Daunorubicin HCl
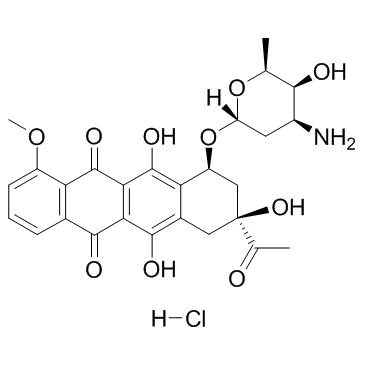
Daunorubicin HCl structure
|
Common Name | Daunorubicin HCl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23541-50-6 | Molecular Weight | 563.981 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 770ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H30ClNO10 | Melting Point | 188 - 190ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 419.5ºC | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Daunorubicin HClDaunorubicin hydrochloride is a topoisomerase II inhibitor with potent antineoplastic activities. |
| Name | Daunorubicin hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Daunorubicin hydrochloride is a topoisomerase II inhibitor with potent antineoplastic activities. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase II |
| In Vitro | The mean IC50 value is 0.04 μM for Daunorubicin (Dnr) in Molt-4 cells. Daunorubicin belongs to the anthracyclines, a group of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics. The cytotoxic effects of anthracyclines are caused by DNA intercalation and the ability to interfere with DNA transcription and replication by inhibiting Topoisomerase II as well as by producing reactive oxygen species[2] Daunorubicin inhibits of both DNA and RNA syntheses in HeLa cells over a concentration range of 0.2 through 2 μM. The IC50 value is 0.4 μM for Daunorubicin (Dnr) in human pancreatic cell line L3.6[3]. |
| In Vivo | Urinary protein excretion, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level are significantly increased in group Daunorubicin (3 mg/kg, i.v.) compared with those in group Control. Administration of Daunorubicin (DNR) causes a significant increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) level in renal tissue compared with that in the control group[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The chemosensitivity to Daunorubicin is assessed using the MTT assay. In brief, the 96 well plates are set up with cells at the initial density of 2×105 cells/mL and are incubated at 37°C for 72 h in an atmosphere of 5% CO2 in the absence and presence of nine different concentrations of Daunorubicin (Dnr) or Dox ranging from 1.90 to 0.007 μM in triplicate. After incubation, 10 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL tetrazolium salt) is added to each well and the plates are incubated for a further 4 h at 37°C. The formazan salt crystals are dissolved by adding 100 μL 10% SDS in 10 mM HCl solution and incubating over night at 37°C. The absorbance is measured at 540 nm with a reference at 650 nm by a 96-well enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate reader. Chemosensitivity is expressed as the IC50, which is the concentration of drug causing 50% cell survival compare to control cells grown without drug. Calculations are carried out using Microsoft Excel[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rat[4] Eight-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats are used. The animals are quarantined and acclimatized for the additional 2 weeks prior to the initiation of the experiments. On day 0, each animal receives a single intravenous injection of Daunorubicin at a dose of 3 mg/kg (i.v.). Daunorubicin is administered in three equal injections at 48 h intervals for a period of one week to achieve an accumulative dose of 9 mg/kg, which is well documented to produce cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Age-matched rats are injected with corresponding volumes of 0.9% NaCl and used as a control (group Control;n=5). Twenty-two DNR-treated rats are randomly divided into two groups and received oral administration of Telmisartan (10 mg/kg/day; group Daunorubicin+Telmisartan; n=10) or vehicle (group Daunorubicin; n=12). The dose of Telmisartan is chosen on the basis of a previous report. Administration of Telmisartan is started on the same day as Daunorubicin administration and continued for 5 additional weeks after cessation of Daunorubicin administration (6 weeks total period). This duration of study is chosen on the basis of previous reports. On day 41, rats are placed individually in metabolic cages for 24-h urine collections for the measurement of protein concentrations and body weight (BW) is measured. After the end of the study period (6 weeks), rats are sacrificed and kidney tissue is harvested for semi-quantitative immunoblotting and immunohistochemical studies. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 770ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 188 - 190ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C27H30ClNO10 |
| Molecular Weight | 563.981 |
| Flash Point | 419.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 563.155823 |
| PSA | 185.84000 |
| LogP | 2.53120 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.99E-26mmHg at 25°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H334-H351 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P281-P301 + P310-P342 + P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R40;R42/43 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | HB7878000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: US6677309 B1, ; Page/Page column 17; 18; 56 ; |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
|
~% 
Daunorubicin HCl CAS#:23541-50-6 |
| Literature: Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 398 - 402 Khimiko-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal, , vol. 21, # 6 p. 663 - 667 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Influence of dose and animal species on accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin.
Int. J. Pharm. 476(1-2) , 205-12, (2015) We recently demonstrated that Doxil loses its long-circulating properties when injected repeatedly at doses below 2 mg/m(2) in dogs. In studies using other animal species, PEGylated liposomal doxorubi... |
|
|
Resistance to daunorubicin, imatinib, or nilotinib depends on expression levels of ABCB1 and ABCG2 in human leukemia cells.
Chem. Biol. Interact. 219 , 203-10, (2014) The effect of ABCB1 (P-gp, (P-glycoprotein), MDR1) and ABCG2 (BCRP1, (breast cancer resistance protein 1)) expressions on cell resistance to daunorubicin (DRN), imatinib, and nilotinib was studied in ... |
|
|
Orientia tsutsugamushi Strain Ikeda Ankyrin Repeat-Containing Proteins Recruit SCF1 Ubiquitin Ligase Machinery via Poxvirus-Like F-Box Motifs.
J. Bacteriol. 197 , 3097-109, (2015) A rising theme among intracellular microbes is the delivery of ankyrin repeat-containing effectors (Anks) that interact with target proteins to co-opt host cell functions. Orientia tsutsugamushi, an o... |
| (8S,10S)-8-Acetyl-10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-5,12-naphthacenedione Hydrochloride |
| DAUNOBLASTINE |
| Daunorubicin hydrochloride |
| (1S,3S)-3-acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride |
| daunoblastin |
| (1S,3S)-3-Acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-1-tetracenyl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride (1:1) |
| Daunorubicin HCl |
| (1S,3S)-3-Acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride (1:1) |
| (8S-cis)-8-Acetyl-10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-5,12-naphthacenedione Hydrochloride |
| Daunorubicin (Hydrochloride) |
| (8S,10S)-8-acetyl-10-{[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione hydrochloride |
| (8S,10S)-8-Acetyl-10-{[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracen-5,12-dionhydrochlorid |
| Daunoblastina |
| (8S,10S)-8-acétyl-10-{[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-méthyltétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-méthoxy-7,8,9,10-tétrahydrotétracène-5,12-dione chlorhydrate |
| Rubidomycin hydrochloride |
| Cerubidine |
| 5,12-Naphthacenedione, 8-acetyl-10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-, (8S,10S)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 5,12-naphthacenedione, 8-acetyl-10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-, (8S,10S)-, hydrochloride |
| ndc0082-4155 |
| Daunomycin, monohydrochloride |
| (1S,3S)-3-acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-10-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside hydrochloride |
| DAUNOMYCINE HCL |
| MFCD00076118 |
| daunorubcin hydrochloride |
| Daunomycin hydrochloride |
| Dau hydrochloride |
| Daunorubicinol hydrochloride |
| Daunomycin HCl |
| WP900 HYDROCHLORIDE |
| EINECS 245-723-4 |
| Ondena |
| Hydroxydaunorubicin Hydrochloride |
| Daunorubicin.HCl |

