2'-岩藻糖基乳糖
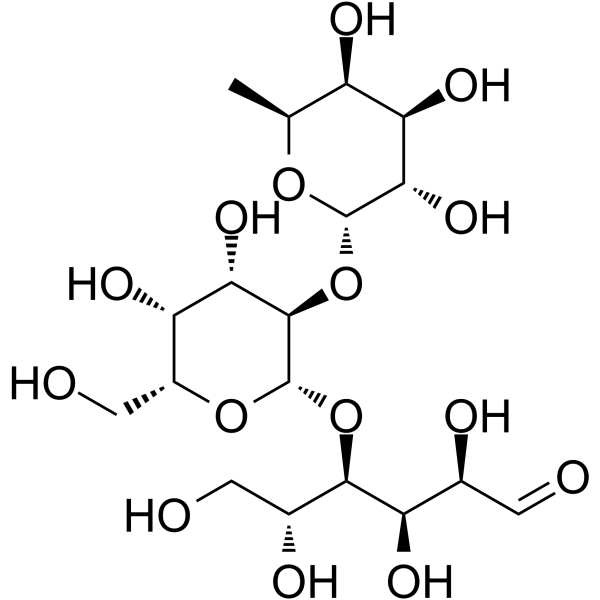
2'-岩藻糖基乳糖结构式

|
常用名 | 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖 | 英文名 | 2'-Fucosyllactose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 41263-94-9 | 分子量 | 488.43800 | |
| 密度 | 1.68g/cm3 | 沸点 | 902.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C18H32O15 | 熔点 | 230-231 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 311.9ºC |
2'-岩藻糖基乳糖用途2'-岩藻糖基乳糖(2'-FL)是一种可以从母乳中提取的低聚糖。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖调节CD14的表达,缓解结肠炎并调节肠道微生物。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖刺激T细胞增加IFN-γ的生成,并降低IL-6、IL-17和TNF-α的细胞因子生成[1][2]。 |
| 中文名 | 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 2′-Fucosyl-D-lactose |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖(2'-FL)是一种可以从母乳中提取的低聚糖。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖调节CD14的表达,缓解结肠炎并调节肠道微生物。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖刺激T细胞增加IFN-γ的生成,并降低IL-6、IL-17和TNF-α的细胞因子生成[1][2]。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点实验 |
Target: IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-17, and TNF-α[1] |
| 体外研究 | 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖(2'-FL;0-12 mg/mL;48 h)抑制T84细胞中细胞相关CD14表达,并减弱LPS(100μg/mL)刺激的IL-8分泌[1]。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖(2 mg/mL;48 h;T84和HCT8细胞)可改善细菌入侵引起的炎症。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖抑制ETEC侵袭并减弱随后的IL-8分泌[1]。2'-岩藻糖基乳糖(2 mg/mL;48 h;T84和HCT8细胞)诱导巨噬细胞移动抑制因子信号通路,抑制炎症[1]。Western Blot分析[1]细胞系:T84细胞浓度:0、2和4 mg/mL培养时间:48小时结果:抑制CD14 mRNA并降低细胞相关CD14蛋白表达。Western Blot分析[1]细胞系:T84和HCT8细胞T84和HCT8细胞浓度:2 mg/mL培养时间:48小时结果:抑制CD14 mRNA并降低细胞相关CD14蛋白表达。抑制CD14和NF-κB的诱导。诱导iκB和SOCS2表达和STAT3磷酸化。 |
| 体内研究 | 2'-岩藻糖基乳糖(2'-FL;100 mg(200μL);i、 例如。;每日,连续4d;感染AIEC的C57BL/6小鼠)抑制体内AIEC感染和炎症[1]。动物模型:AIEC感染C57BL/6小鼠(8周)[1]剂量:100 mg(200μL)口服;结果:结肠长度接近正常值。抑制O83阳性细菌对结肠粘膜的定植。结肠中CD14表达、CD14 mRNA水平、IL-6、IL-17和TNF-α水平降低。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.68g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 902.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 230-231 °C |
| 分子式 | C18H32O15 |
| 分子量 | 488.43800 |
| 闪点 | 311.9ºC |
| 精确质量 | 488.17400 |
| PSA | 248.45000 |
| InChIKey | HWHQUWQCBPAQQH-BWRPKUOHSA-N |
| SMILES | CC1OC(OC2C(OC(C(O)CO)C(O)C(O)C=O)OC(CO)C(O)C2O)C(O)C(O)C1O |
| 外观性状 | 固体 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.631 |
| 储存条件 | -20°C,密封,惰性气体 |
|
[Studies of oligosaccharide specificity of perch roe fucolectin, using gold labeled neoglycoproteins].
Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 39 , 105-109, (2003) The specificity of perch (Perca fluviatilis) roe fucolectin was studied using the protein dot blot technique, followed by detection with colloidal gold-labeled neoglycoproteins bearing human milk poly... |
|
|
Human milk oligosaccharides influence maturation of human intestinal Caco-2Bbe and HT-29 cell lines.
J. Nutr. 144(5) , 586-91, (2014) Stimulation of gastrointestinal tract maturation is 1 of the many benefits of human milk. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are abundant in human milk and are reported to promote enterocyte different... |
|
|
Lacto-N-tetraose, fucosylation, and secretor status are highly variable in human milk oligosaccharides from women delivering preterm.
J. Proteome Res. 11(9) , 4662-72, (2012) Breast milk is the ideal nutrition for term infants but must be supplemented to provide adequate growth for most premature infants. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are remarkably abundant and diver... |
| (2R,3R,4R,5R)-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(2S,3S,4R,5S,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-2,3,5,6-tetrahydroxyhexanal |


