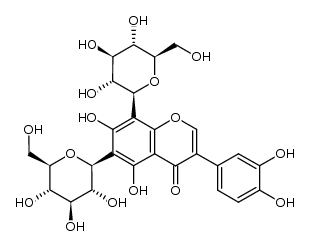
Orobol
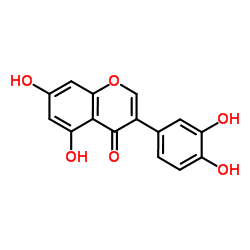
Orobol structure
|
Common Name | Orobol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 480-23-9 | Molecular Weight | 286.236 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 616.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 239.5±25.0 °C | |
Use of OrobolOrobol is one of the major soy isoflavones and has various pharmacological activities, including anti-skin-aging and anti-obesity effects. Orobol inhibits CK1ε, VEGFR2, MAP4K5, MNK1, MUSK, TOPK, and TNIK (IC50=1.24-4.45 μM). Orobol also inhibits PI3K isoforms (IC50=3.46-5.27 μM for PI3K α/β/γ/K/δ)[1][2]. |
| Name | orobol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Orobol is one of the major soy isoflavones and has various pharmacological activities, including anti-skin-aging and anti-obesity effects. Orobol inhibits CK1ε, VEGFR2, MAP4K5, MNK1, MUSK, TOPK, and TNIK (IC50=1.24-4.45 μM). Orobol also inhibits PI3K isoforms (IC50=3.46-5.27 μM for PI3K α/β/γ/K/δ)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Orobol binds to CK1ε in an ATP-competitive manner and exerts anti-obesity effects by targeting casein kinase 1 epsilon[2]. Orobol (5-20 μM) effectively suppresses MDI (isobutylmethylxanthine, dexamethasone and insulin (MDI))-induced phosphorylation of 4E-BP1[2]. |
| In Vivo | Orobol attenuates high fat diet-induced weight gain and lipid accumulation without affecting food intake in C57BL/6J mice[2]. Animal Model: HFD-induced obesity in C57BL/6J mice[2] Dosage: 10 mg/kg Administration: Intragastrically; daily for 23 weeks Result: Significantly reduced body weight by 17.3% compared to the HFD group. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 616.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 286.236 |
| Flash Point | 239.5±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 286.047729 |
| PSA | 111.13000 |
| LogP | 2.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.768 |
| InChIKey | IOYHCQBYQJQBSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=c1c(-c2ccc(O)c(O)c2)coc2cc(O)cc(O)c12 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~% 
Orobol CAS#:480-23-9 |
| Literature: Chemler, Joseph A.; Lim, Chin Giaw; Daiss, John L.; Koffas, Mattheos A.G. Chemistry and Biology, 2010 , vol. 17, # 4 p. 392 - 401 |
|
~% 
Orobol CAS#:480-23-9 |
| Literature: Narasimhachari; Seshadri Proceedings - Indian Academy of Sciences, Section A, 1950 , # 32 p. 342,345 |
|
~% 
Orobol CAS#:480-23-9 |
| Literature: Anhut, Siegbert; Zinsmeister, H. Dietmar; Mues, Ruediger; Barz, Wolfgang; Mackenbrock, Klaus; et al. Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1984 , vol. 23, # 5 p. 1073 - 1076 |
|
~% 
Orobol CAS#:480-23-9 |
| Literature: Roberts-Kirchhoff, Elizabeth S.; Crowley, Jan R.; Hollenberg, Paul F.; Kim, Hyesook Chemical Research in Toxicology, 1999 , vol. 12, # 7 p. 610 - 616 |
|
~% 
Orobol CAS#:480-23-9 |
| Literature: Heerden, Fanie R. van; Brandt, E. Vincent; Roux, David G. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: Organic and Bio-Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), 1980 , p. 2463 - 2469 |
|
~% 
Orobol CAS#:480-23-9 |
| Literature: Heerden, Fanie R. van; Brandt, E. Vincent; Roux, David G. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: Organic and Bio-Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), 1980 , p. 2463 - 2469 |
|
Name: Inhibition of recombinant human PTP-sigma (residues 1367 to 1948) using para-nitrophe...
Source: ChEMBL
Target: Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase S
External Id: CHEMBL3744703
|
|
Name: Inhibition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fatty acid synthase
Source: ChEMBL
Target: N/A
External Id: CHEMBL943598
|
|
Name: Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induc...
Source: ChEMBL
Target: NON-PROTEIN TARGET
External Id: CHEMBL2399681
|
|
Name: Cytotoxicity against mouse RAW264.7 cells by CCK assay
Source: ChEMBL
Target: N/A
External Id: CHEMBL2399680
|
|
Name: Antifungal activity against Cryptococcus neoformans ATCC 90113
Source: ChEMBL
Target: Cryptococcus neoformans
External Id: CHEMBL943600
|
|
Name: Antifungal activity against Candida albicans ATCC 90028
Source: ChEMBL
Target: Candida albicans
External Id: CHEMBL943599
|
|
Name: Inhibition of recombinant human PTP-sigma (residues 1367 to 1948) using para-nitrophe...
Source: ChEMBL
Target: Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase S
External Id: CHEMBL3744704
|
|
Name: ASTRAZENECA: Octan-1-ol/water (pH7.4) distribution coefficent measured by a shake fl...
Source: ChEMBL
Target: N/A
External Id: CHEMBL3301363
|
|
Name: Antiproliferative activity against human U937 cells after 48 hrs by WST-8 assay
Source: ChEMBL
Target: U-937
External Id: CHEMBL885742
|
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one |
| 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxyisoflavone |
| 3'-hydroxygenistein |
| Orobol |
| Norsantal |
| 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyisoflavone |
| Santol |
| 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxychromen-4-one |
| Isoluteolin |

![3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-7-[(2S,3R,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6- (hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-chromen-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/223/20486-33-3.png)