| Description |
Coumestrol, a phytoestrogen present in soybean products, exhibits activities against cancers, neurological disorders, and autoimmune diseases. It suppresses proliferation of ES2 cells with an IC50 of 50 μM.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
IC50: 50 μM[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Coumestrol exerts chemotherapeutic effects via PI3K and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways. Coumestrol inhibits viability and invasion, and induces apoptosis of ES2 (clear cell-/serous carcinoma origin) cells. In addition, immunoreactive PCNA and ERBB2, markers of proliferation of ovarian carcinoma, are attenuated in their expression in coumestrol-induced death of ES2 cells. Phosphorylation of AKT, p70S6K, ERK1/2, JNK1/2 and p90RSK is inactivated by coumestrol treatment in a dose- and time-dependent manner[1]. Coumestrol inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells, which is prevented by copper chelator neocuproine and ROS scavengers. Coumestrol treatment induces ROS generation coupled to DNA fragmentation, up-regulation of p53/p21, cell cycle arrest at G1/S phase, mitochondrial membrane depolarization and caspases 9/3 activation[2].
|
| Cell Assay |
To determine dose-dependent effects of coumestrol, ES2 cells are treated with different concentrations (0, 1, 10, 20, 50 or 100 μM) of coumestrol[1]. Coumestrol is dissolved in DMSO to prepare a 3 mM stock. Breast cancer MCF-7 cells are treated with increasing concentrations of coumestrol for 24, 48 and 72 h. Then, 20 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL) is added each well and re-incubated for additional 3 h. Formazan blue crystals formed are dissolved in 100 μL of DMSO. Absorbance is read at 570 nm using ELISA plate reader[2].
|
| References |
[1]. Lim W, et al. Coumestrol suppresses proliferation of ES2 human epithelial ovarian cancer cells. J Endocrinol. 2016 Mar;228(3):149-60. [2]. Zafar A, et al. Cytotoxic activity of soy phytoestrogen coumestrol against human breast cancer MCF-7 cells: Insights into the molecular mechanism. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Jan;99:149-161.
|
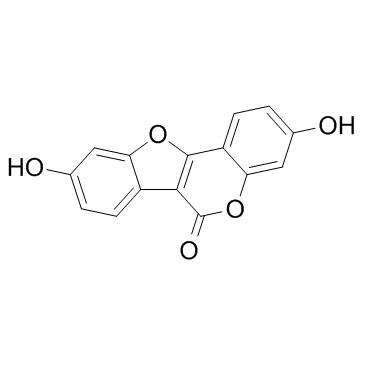
 CAS#:3172-99-4
CAS#:3172-99-4![3-hydroxy-6-oxo-6H-benzofuro[3,2-c]chromen-9-yl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/127/870456-46-5.png) CAS#:870456-46-5
CAS#:870456-46-5![2-(2,4-diacetoxyphenyl)-3-iodo-6-(tosyloxy)benzo[b]furan Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/165/870456-45-4.png) CAS#:870456-45-4
CAS#:870456-45-4 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2![Methyl 6-hydroxy-2-[2-hydroxy-4-(tosyloxy)phenyl]benzo[b]furan-3-carboxylate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/170/328945-98-8.png) CAS#:328945-98-8
CAS#:328945-98-8 CAS#:6626-15-9
CAS#:6626-15-9 CAS#:137396-01-1
CAS#:137396-01-1 CAS#:328945-90-0
CAS#:328945-90-0 CAS#:328945-93-3
CAS#:328945-93-3
