α-Lipoic Acid
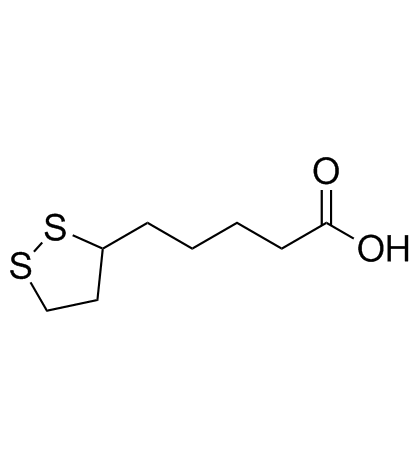
α-Lipoic Acid structure
|
Common Name | α-Lipoic Acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1077-28-7 | Molecular Weight | 206.326 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 362.5±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14O2S2 | Melting Point | 60-62ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 173.0±19.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of α-Lipoic Acidα-Lipoic Acid is an antioxidant, which is an essential cofactor of mitochondrial enzyme complexes. α-Lipoic Acid inhibits NF-κB-dependent HIV-1 LTR activation. |
| Name | DL-Thioctic Acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | α-Lipoic Acid is an antioxidant, which is an essential cofactor of mitochondrial enzyme complexes. α-Lipoic Acid inhibits NF-κB-dependent HIV-1 LTR activation. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NF-κB HIV Mitochondrial bioenergetics |
| In Vitro | The long terminal repeat (LTR) of HIV-1 is the target of cellular transcription factors such as NF-κB, and serves as the promoter-enhancer for the viral genome when integrated in host DNA[1]. α-Lipoic Acid (Alpha-Lipoic acid, ALA), a naturally occurring dithiol compound, plays an essential role in mitochondrial bioenergetics. α-Lipoic Acid reduces lipid accumulation in the liver by regulating the transcriptional factors SREBP-1, FoxO1, and Nrf2, and their downstream lipogenic targets via the activation of the SIRT1/LKB1/AMPK pathway. Treatment of cells with α-Lipoic Acid (250, 500 and 1000 μM) significantly increases the NAD+/NADH ratio in HepG2 cells (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Treatment with α-Lipoic Acid (50, 125, 250 and 500 μM) increases SIRT1 activity in HepG2 cells. α-Lipoic Acid (50, 125, 250, 500 and 1000 μM) increases phosphorylation of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) in HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent fashion[1]. |
| In Vivo | C57BL/6J mice, divided into four groups, are fed an high-fat diet (HFD) for 24 weeks to induce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) followed by daily administration of α-Lipoic Acid. Then, the effects of α-Lipoic Acid on hepatic lipid accumulation in long-term HFD-fed mice are assessed. Administration of α-Lipoic Acid (100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg) markedly reduces visceral fat mass in mice. In addition, α-Lipoic Acid (100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg) treatment inhibits the appetite and causes a dramatic weight loss (all P<0.05)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line is cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C and 5% CO2. HepG2 cells are treated with AMPK inhibitor (CC, 20 μM, 0.5 h), SIRT1 inhibitor (NA, 10 mM, 12 or 24 h), and AMPK activator (AICAR, 2 mM, 1 h), Palmitate (PA, 125 μM, 12 h) and α-Lipoic Acid (250 μM, 6 or 12 h)[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] Male C57BL/6J mice (6-week-old; body weight: 22-24 g) are allowed ad libitum access to normal diet and water for 2 weeks before dividing into four groups (n=8): normal diet (ND) (10% energy from fat), high-fat diet (HFD) (60% energy from fat) and HFD plus α-Lipoic Acid (100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg). After 24 weeks of treatment, blood samples are collected after the eyeballs of the mice are extracted for serum preparation by centrifugation at 2000×g for 10 min at 4°C. The liver tissues are harvested in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 362.5±11.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 60-62ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 206.326 |
| Flash Point | 173.0±19.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 206.043518 |
| PSA | 87.90000 |
| LogP | 2.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.562 |
| InChIKey | AGBQKNBQESQNJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCCC1CCSS1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | ethanol: 50 mg/mL | 0.9 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 37/39-26-24/25-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | JP1192000 |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Identification and Characterization of EDTA Test Strip Interfering Substances Using a Digital Color Detector.
Clin. Lab. 61 , 785-91, (2015) Rapid test strips for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) can be used to verify correct specimen types for clinical assays which require, or cannot be performed on, plasma collection tubes containi... |
|
|
Alpha-lipoic acid activates eNOS through activation of PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.
Vascul. Pharmacol. 64 , 28-35, (2015) Lipoic acid (LA) exerts therapeutic effects on cardiovascular diseases. However, the mechanisms underlying these therapeutic effects remain elusive. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) plays a cr... |
|
|
All-trans retinoic acid prevents oxidative stress-induced loss of renal tight junction proteins in type-1 diabetic model.