![Benzoic acid,2-[1-[(2S,4S)-4-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-a-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydro-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenyl]ethylidene]hydrazide,hydrochloride (1:1) structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/053/36508-71-1.png)
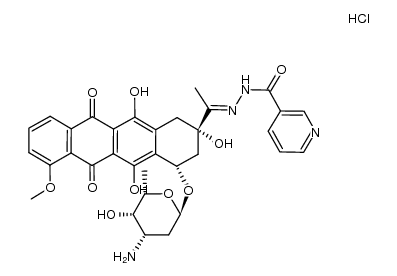
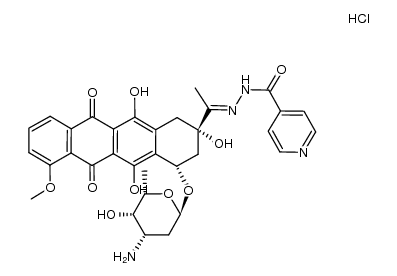

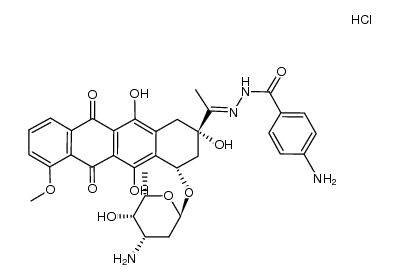
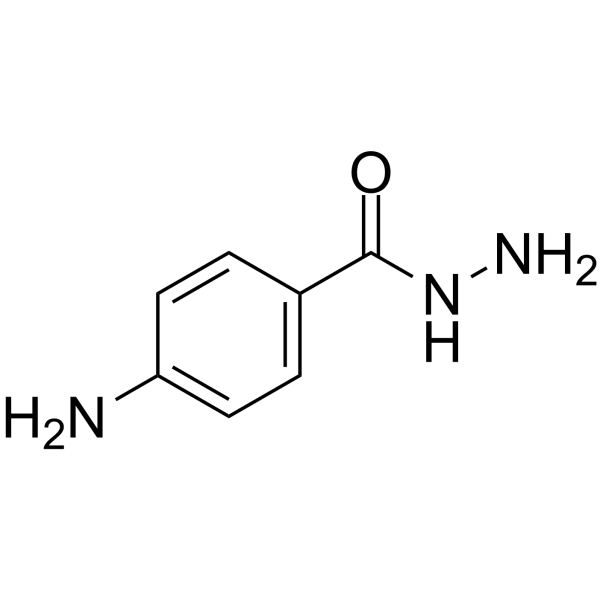
![N-[1-[4-(4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-oxan-2-yl)oxy-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-2-yl]ethylideneamino]-4-hydroxy-benzamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/004/66996-57-4.png)
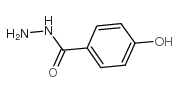



![(7S,9S)-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-9-(2-bromo-1,1-dimethoxyethyl)-6,9,11-trihydroxy-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/243/106401-68-7.png) CAS#:106401-68-7
CAS#:106401-68-7 CAS#:52744-22-6
CAS#:52744-22-6 CAS#:20830-81-3
CAS#:20830-81-3 CAS#:58957-92-9
CAS#:58957-92-9 CAS#:57852-57-0
CAS#:57852-57-0 CAS#:21794-55-8
CAS#:21794-55-8 CAS#:18977-93-0
CAS#:18977-93-0![6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(1-hydroxyethyl)-10-[(4S,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-morpholin-4-yl-oxan-2-yl]oxy-1-methoxy-9,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5, 12-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/476/79867-79-1.png) CAS#:79867-79-1
CAS#:79867-79-1 CAS#:79867-78-0
CAS#:79867-78-0 CAS#:32384-98-8
CAS#:32384-98-8
