:7297-88-3
CAS#:7297-88-3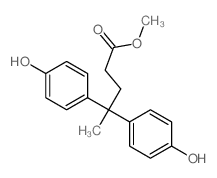 CAS#:7297-85-0
CAS#:7297-85-0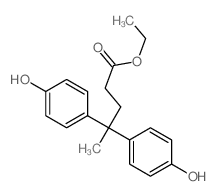 CAS#:7297-86-1
CAS#:7297-86-1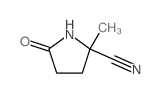 CAS#:86240-21-3
CAS#:86240-21-3