J. Nutr. Biochem. 26 , 441-54, (2015) We previously reported that diabetes decreased the expression of renal tight junction (TJ) proteins claudin-5 in glomerulus, and claudin-2 and occludin in proximal tubule through an oxidative stress d... |
| (S)-5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid |
| Thioctic acid |
| 5-[(3S)-Dithiolan-3-yl]pentanoic acid |
| (S)-6,8-Thioctic acid (S)-1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid |
| DL-Thioctic acid |
| 5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid |
| DL-α-Lipoic acid |
| (±)-α-Lipoic acid |
| 5-(dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid |
| 6,8-Dithiooctanoic acid |
| MFCD00005474 |
| 1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid |
| (±)-1,2-Dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid |
| (±)-1,2-Dithiolane-3-valeric acid |
| 6,8-Dihydrothioctic acid |
| lipoic acid |
| UNII:73Y7P0K73Y |
| DL-6,8-Thioctic acid |
| EINECS 214-071-2 |
| α-Lipoic Acid |
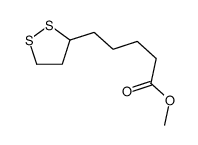 CAS#:46236-19-5
CAS#:46236-19-5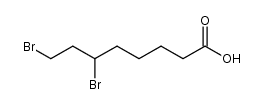 CAS#:138152-63-3
CAS#:138152-63-3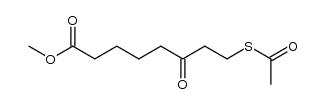 CAS#:100053-64-3
CAS#:100053-64-3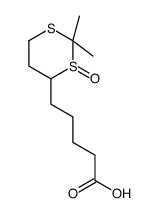 CAS#:88987-43-3
CAS#:88987-43-3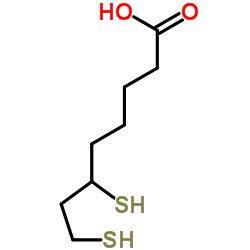 CAS#:462-20-4
CAS#:462-20-4 CAS#:35444-44-1
CAS#:35444-44-1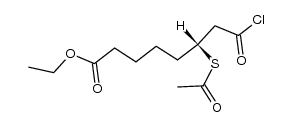 CAS#:104665-85-2
CAS#:104665-85-2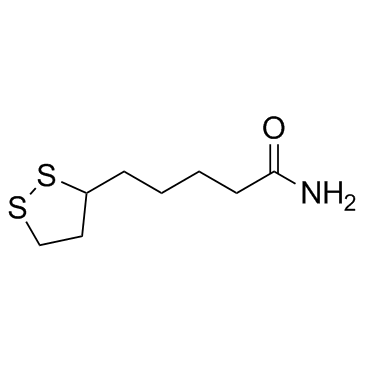 CAS#:940-69-2
CAS#:940-69-2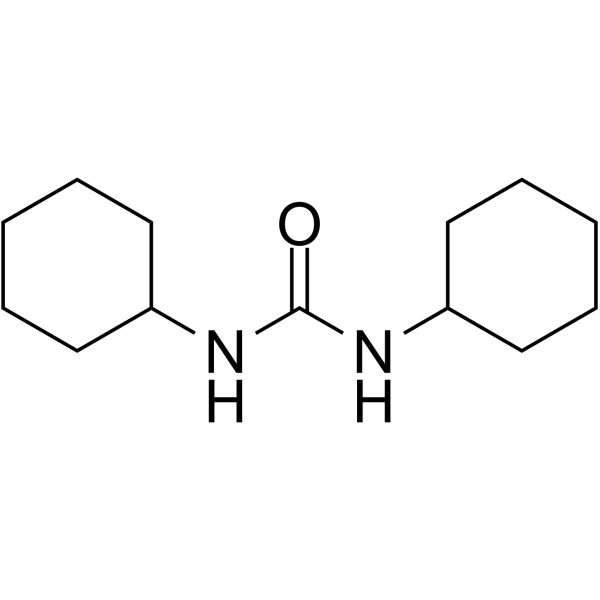 CAS#:2387-23-7
CAS#:2387-23-7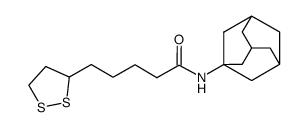 CAS#:458529-20-9
CAS#:458529-20-9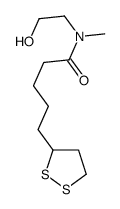 CAS#:257926-20-8
CAS#:257926-20-8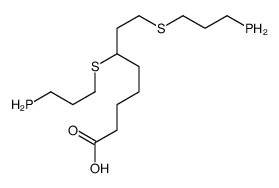 CAS#:244007-29-2
CAS#:244007-29-2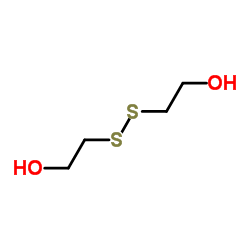 CAS#:1892-29-1
CAS#:1892-29-1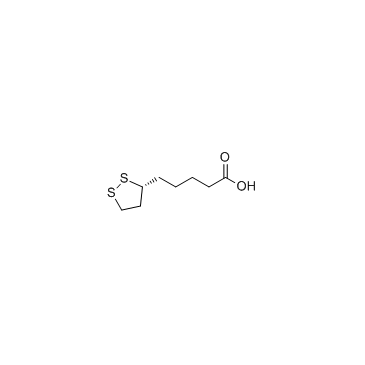 CAS#:1200-22-2
CAS#:1200-22-2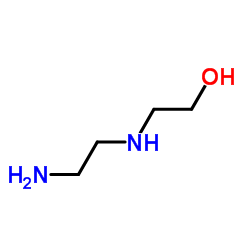 CAS#:111-41-1
CAS#:111-41-1
