α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid
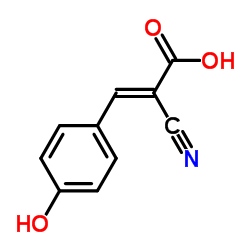
α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid structure
|
Common Name | α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 28166-41-8 | Molecular Weight | 189.167 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 398.1±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7NO3 | Melting Point | 245-250 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 194.5±25.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acidα-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamate) is a potent and non-competitive inhibitor of monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs). α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid inhibits mitochondrial pyruvate transporter with a Ki of 6.3 μM. α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid is used as a matrix to facilitate peptide ionization in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry applications[1][2]. |
| Name | α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamate) is a potent and non-competitive inhibitor of monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs). α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid inhibits mitochondrial pyruvate transporter with a Ki of 6.3 μM. α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid is used as a matrix to facilitate peptide ionization in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry applications[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamate) inhibits monocarboxylates transport such as lactate and pyruvate[2]. α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (CHC; 0.5 mM and 1 mM) of 1 mM has a significant inhibitory effect on branching morphogenesis and decreases the epithelial perimeter and area of lung explants in a dose dependent way[2]. At 100 μM concentration, α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid rapidly and almost totally inhibits O2 uptake by rat heart mitochondria oxidizing pyruvate. Inhibition can be detected at concentrations of inhibitor as low as 1 μM although inhibition took time to develop at this concentration. Inhibition can be reversed by diluting out the inhibitor[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 398.1±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 245-250 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 189.167 |
| Flash Point | 194.5±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 189.042587 |
| PSA | 81.32000 |
| LogP | 1.53 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.674 |
| InChIKey | AFVLVVWMAFSXCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N#CC(=Cc1ccc(O)cc1)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | methanol: 10 mg/mL, clear |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2926909090 other nitrile-function compounds VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Proteome mapping of epidermal growth factor induced hepatocellular carcinomas identifies novel cell metabolism targets and mitogen activated protein kinase signalling events.
BMC Genomics 16 , 124, (2015) Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is on the rise and the sixth most common cancer worldwide. To combat HCC effectively research is directed towards its early detection and the development of targeted the... |
|
|
Simple analytical strategy for MALDI-TOF-MS and nanoUPLC-MS/MS: quantitating curcumin in food condiments and dietary supplements and screening of acrylamide-induced ROS protein indicators reduced by curcumin.
Food Chem. 174 , 571-6, (2014) Curcumin is the major active ingredient of turmeric and is widely used as a preservative, flavouring and colouring agent. Curcumin is a potent substance with several functions, including antioxidant, ... |
|
|
High-throughput workflow for identification of phosphorylated peptides by LC-MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS coupled to in situ enrichment on MALDI plates functionalized by ion landing.
J. Mass Spectrom. 50 , 802-11, (2015) We report an MS-based workflow for identification of phosphorylated peptides from trypsinized protein mixtures and cell lysates that is suitable for high-throughput sample analysis. The workflow is ba... |
| (2E)-2-Cyano-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylic acid |
| Ganaxolone |
| 2-Propenoic acid, 2-cyano-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, (2E)- |
| 4-HCCA |
| α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid |
| 2-Cyano-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acrylic Acid |
| alpha-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid |
| MFCD00004204 |
| (2E)-2-cyano-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid |
| EINECS 248-879-1 |
| A-CYANO-4-HYDROXYCINNAMIC ACID |
| ACCA |

