2-Guanidinoacetic acid
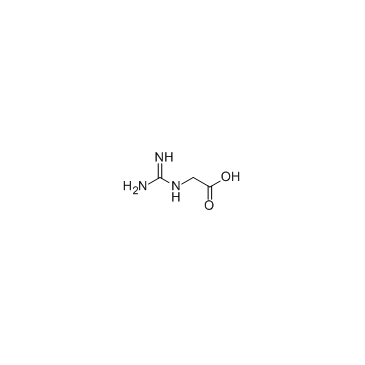
2-Guanidinoacetic acid structure
|
Common Name | 2-Guanidinoacetic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 352-97-6 | Molecular Weight | 117.107 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 294.2±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7N3O2 | Melting Point | 300 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 131.7±27.9 °C | |
Use of 2-Guanidinoacetic acid2-Guanidinoacetic acid, a precursor of creatine, is a replacement of dietary arginine and could support overall energy homeostasis of the bird. |
| Name | guanidinoacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Guanidinoacetic acid, a precursor of creatine, is a replacement of dietary arginine and could support overall energy homeostasis of the bird. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 294.2±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 300 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 117.107 |
| Flash Point | 131.7±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 117.053825 |
| PSA | 99.20000 |
| LogP | -1.85 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
| InChIKey | BPMFZUMJYQTVII-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(N)=NCC(=O)O |
| Water Solubility | 6 M NaOH : 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MB7700000 |
| HS Code | 29252000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 8 | |
| HS Code | 2925290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2925290090 other imines and their derivatives; salts thereof。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
High-throughput tandem mass spectrometry multiplex analysis for newborn urinary screening of creatine synthesis and transport disorders, Triple H syndrome and OTC deficiency.
Clin. Chim. Acta 436 , 249-55, (2014) Creatine synthesis and transport disorders, Triple H syndrome and ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency are treatable inborn errors of metabolism. Early screening of patients was found to be beneficia... |
|
|
Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine.
Kidney Int. 79(11) , 1244-53, (2011) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequent cause of kidney failure; however, urinary biomarkers for the disease are lacking. In a step towards identifying such markers, we used... |
|
|
Dimethylglycine accumulates in uremia and predicts elevated plasma homocysteine concentrations.
Kidney Int. 59(6) , 2267-72, (2001) Hyperhomocysteinemia is a risk factor for atherosclerosis that is common in chronic renal failure (CRF), but its cause is unknown. Homocysteine metabolism is linked to betaine-homocysteine methyl tran... |
| Guanidinoacetic acid |
| Acide carbamimidamidoacétique |
| Guanyl glycine |
| Guanidineacetic acid |
| [(aminoiminomethyl)amino]-Acetic acid |
| (carboxymethyl)-Guanidine |
| Betasyamine |
| α-Guanidinoacetic acid |
| N-Amidinoglycine |
| Guanidylacetic acid |
| amidinoglycine |
| N-(Aminoiminomethyl)glycine |
| N-amidino-Glycine |
| 2-(diaminomethylideneamino)acetic acid |
| Glycine, N-(aminoiminomethyl)- |
| 2-[[Amino(imino)methyl]amino]acetic acid |
| Glycocyamine |
| N-Carbamimidoylglycine |
| a-Guanidinoacetic acid |
| Carbamimidamidoacetic acid |
| Guanidoacetic acid |
| EINECS 206-529-5 |
| N-Guanylglycine |
| {[Ammonio(imino)methyl]amino}acetate |
| Guanidinooacetic Acid |
| 2-Guanidinoacetic acid |
| Betacyamine |
| MFCD00004278 |
 CAS#:56-40-6
CAS#:56-40-6 CAS#:1184-90-3
CAS#:1184-90-3 CAS#:74-79-3
CAS#:74-79-3 CAS#:1758-73-2
CAS#:1758-73-2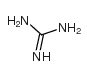 CAS#:113-00-8
CAS#:113-00-8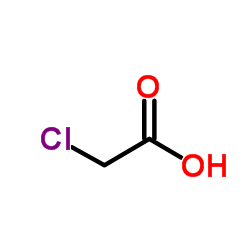 CAS#:79-11-8
CAS#:79-11-8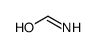 CAS#:77287-34-4
CAS#:77287-34-4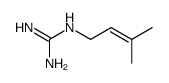 CAS#:543-83-9
CAS#:543-83-9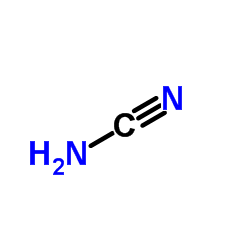 CAS#:420-04-2
CAS#:420-04-2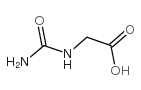 CAS#:462-60-2
CAS#:462-60-2 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9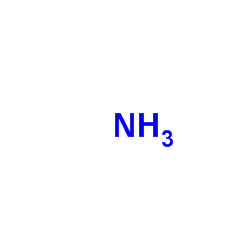 CAS#:7664-41-7
CAS#:7664-41-7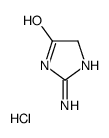 CAS#:18221-88-0
CAS#:18221-88-0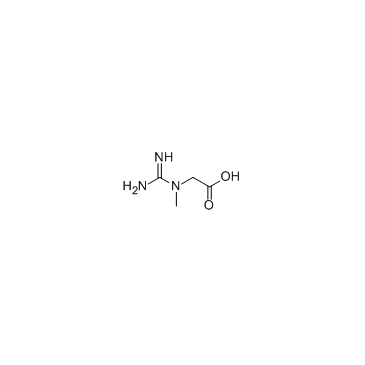 CAS#:57-00-1
CAS#:57-00-1 CAS#:57-13-6
CAS#:57-13-6![2-[[amino-(phosphonoamino)methylidene]amino]acetic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/309/5115-19-5.png) CAS#:5115-19-5
CAS#:5115-19-5
