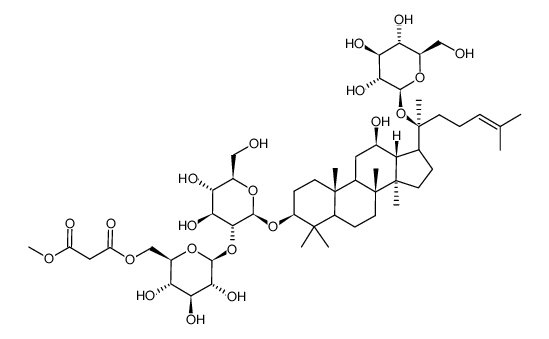
ginsenoside Rd
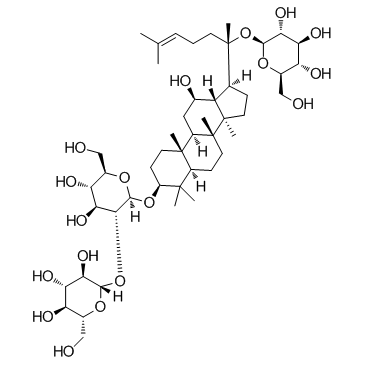
ginsenoside Rd structure
|
Common Name | ginsenoside Rd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 52705-93-8 | Molecular Weight | 947.154 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1015.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C48H82O18 | Melting Point | 207 °C(dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 568.0±34.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of ginsenoside RdGinsenoside Rd inhibits TNFα-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity with an IC50 of 12.05±0.82 μM in HepG2 cells. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits expression of COX-2 and iNOS mRNA. Ginsenoside Rd also inhibits Ca2+ influx. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP2C9, with IC50s of 58.0±4.5 μM, 78.4±5.3 μM, 81.7±2.6 μM, and 85.1±9.1 μM, respectively. |
| Name | ginsenoside Rd |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ginsenoside Rd inhibits TNFα-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity with an IC50 of 12.05±0.82 μM in HepG2 cells. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits expression of COX-2 and iNOS mRNA. Ginsenoside Rd also inhibits Ca2+ influx. Ginsenoside Rd inhibits CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP2C9, with IC50s of 58.0±4.5 μM, 78.4±5.3 μM, 81.7±2.6 μM, and 85.1±9.1 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
NF-κB:12.05 μM (IC50, in HepG2 cells) COX-2 L-type calcium channel CYP2D6:58 μM (IC50) CYP1A2:78.4 μM (IC50) CYP3A4:81.7 μM (IC50) CYP2C9:85.1 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Ginsenoside Rd is one of the most abundant ingredients of Panax ginseng. Ginsenoside Rd significantly inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity with an IC50 of 12.05±0.82 in HepG2 cells. Ginsenoside Rd also inhibits expression of COX-2 and iNOS mRNA and iNOS promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner. To determine nontoxic concentrations, HepG2 cells are treated with various concentrations (0.1, 1, and 10 μM) of compounds (e.g., Ginsenoside Rd) and cell viability is measured using an MTS assay. No compounds are significantly cytotoxic at up to 10 μM, indicating that NF-κB inhibition is not due to cell toxicity[1]. Ginsenoside Rd is one of the most abundant ingredients of Panax ginseng, protects the heart via multiple mechanisms including the inhibition of Ca2+ influx. Ginsenoside Rd reduces ICa,L peak amplitude in a concentration-dependent manner (IC50=32.4±7.1 μM)[2]. Ginsenoside Rd exhibits an inhibition against the activity of CYP2D6 in human liver microsomes with an IC50 of 58.0±4.5 μM, a weak inhibition against the activity of CYP1A2, CYP3A4, and CYP2C9 in human liver microsomes with IC50s of 78.4±5.3, 81.7±2.6, and 85.1±9.1, respectively, and an even weaker inhibition against the activity of CYP2A6 in human liver microsomes with an IC50 value of more than 100 μM[4]. |
| In Vivo | Ginsenosides Rd is a major compound isolated from Gynostemma pentaphyllum that holistically improves gut microenvironment and induces anti-polyposis in ApcMin/+ mice. Six-weeks-old mice are subjected to Ginsenoside Rd treatment, before the appearance of the intestinal polyps. All the mice are monitored for food intake, water consumption, and weight changes. Throughout the experiment, no Rb3/ Ginsenoside Rd-associated weight loss in mice is observed. In addition, none of the treated mice show variations in food and water consumption. Whereas, the number and size of the polyps are effectively reduced by Ginsenoside Rd treatments[3]. |
| Cell Assay | An MTS assay is used to analyze the effects of the compounds on cell viability. HepG2 cells are cultured overnight in a 96-well plate (1×104 cells/well). Cell viability is assessed after adding the compounds (e.g., Ginsenoside Rd; 0.1, 1, and 10 μM) for 24 h. The number of viable cells is determined by the A490nm of the dissolved formazan product, after addition of MTS for 30 min[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Heterozygous male ApcMin/+ (C57BL/6J-ApcMin/+) mice are used. Total 32 male ApcMin/+ mice (aged 6 weeks) are divided into three groups; 10 mice in the control group and 22 mice equally divided for Rb3 and Rd treatments. The mice are daily gavage with a single dose of Ginsenoside Rb3 or Ginsenoside Rd at 20 mg/kg, or solvent control. The treatments are carried out for 8 consecutive weeks. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1015.6±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 207 °C(dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C48H82O18 |
