Betahistine Dihydrochloride
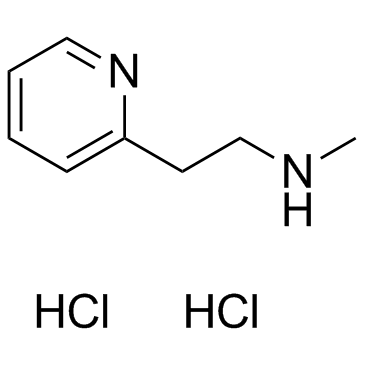
Betahistine Dihydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Betahistine Dihydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5579-84-0 | Molecular Weight | 209.116 | |
| Density | 0.967 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 210.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14Cl2N2 | Melting Point | 150-154 °C | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 96.7ºC | |
Use of Betahistine DihydrochlorideBetahistine Dihydrochloride is a histamine H3 receptors inhibitor used as an antivertigo drug.Target: Histamine ReceptorBetahistine, a structural analogue of histamine with weak histamine H(1) receptor agonist and more potent H(3) receptor antagonist properties. Betahistine acts centrally by enhancing histamine synthesis within tuberomammillary nuclei of the posterior hypothalamus and histamine release within vestibular nuclei through antagonism of H(3) autoreceptors [1].Therapeutic effects of betahistine in vestibular disorders result from its antagonist properties at histamine H(3) receptors (H(3)Rs). On inhibition of cAMP formation and [(3)H]arachidonic acid release, betahistine behaved as a nanomolar inverse agonist and a micromolar agonist. After acute oral administration, Betahistine increased t-MeHA levels with an ED(50) of 2 mg/kg, a rightward shift probably caused by almost complete first-pass metabolism. Therapeutic effects of betahistine result from an enhancement of histamine neuron activity induced by inverse agonism at H(3) autoreceptors [2]. |
| Name | Betahistine dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Betahistine Dihydrochloride is a histamine H3 receptors inhibitor used as an antivertigo drug.Target: Histamine ReceptorBetahistine, a structural analogue of histamine with weak histamine H(1) receptor agonist and more potent H(3) receptor antagonist properties. Betahistine acts centrally by enhancing histamine synthesis within tuberomammillary nuclei of the posterior hypothalamus and histamine release within vestibular nuclei through antagonism of H(3) autoreceptors [1].Therapeutic effects of betahistine in vestibular disorders result from its antagonist properties at histamine H(3) receptors (H(3)Rs). On inhibition of cAMP formation and [(3)H]arachidonic acid release, betahistine behaved as a nanomolar inverse agonist and a micromolar agonist. After acute oral administration, Betahistine increased t-MeHA levels with an ED(50) of 2 mg/kg, a rightward shift probably caused by almost complete first-pass metabolism. Therapeutic effects of betahistine result from an enhancement of histamine neuron activity induced by inverse agonism at H(3) autoreceptors [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.967 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 210.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 150-154 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H14Cl2N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 209.116 |
| Flash Point | 96.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 208.053406 |
| PSA | 24.92000 |
| LogP | 2.83840 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Differential thermodynamic driving force of first- and second-generation antihistamines to determine their binding affinity for human H1 receptors.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 91(2) , 231-41, (2014) Differential binding sites for first- and second-generation antihistamines were indicated on the basis of the crystal structure of human histamine H1 receptors. In this study, we evaluated differences... |
|
|
Development of novel sustained release matrix pellets of betahistine dihydrochloride: effect of lipophilic surfactants and co-surfactants.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 17(5) , 583-93, (2012) Sustained release matrix pellets of the freely water soluble drug, betahistine dihydrochloride (BH), were prepared using freeze pelletization technique. Different waxes and lipids (cetyl alcohol, bees... |
|
|
Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy of a fixed low-dose combination of cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate with betahistine in vestibular neuritis: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority study.
Clin. Drug Investig. 32(6) , 387-99, (2012) Vestibular neuritis (VN) is a strongly disabling disease of the peripheral vestibular system. Rapid and effective relief of symptoms is important to allow patients to promptly return to normal physica... |
| MFCD00012813 |
| N-Methyl-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethanamine dihydrochloride |
| N-methyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethanamine dihydrochloride |
| 2-Pyridineethanamine, N-methyl-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| Betahistine Hydrochloride |
| N-Methyl-2-pyridineethanamine Dihydrochloride |
| N-methyl-2-pyridin-2-ylethanamine,dihydrochloride |
| EINECS 226-966-5 |
| Betahistine (dihydrochloride) |