Betahistine
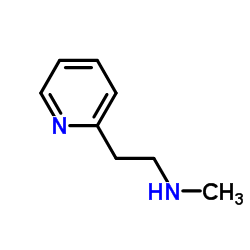
Betahistine structure
|
Common Name | Betahistine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5638-76-6 | Molecular Weight | 136.194 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 210.9±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 96.7±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of BetahistineBetahistine is an orally active histamine H1 receptor agonist and a H3 receptor antagonist[1]. Betahistine is used for the study of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)[3]. |
| Name | betahistine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Betahistine is an orally active histamine H1 receptor agonist and a H3 receptor antagonist[1]. Betahistine is used for the study of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
H1 Receptor H3 receptor |
| In Vitro | Betahistine (0-10 μM) inhibits [125I]iodoproxyfan binding to membranes of CHO (rH3(445)R) and CHO (hH3(445)R) cells with IC50 values of 1.9 μM and 3.3 μM, respectively. Lead to Ki values of 1.4 μM and 2.5 μM, respectively[2]. Betahistine (0-10 μM) has a regulating function on cAMP formation in CHO (rH3(445)R), CHO (rH3(413)R), and CHO (hH3(445)R) cells. At low concentrations, betahistine behaves an apparent inverse agonist, and progressively enhances cAMP formation with EC50 values of 0.1 nM, 0.05 nM and 0.3 nM, respectively. In contrast, at concentrations higher than 10 nM, betahistine inhibits cAMP formation with an EC50 value of 0.1 μM in CHO (rH3(445)R) and full agonist activity[2]. |
| In Vivo | Betahistine (intraperitoneal or oral administration; 0.1-30 mg/kg; single dose) with acute administration has increased tele-methylhistamine (t-MeHA) levels with an ED50 of 0.4 mg/kg, indicating the inverse agonism. Besides, after acute oral administration, it increases t-MeHA levels with an ED50 of 2 mg/kg in male Swissmice[2]. Betahistine (oral adminstration; 1 and 5 mg/kg; daily for 3 weeks) attenuates the severity of arthritis and reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the paw tissues of CIA mice[3]. Animal Model: Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) DBA/1 male mouse model[3] Dosage: 1 mg/kg; 5mg/kg Administration: Oral adminstration; day 21 to day 42 after a 21-day CIA induction Result: Ameliorated mouse CIA by decreasing joint destruction. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 210.9±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 136.194 |
| Flash Point | 96.7±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 136.100052 |
| PSA | 24.92000 |
| LogP | 0.10 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.510 |
| InChIKey | UUQMNUMQCIQDMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CNCCc1ccccn1 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant;C: Corrosive; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN2735 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | UT5552000 |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2933399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933399090. other compounds containing an unfused pyridine ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Development of novel sustained release matrix pellets of betahistine dihydrochloride: effect of lipophilic surfactants and co-surfactants.
Pharm. Dev. Technol. 17(5) , 583-93, (2012) Sustained release matrix pellets of the freely water soluble drug, betahistine dihydrochloride (BH), were prepared using freeze pelletization technique. Different waxes and lipids (cetyl alcohol, bees... |
|
|
Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy of a fixed low-dose combination of cinnarizine and dimenhydrinate with betahistine in vestibular neuritis: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority study.
Clin. Drug Investig. 32(6) , 387-99, (2012) Vestibular neuritis (VN) is a strongly disabling disease of the peripheral vestibular system. Rapid and effective relief of symptoms is important to allow patients to promptly return to normal physica... |
|
|
Betahistine or Cinnarizine for treatment of Meniere's disease.
Med. Arh. 66(6) , 396-8, (2012) Meniere's disease is a condition with sudden attacks of vertigo with nausea and vomiting accompanied by loss of hearing and buzzing sensation in the ears, most commonly unilateral. The exact cause of ... |
| 2-(b-Methylaminoethyl)pyridine |
| N-methyl-2-pyridin-2-ylethanamine |
| Pyridine, 2-[2- (methylamino)ethyl]- |
| MFCD00006362 |
| N-Methyl-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethanamine |
| EINECS 227-086-4 |
| Suzutolon |
| 2-Pyridineethanamine, N-methyl- |
| 2-(2-Methylaminoethyl)pyridine |
| N-methyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethanamine |
| N-Methyl-2-pyridineethanamine |
| Betahistine |
 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:2706-56-1
CAS#:2706-56-1 CAS#:557-04-0
CAS#:557-04-0 CAS#:6304-27-4
CAS#:6304-27-4 CAS#:143185-43-7
CAS#:143185-43-7 CAS#:100-69-6
CAS#:100-69-6 CAS#:593-51-1
CAS#:593-51-1 CAS#:103-74-2
CAS#:103-74-2 CAS#:6998-30-7
CAS#:6998-30-7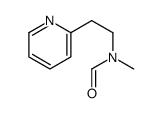 CAS#:88780-61-4
CAS#:88780-61-4![2-METHYLPYRAZOLO[1,5-A]PYRIMIDINE-5,7-DIOL structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/065/939979-42-7.png) CAS#:939979-42-7
CAS#:939979-42-7