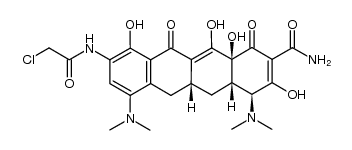
Tigecycline
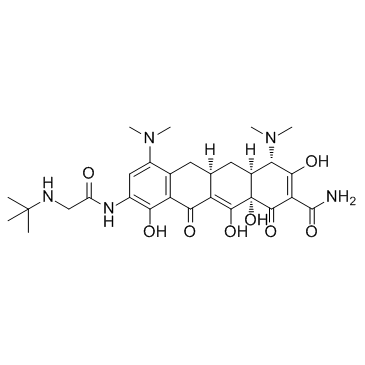
Tigecycline structure
|
Common Name | Tigecycline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 220620-09-7 | Molecular Weight | 585.649 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 890.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39N5O8 | Melting Point | 164-166°C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 492.6±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of TigecyclineTigecycline is a first-in-class, broad spectrum antibiotic with activity against antibiotic-resistant organisms.Target: AntibacterialTigecycline is active against a broad range of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial species including clinically important multidrug-resistant nosocomial and community-acquired bacterial pathogens. Tigecycline has been shown to inhibit the translation elongation step by binding to the ribosome 30S subunit and preventing aminoacylated tRNAs to accommodate in the ribosomal A site [1]. Tigecycline has also been found to be effective for the treatment of community- as well as hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia and bacteremia, sepsis with shock and urinary tract infections. Tigecycline appears to be a valuable treatment option for the management of superbugs, especially where conventional therapy has failed [2].Fifteen patients received tigecycline for 16 episodes of CPKP infection. The main infections were pneumonia (31%), urinary tract infection (31%), peritonitis (20%), catheter-related bacteraemia (12%), and meningitis (6%). Most infections were complicated with severe sepsis (44%), septic shock (12%), and/or bacteraemia (19%). The daily maintenance dose of tigecycline was 200 mg in 10 episodes and 100 mg in 6 episodes. The overall 30-day mortality rate was 25%. Univariate analysis showed that mortality was significantly associated (p < 0.01) with mean APACHE II and SOFA scores and the presence of immunosuppression, but not with the tigecycline dose [3]. |
| Name | tigecycline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Tigecycline is a first-in-class, broad spectrum antibiotic with activity against antibiotic-resistant organisms.Target: AntibacterialTigecycline is active against a broad range of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial species including clinically important multidrug-resistant nosocomial and community-acquired bacterial pathogens. Tigecycline has been shown to inhibit the translation elongation step by binding to the ribosome 30S subunit and preventing aminoacylated tRNAs to accommodate in the ribosomal A site [1]. Tigecycline has also been found to be effective for the treatment of community- as well as hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia and bacteremia, sepsis with shock and urinary tract infections. Tigecycline appears to be a valuable treatment option for the management of superbugs, especially where conventional therapy has failed [2].Fifteen patients received tigecycline for 16 episodes of CPKP infection. The main infections were pneumonia (31%), urinary tract infection (31%), peritonitis (20%), catheter-related bacteraemia (12%), and meningitis (6%). Most infections were complicated with severe sepsis (44%), septic shock (12%), and/or bacteraemia (19%). The daily maintenance dose of tigecycline was 200 mg in 10 episodes and 100 mg in 6 episodes. The overall 30-day mortality rate was 25%. Univariate analysis showed that mortality was significantly associated (p < 0.01) with mean APACHE II and SOFA scores and the presence of immunosuppression, but not with the tigecycline dose [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[2]. Bhattacharya M, et al. Tigecycline. J Postgrad Med. 2009 Jan-Mar;55(1):65-8. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 890.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 164-166°C |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39N5O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 585.649 |
| Flash Point | 492.6±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 585.279846 |
| PSA | 205.76000 |
| LogP | -1.30 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.675 |
| Storage condition | Amber Vial, -20°C Freezer |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H319-H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 3004909090 |
|
~89% 
Tigecycline CAS#:220620-09-7 |
| Literature: SANDOZ AG Patent: WO2009/92680 A2, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 7 ; |
|
~% 
Tigecycline CAS#:220620-09-7 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 9, # 10 p. 1459 - 1462 |
| HS Code | 3004909090 |
|---|
| WAY-GAR 936 |
| TIGECYCLINE POWDER |
| 9-t-Butylglycylamido-minocycline hydrate |
| 2-Naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-((((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)acetyl)amino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)- |
| Tigercycline |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-9-{[(tert-butylamino)acetyl]amino}-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide |
| 2-naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-[[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]acetyl]amino]-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)- |
| 2-NAPHTHACENECARBOXAMIDE |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-9-[(N-tert-Butylglycyl)amino]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide |
| Glycylcycline |
| (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)-4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-9-{[N-(2-methyl-2-propanyl)glycyl]amino}-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-2-tetracenecarboxamide |
| 2-Naphthacenecarboxamide, 4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-9-[[2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]acetyl]amino]-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-, (4S,4aS,5aR,12aS)- |
| Tygacil |
| MFCD00935753 |
| Tigecycline |
| TIGECYCLINE GLYCYLCYCLINE |
| Tegecycline |