Acetohydroxamic acid
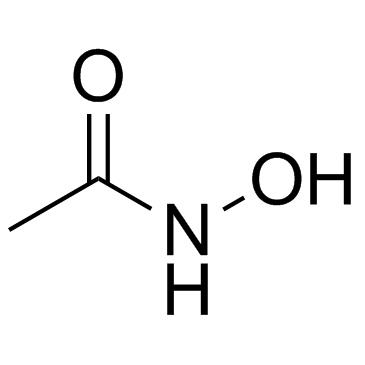
Acetohydroxamic acid structure
|
Common Name | Acetohydroxamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 546-88-3 | Molecular Weight | 75.067 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 231.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5NO2 | Melting Point | 88-90 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Acetohydroxamic acidAcetohydroxamic acid is a potent and irreversible inhibitor of bacterial and plant urease and also used as adjunctive therapy in chronic urinary infection.Target: UreaseAcetohydroxamic acid selectively inhibits arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase and thus has potential use in the treatment of asthma. |
| Name | acetohydroxamic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent and irreversible inhibitor of bacterial and plant urease and also used as adjunctive therapy in chronic urinary infection.Target: UreaseAcetohydroxamic acid selectively inhibits arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase and thus has potential use in the treatment of asthma. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 231.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 88-90 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C2H5NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 75.067 |
| Exact Mass | 75.032028 |
| PSA | 49.33000 |
| LogP | -1.59 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.421 |
| Stability | Moisture and Temperature Sensitive |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R61 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45 |
| RIDADR | 3263 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AK8157000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
CDK1 substitutes for mTOR kinase to activate mitotic cap-dependent protein translation.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 , 5875-82, (2015) Mitosis is commonly thought to be associated with reduced cap-dependent protein translation. Here we show an alternative control mechanism for maintaining cap-dependent translation during mitosis reve... |
|
|
BDNF stimulation of protein synthesis in cortical neurons requires the MAP kinase-interacting kinase MNK1.
J. Neurosci. 35(3) , 972-84, (2015) Although the MAP kinase-interacting kinases (MNKs) have been known for >15 years, their roles in the regulation of protein synthesis have remained obscure. Here, we explore the involvement of the MNKs... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
| Acetamide, N-hydroxy- |
| Acetohydroxamic acid |
| methanecarbohydroxamic acid |
| EINECS 208-913-8 |
| N-Hydroxyacetamide |
| N-acetylhydroxylamine |
| Acetomenadione |
| acethydroxamic acid |
| methylenehydroxamic acid |
| Acetylhydroxylamine |
| AHA |
| Lithostat |
| Acethydroxamsaure |
| MFCD00009994 |
| Acetohydroxamic |
| Acetic acid,oxime |
| Acetic Acid Oxime |
 CAS#:108-24-7
CAS#:108-24-7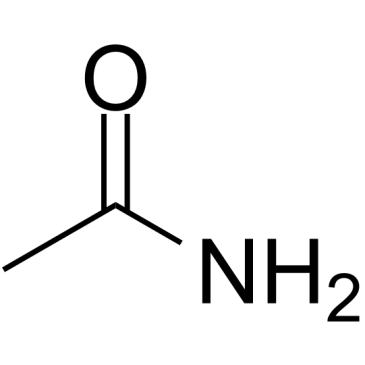 CAS#:60-35-5
CAS#:60-35-5 CAS#:141-78-6
CAS#:141-78-6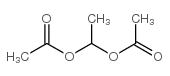 CAS#:542-10-9
CAS#:542-10-9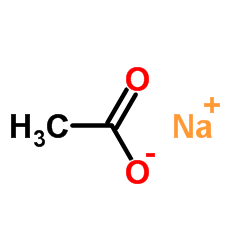 CAS#:127-09-3
CAS#:127-09-3 CAS#:463-51-4
CAS#:463-51-4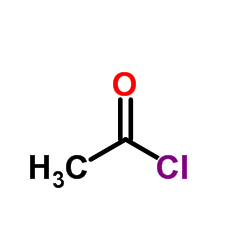 CAS#:75-36-5
CAS#:75-36-5 CAS#:79-24-3
CAS#:79-24-3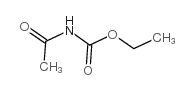 CAS#:2597-54-8
CAS#:2597-54-8 CAS#:869669-06-7
CAS#:869669-06-7![5-Bromobenzo[d]isoxazol-3-ylamine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/299/455280-00-9.png) CAS#:455280-00-9
CAS#:455280-00-9![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/057/36216-80-5.png) CAS#:36216-80-5
CAS#:36216-80-5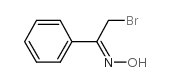 CAS#:14181-72-7
CAS#:14181-72-7![6-Bromobenzo[d]isoxazol-3-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/346/177995-39-0.png) CAS#:177995-39-0
CAS#:177995-39-0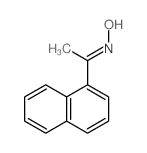 CAS#:1956-40-7
CAS#:1956-40-7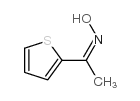 CAS#:1956-45-2
CAS#:1956-45-2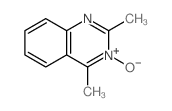 CAS#:1837-71-4
CAS#:1837-71-4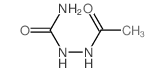 CAS#:2302-87-6
CAS#:2302-87-6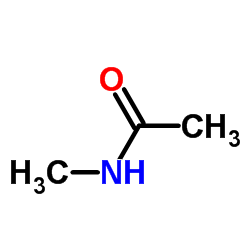 CAS#:79-16-3
CAS#:79-16-3 CAS#:588-46-5
CAS#:588-46-5
