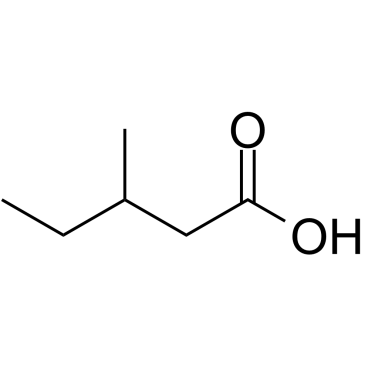
Valnoctamide
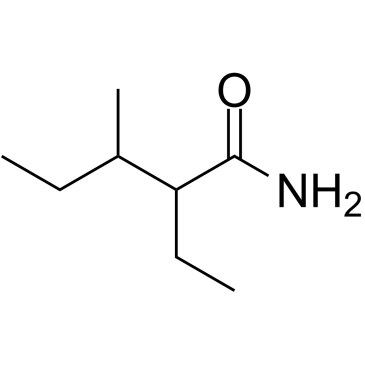
Valnoctamide structure
|
Common Name | Valnoctamide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 4171-13-5 | Molecular Weight | 143.22700 | |
| Density | 0.883g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 274.4ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO | Melting Point | 113.5-114ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 119.8ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ValnoctamideValnoctamide (Valmethamide), a derivative of valproate, suppresses benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus. Valnoctamide (Valmethamide) acts directly on GABAA receptors[1]. |
| Name | 2-ethyl-3-methyl-pentanamide Axiquel Nirvanil |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Valnoctamide (Valmethamide), a derivative of valproate, suppresses benzodiazepine-refractory status epilepticus. Valnoctamide (Valmethamide) acts directly on GABAA receptors[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
GABAA receptor[1] |
| References |
| Density | 0.883g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 274.4ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 113.5-114ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO |
| Molecular Weight | 143.22700 |
| Flash Point | 119.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 143.13100 |
| PSA | 43.09000 |
| LogP | 2.24430 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.438 |
| InChIKey | QRCJOCOSPZMDJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(CC)C(N)=O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 
Valnoctamide CAS#:4171-13-5 |
| Literature: Kaufmann, Dan; Bialer, Meir; Shimshoni, Jakob Avi; Devor, Marshall; Yagen, Boris Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2009 , vol. 52, # 22 p. 7236 - 7248 |
|
~% 
Valnoctamide CAS#:4171-13-5 |
| Literature: Freifelder,M. et al. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1961 , vol. 26, p. 203 - 206 |
|
~% 
Valnoctamide CAS#:4171-13-5 |
| Literature: Kaufmann, Dan; Yagen, Boris; Minert, Anne; Wlodarczyk, Bogdan; Finnell, Richard H.; Schurig, Volker; Devor, Marshall; Bialer, Meir Neuropharmacology, 2010 , vol. 58, # 8 p. 1228 - 1236 |
|
~% 
Valnoctamide CAS#:4171-13-5 |
| Literature: Katznelson; Kondakowa Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1934 , p. II 24 Chem. Zentralbl., 1935 , vol. 106, # I p. 2521 |
|
~% 
Valnoctamide CAS#:4171-13-5 |
| Literature: Katznelson; Kondakowa Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1934 , p. II 24 Chem. Zentralbl., 1935 , vol. 106, # I p. 2521 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Structure activity relationship of human microsomal epoxide hydrolase inhibition by amide and acid analogues of valproic acid.
Pharm. Res. 17(2) , 216-21, (2000) The purpose of this study was to evaluate the in vitro inhibitory potency of various amide analogues and derivatives of valproic acid toward human microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH).mEH inhibition was... |
|
|
A comparative electrographic analysis of the effect of sec-butyl-propylacetamide on pharmacoresistant status epilepticus.
Neuroscience 231 , 145-56, (2013) Better treatment of status epilepticus (SE), which typically becomes refractory after about 30 min, will require new pharmacotherapies. The effect of sec-butyl-propylacetamide (SPD), an amide derivati... |
|
|
Amidic modification of valproic acid reduces skeletal teratogenicity in mice.
Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 71(1) , 47-53, (2004) The antiepileptic drug valproic acid (VPA) is well known to cause neural tube and skeletal defects in both humans and animals. The amidic VPA analogues valpromide (VPD) and valnoctamide (VCD) have muc... |
| 2-ethyl-3-methylpentanamide |
| Valnoctamide |