| Molecular Weight | 947.154 |
| Flash Point | 568.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 946.550110 |
| PSA | 298.14000 |
| LogP | 3.24 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.611 |
| InChIKey | RLDVZILFNVRJTL-IWFVLDDISA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)=CCCC(C)(OC1OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C1O)C1CCC2(C)C1C(O)CC1C3(C)CCC(OC4OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C4OC4OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C4O)C(C)(C)C3CCC12C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 
ginsenoside Rd CAS#:52705-93-8 |
| Literature: Kitagawa; Taniyama; Yoshikawa; Ikenishi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1989 , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
ginsenoside Rd CAS#:52705-93-8 |
| Literature: Kitagawa; Taniyama; Yoshikawa; Ikenishi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1989 , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
ginsenoside Rd CAS#:52705-93-8 |
| Literature: Kitagawa; Taniyama; Yoshikawa; Ikenishi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1989 , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
~% 
ginsenoside Rd CAS#:52705-93-8 |
| Literature: Kitagawa; Taniyama; Yoshikawa; Ikenishi; Nakagawa Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1989 , vol. 37, # 11 p. 2961 - 2970 |
|
Transcriptome analysis of Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidicus discovers putative ocotillol-type ginsenosides biosynthesis genes and genetic markers.
BMC Genomics 16 , 159, (2015) P. vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus, called "Yesanqi" in Chinese, is a new variety of P. vietnamensis, which was first found in Jinping County, the southern part of Yunnan Province, China. Compared with ... |
|
|
Protective effects of ginsenoside Rd on PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide.
Biol. Pharm. Bull. 31(10) , 1923-7, (2008) Oxidative stress-induced cell damage has been implicated in a variety of neurodegenerative disorders. In the current study, we investigated the protective role of ginsenoside Rd against the cytotoxici... |
|
|
Bioconversion of ginsenoside Rc into Rd by a novel α-L-arabinofuranosidase, Abf22-3 from Leuconostoc sp. 22-3: cloning, expression, and enzyme characterization.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103(4) , 747-54, (2013) A novel α-L-arabinofuranosidase (Abf22-3) that could biotransform ginsenoside Rc into Rd was obtained from the ginsenoside converting Leuconostoc sp. strain 22-3, isolated from the Korean fermented fo... |
| GINSENOOSIDERD |
| ginsenoside Rd |
| (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-Dihydroxy-6-(hydroxyméthyl)-2-({(3S,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentaméthyl-17-[(2S)-6-méthyl-2-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-5-heptèn-2-yl]hexadécahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phénanthrén-3-yl}oxy)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol |
| Herba Gynostemmatis Pentaphylli |
| (3β,12β)-20-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-12-hydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl-2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| (3β,12β)-20-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-12-hydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranoside |
| Gypenoside VIII |
| GinsenosideRd |
| EINECS 258-118-5 |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,12β)-20-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-12-hydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl- |
| ginsenoside--Rd standard |
| MFCD00210508 |
| (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-Dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-({(3S,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-[(2S)-6-methyl-2-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-5-hepten-2-yl]hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl}oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol |