2'-Fucosyllactose
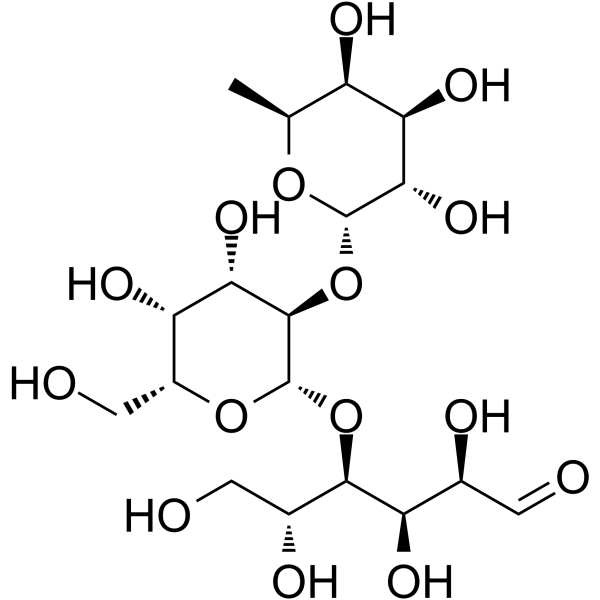
2'-Fucosyllactose structure
|
Common Name | 2'-Fucosyllactose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 41263-94-9 | Molecular Weight | 488.43800 | |
| Density | 1.68g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 902.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H32O15 | Melting Point | 230-231 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 311.9ºC | |
Use of 2'-Fucosyllactose2'-Fucosyllactose (2'-FL) is an oligosaccharide that could be derived from human milk. 2'-Fucosyllactose regulates the expression of CD14, alleviates colitis and regulates the gut microbiome. 2'-Fucosyllactose stimulates T cells to increase IFN-γ production and decreases IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α production of cytokines[1][2]. |
| Name | 2′-Fucosyl-D-lactose |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2'-Fucosyllactose (2'-FL) is an oligosaccharide that could be derived from human milk. 2'-Fucosyllactose regulates the expression of CD14, alleviates colitis and regulates the gut microbiome. 2'-Fucosyllactose stimulates T cells to increase IFN-γ production and decreases IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α production of cytokines[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Target: IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α[1] |
| In Vitro | 2'-Fucosyllactose (2'-FL; 0-12 mg/mL; 48 h) suppress cell-associated CD14 expression and to attenuate LPS (100 μg/mL) stimulated IL-8 secretion in T84 cells[1]. 2'-Fucosyllactose (2 mg/mL; 48 h; T84 and HCT8 cells) ameliorates inflammation induced by bacterial invasion. 2'-Fucosyllactose inhibits ETEC invasion and attenuated the consequent IL-8 secretion[1]. 2'-Fucosyllactose (2 mg/mL; 48 h; T84 and HCT8 cells) induces macrophage migration inhibitory factor signal pathways that suppress inflammation[1]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: T84 cells Concentration: 0, 2, and 4 mg/mL Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Suppressed CD14 mRNA and reduced cell-associated CD14 protein expression. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: T84 and HCT8 cellsT84 and HCT8 cells Concentration: 2 mg/mL Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Suppressed CD14 mRNA and reduced cell-associated CD14 protein expression. Inhibited CD14 and NF-κB induction. Induced iκB and SOCS2 expression and STAT3 phosphorylation. |
| In Vivo | 2'-Fucosyllactose (2'-FL; 100 mg (200 μL); i.g.; daily, for 4 d; C57BL/6 mice with AIEC infection) inhibits AIEC infection and inflammation in vivo[1]. Animal Model: C57BL/6 mice (8 weeks) with AIEC (uropathogenic E. coli, and adherent-invasive E. coli) infection[1] Dosage: 100 mg (200 μL) Administration: Oral gavage; daily, for 4 days Result: Had colons lengths were closer to normal. Inhibited the colonisation of the colonic mucosa by O83-positive bacteria. Decreased CD14 expression, CD14 mRNA levels, IL-6, IL-17 and TNF-α levels in colonic. |
| References |
| Density | 1.68g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 902.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 230-231 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C18H32O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 488.43800 |
| Flash Point | 311.9ºC |
| Exact Mass | 488.17400 |
| PSA | 248.45000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.631 |
|
[Studies of oligosaccharide specificity of perch roe fucolectin, using gold labeled neoglycoproteins].
Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 39 , 105-109, (2003) The specificity of perch (Perca fluviatilis) roe fucolectin was studied using the protein dot blot technique, followed by detection with colloidal gold-labeled neoglycoproteins bearing human milk poly... |
|
|
Human milk oligosaccharides influence maturation of human intestinal Caco-2Bbe and HT-29 cell lines.
J. Nutr. 144(5) , 586-91, (2014) Stimulation of gastrointestinal tract maturation is 1 of the many benefits of human milk. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are abundant in human milk and are reported to promote enterocyte different... |
|
|
Lacto-N-tetraose, fucosylation, and secretor status are highly variable in human milk oligosaccharides from women delivering preterm.
J. Proteome Res. 11(9) , 4662-72, (2012) Breast milk is the ideal nutrition for term infants but must be supplemented to provide adequate growth for most premature infants. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are remarkably abundant and diver... |
| (2R,3R,4R,5R)-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(2S,3S,4R,5S,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-2,3,5,6-tetrahydroxyhexanal |