Dihydrolipoic acid
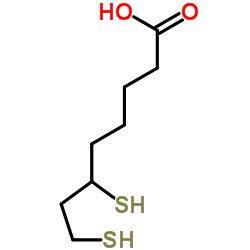
Dihydrolipoic acid structure
|
Common Name | Dihydrolipoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 462-20-4 | Molecular Weight | 208.341 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 360.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16O2S2 | Melting Point | 60ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 172.0±25.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Dihydrolipoic acidDihydrolipoic Acid (DHLA) is an excellent antioxidant capable of scavenging almost any oxygen-centered radical[1]. Dihydrolipoic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in various diseases. Dihydrolipoic Acid exerts a preventive effect via ERK/Nrf2/HO-1/ROS/NLRP3 pathway in LPS-induced sickness behavior rats. Dihydrolipoic Acid can be used for the reaserch of depression[2]. |
| Name | dihydrolipoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dihydrolipoic Acid (DHLA) is an excellent antioxidant capable of scavenging almost any oxygen-centered radical[1]. Dihydrolipoic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in various diseases. Dihydrolipoic Acid exerts a preventive effect via ERK/Nrf2/HO-1/ROS/NLRP3 pathway in LPS-induced sickness behavior rats. Dihydrolipoic Acid can be used for the reaserch of depression[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Dihydrolipoic Acid is an antioxidant. DHLA is capable of scavenging •OH radicals and scavenging superoxide radical anions with a rate constant of 3.3×105 M-1 s-1. Dihydrolipoic Acid is an excellent antioxidant, and that is very important because O2•- is a relatively mild oxidant that is therefore much more selective and can be useful to discriminate between the antioxidant capacities of different substrates[1]. |
| In Vivo | Dihydrolipoic Acid (DHLA) treatment exerts preventive effects in LPS-induced sickness behavior rats. Dihydrolipoic Acid increases the expression of ERK, Nrf2, and HO-1 but decreases the ROS generation levels and reduces the expression of NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β in LPS-induced sickness behavior rats. Dihydrolipoic Acid is a reduced form of α-lipoic acid (LA) that can decrease oxidative stress and act as a strong antioxidant[2]. Dihydrolipoic Acid treatment reverses the LPS-induced sickness behavior[2]. Animal Model: Adult male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (weight, 200-220 g)[2] Dosage: 15 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg Administration: Injected intraperitoneally daily Result: Treatment with 30 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg improved the body weight gain as compared to the LPS group. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 360.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 60ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H16O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 208.341 |
| Flash Point | 172.0±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 208.059174 |
| PSA | 114.90000 |
| LogP | 2.07 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.527 |
| InChIKey | IZFHEQBZOYJLPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCCC(S)CCS |
| Storage condition | +2C to +8C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RH0525000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Wash-free magnetic immunoassay of the PSA cancer marker using SERS and droplet microfluidics.
Lab Chip 16 , 1022-9, (2016) We report a novel wash-free magnetic immunoassay technique for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) that uses a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based microdroplet sensor. The magnetic bar embedded... |
|
|
Delivery and tracking of quantum dot peptide bioconjugates in an intact developing avian brain.
ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6(3) , 494-504, (2015) Luminescent semiconductor ∼9.5 nm nanoparticles (quantum dots: QDs) have intrinsic physiochemical and optical properties which enable us to begin to understand the mechanisms of nanoparticle mediated ... |
|
|
Colloidal stability of gold nanoparticles modified with thiol compounds: bioconjugation and application in cancer cell imaging.
Langmuir 28(9) , 4464-71, (2012) Gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are attractive alternative optical probes and good biocompatible materials due to their special physical and chemical properties. However, GNPs have a tendency to aggregate p... |
| DL-Dihydrolipoic acid |
| dihydrothiocticacid |
| Dihydroliponsure |
| (±)-dihydrolipoic acid |
| Gamma-Lipoic Acid |
| 6,8-Dimercaptooctanoic acid |
| 6,8-Disulfanyloctanoic acid |
| dihydro-thiocticaci |
| dihydrolipoate |
| Octanoic acid, 6,8-dimercapto- |
| DIHYDROLIPOIC ACID |
| usafxr-12 |
| dihydro-lipoicaci |
| DHLA |
| 6,8-Dihydrothioctic acid |
| reducedlipoicacid |
 CAS#:60-24-2
CAS#:60-24-2 CAS#:1077-28-7
CAS#:1077-28-7![6,8-bis[(dimethylarsanyl)thio]octanoic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/466/69819-89-2.png) CAS#:69819-89-2
CAS#:69819-89-2 CAS#:27565-41-9
CAS#:27565-41-9 CAS#:131760-67-3
CAS#:131760-67-3