LFM-A13
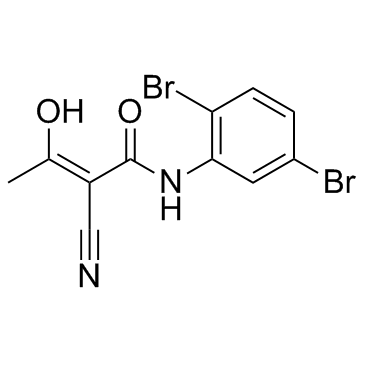
LFM-A13 structure
|
Common Name | LFM-A13 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 244240-24-2 | Molecular Weight | 360.001 | |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 487.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8Br2N2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 248.9±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of LFM-A13LFM-A13 is a potent BTK, JAK2, PLK inhibitor, inhibits recombinant BTK, Plx1 and PLK3 with IC50s of 2.5 μM, 10 μM and 61 μM; LFM-A13 shows no effects on JAK1 and JAK3, Src family kinase HCK, EGFR and IRK. |
| Name | lfm-a13 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | LFM-A13 is a potent BTK, JAK2, PLK inhibitor, inhibits recombinant BTK, Plx1 and PLK3 with IC50s of 2.5 μM, 10 μM and 61 μM; LFM-A13 shows no effects on JAK1 and JAK3, Src family kinase HCK, EGFR and IRK. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Plx1:10 μM (IC50) PLK3:61 μM (IC50) BRK:267 μM (IC50) BMX:281 μM (IC50) FYN:240 μM (IC50) Hepatocyte growth factor receptor kinase (Met):215 μM (IC50) BTK:2.5 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | LFM-A13 significantly inhibits BTK activity with an IC50 of 6.2 ± 0.3 μg/mL (= 17.2 ± 0.8 μM). The calculated Kis of LFM-A13 for BTK, JAK1, JAK3, IRK, EGFR and HCK are 1.4, 110, 148, 31.6, 166 and 214 μM. LFM-A13 (200 μM) markedly increases the chemosensitivity of ALL-1 cells to ceramide-induced apoptosis[1]. LFM-A13 (100 μM) suppresses Epo-induced phosphorylation of EpoR, Jak2, Btk, Stat5 and Erk1/2 in R10 cells. LFM-A13 (100 μM) inhibits auto-phosphorylation of Jak2, Tec and Btk rather than Lyn kinase auto-phosphorylation in COS cells[2]. LFM-A13 potently inhibits Plx1 with IC50 of 10 μM; also inhibits BRK, BMX, FYN and with IC50s of 267, 281, 240 and 215 μM[4]. |
| In Vivo | LFM-A13 (25, 50 and 100 mg/kg) shows no apparent toxicity to rats. LFM-A13 (50 mg/kg, three times a week, i.p.) attenuates DMBA-induced mammary tumorigenesis in mice. LFM-A13 alone or in combination with paclitaxel shows marked effect on the DMBA-induced breast tumor incidence, mean tumor numbers, average tumor weight, and size in BALB/c mice. LFM-A13 (50 mg/kg, three times a week, i.p.) significantly decreases PLK1, cyclin D1, CDK-4, P53 and Bcl-2 expression, but increases the expression of p21, IκB, Bax and caspase 3 expression in mice[3]. LFM-A13 (200 mg/kg) does not cause hematologic toxicity in rats. LFM-A13 (10 or 50 mg/kg, i.p.) exhibits anti-tumor effects dose dependently in the MMTV/Neu transgenic mouse model of breast cancer[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Purified His6-Plx1 (250 ng) is added to a 20 μL reaction mixture containing 1× kinase buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM TT), 25 μM cold ATP, and 1 μCi [γ-32P]ATP in the presence of different concentrations of LFM-A13 ranging from 5 μg/mL (13.9 μM) to 100 μg/mL (278 μM). The reaction mixtures are incubated at room temperature for 15-30 min and autophosphorylation is stopped by addition of 2× SDS-PAGE reducing sample buffer. A parallel experiment is performed in the presence of cold ATP. The kinase reactions are then subjected to immunoblotting using the commercially available anti-Plk antibodies. The immunoblots confirmed that the same amount of Plx1 protein is present in each reaction. In addition, we also examined the effects of LFM-A13 on substrate phosphorylation by Plx1. In brief, 250 ng of purified Plx1 is first incubated at room temperature for one hour with different concentrations of LFM-A13. After one hour of incubation, the tubes containing the reaction mixtures are put on ice and the substrate, GST-Cdc25 peptide (254-316) (200 ng), kinase buffer, and [γ-32P]ATP are added and the kinase reaction allowed to proceed for 15 min at room temperature. Immunoblotting with anti-Cdc25 antibodies is used to confirm that equal amounts of the substrate peptide are present in each reaction mixture. Anti-Plk antibodies, the polyclonal antibodies to gluthathione-S-transferase (GST) and ECL kit are used in the assay. The mode of human PLK3 inhibition by LFM-A13 is examined in titration experiments using increasing concentrations of [γ-32P]ATP and purified N-terminal His6-tagged recombinant human PLK3, residues 19-301, expressed by baculovirus in Sf21 insect cells. In brief, in a final reaction volume of 25 μL, PLK3 (h) (5-10 mU) is incubated with 8 mM MOPS, pH 7.0, 0.2 mM EDTA, 2 mg/mL casein, 10 mM Mg acetate, and [γ-32P-ATP] (specific activity approx. 500 cpm/pmol, concentration as required). The reaction is initiated by the addition of the MgATP mix. After incubation for 40 min at room temperature, the reaction is stopped by the addition of 5 μL of a 3% phosphoric acid solution. Ten microliters of the reaction is then spotted onto a P30 filtermat and washed three times for 5 min in 75 mM phosphoric acid and once in methanol prior to drying and scintillation counting. The Ki of PLK3 by LFM-A13 is calculated from the reciprocal plots of the intensity of phosphorylation of the substrate (1/v) versus the concentration of the inhibitor (i) (viz., LFM-A13). From this Dixon plot, the Ki represents the dissociation constants of the EI complex, which is determined by the point of linear intersection[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[4] Neu transgenic mice carrying one or more tumors are randomLy placed in the study. For the evaluation of tumor kinetics, tumor-bearing mice are randomLy assigned to either vehicle control or treatment groups. Tumor growth is determined by the measurement of tumors with a caliper in three dimensions three days a week and expressed as tumor volume in cubic millimeters (mm3). Tumor volumes are calculated using the formula for the volume of a prolate spheroid, V = 4/3 × 3. 14 × length/2 × width/2 × depth/2. Due to the large heterogeneity in transgenic tumor volumes on day 0, tumor growth for each mouse is normalized to the starting volume for that particular tumor. Therefore, each mouse also serves as its own control, and the tumor growth curves are generated to show the rate of change in tumor volumes. LFM-A13 (10 or 50 mg/kg) is administered by twice daily intraperitoneal injections on 5 consecutive days per week. Paclitaxel is administered intraperitoneally on days 1, 3, 5, 8, 10, and 12 at a dose level of 6.7 mg/kg. Gemcitabine is administered on days 1, 8, and 15 at a dose level of 33.7 mg/kg. Rats[4] Lewis rats are kept in microisolater cages containing autoclaved food, water, and bedding. Lewis rats are treated with i.v. injections of LFM-A13 at multiple dose levels. LFM-A13 is administered as a 0.5 mL bolus injection containing 10% DMSO as a vehicle. Animals are electively sacrificed on day 7 to determine the toxicity of LFM-A13 by evaluating multiple organs for the presence of toxic lesions. Blood is collected by intracardiac puncture following anesthesia with ketamine:xylazine and immediately heparinized. Blood counts (red blood cells [RBC], white blood cells [WBC], and platelets [Plt]) are determined using a HESKA Vet ABC-Diff Hematology Analyzer. Absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) and absolute lymphocyte counts (ALC) are calculated from WBC values after determining the percentages of neutrophils and lymphocytes by a manual differential count. Values for the laboratory parameters are pooled for vehicle controls and LFM-A13 treatments, and for each parameter differences between means are evaluated for statistical significance using Students t-test (vehicle vs LFM-A13 treatment, unequal variances, two-tailed). The calculations are performed in Excel spreadsheets. To determine significant effects, the p-values are adjusted using the Bonferroni method to control for random variation. For histopathologic studies, formalin fixed tissues are dehydrated and embedded in paraffin by routine methods. Glass slides with affixed 4-5 micron tissue sections are prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. |
| References |
| Density | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 487.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8Br2N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 360.001 |
| Flash Point | 248.9±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 357.895233 |
| PSA | 73.12000 |
| LogP | 3.42 |
| Appearance of Characters | powder | white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.677 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: 15 mg/mL |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | 20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | 36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~78% 
LFM-A13 CAS#:244240-24-2 |
| Literature: Ghosh, Sutapa; Uckun, Fatih M. Acta Crystallographica Section C: Crystal Structure Communications, 1999 , vol. 55, # 8 p. 1364 - 1365 |
|
~80% 
LFM-A13 CAS#:244240-24-2 |
| Literature: DuMez, Darin; Venkatachalam, Taracad K.; Uckun, Fatih M. Arzneimittel-Forschung/Drug Research, 2007 , vol. 57, # 3 p. 155 - 163 |
|
~% 
LFM-A13 CAS#:244240-24-2 |
| Literature: Tibbles, Heather E.; Samuel, Peter; Erbeck, Doug; Mahajan, Sandeep; Uckun, Fatih M. Arzneimittel-Forschung/Drug Research, 2004 , vol. 54, # 6 p. 330 - 339 |
|
Phagocytosis-dependent activation of a TLR9-BTK-calcineurin-NFAT pathway co-ordinates innate immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus.
EMBO Mol. Med. 7(3) , 240-58, (2015) Transplant recipients on calcineurin inhibitors are at high risk of invasive fungal infection. Understanding how calcineurin inhibitors impair fungal immunity is a key priority for defining risk of in... |
|
|
Epigenetic regulation of CpG promoter methylation in invasive prostate cancer cells.
Mol. Cancer 9 , 267, (2010) Recently, much attention has been focused on gaining a better understanding of the different populations of cells within a tumor and their contribution to cancer progression. One of the most commonly ... |
|
|
Alternatively activated macrophage-derived RELM-{alpha} is a negative regulator of type 2 inflammation in the lung.
J. Exp. Med. 206(4) , 937-52, (2009) Differentiation and recruitment of alternatively activated macrophages (AAMacs) are hallmarks of several inflammatory conditions associated with infection, allergy, diabetes, and cancer. AAMacs are de... |
| 2-Butenamide, 2-cyano-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl)-3-hydroxy-, (2Z)- |
| a-Cyano-b-hydroxy-b-methyl-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl)propenamide |
| (2Z)-2-cyano-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl)-3-hydroxybut-2-enamide |
| trans-4,5-didehydro-neral |
| dehydrocitral |
| trans-dehydroneral |
| 2,4,6-Octatrienal,3,7-dimethyl |
| (2Z)-2-Cyano-N-(2,5-dibromophenyl)-3-hydroxy-2-butenamide |