For-Met-Leu-Phe-OH

For-Met-Leu-Phe-OH structure
|
Common Name | For-Met-Leu-Phe-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59880-97-6 | Molecular Weight | 437.553 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 783.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C21H31N3O5S | Melting Point | 271-274 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 427.6±32.9 °C | |
Use of For-Met-Leu-Phe-OHN-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLP; N-Formyl-MLF) is a chemotactic peptide and a specific ligand of N-formyl peptide receptor (FPR). N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Ph is reported to inhibit TNF-alpha secretion. |
| Name | N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLP; N-Formyl-MLF) is a chemotactic peptide and a specific ligand of N-formyl peptide receptor (FPR). N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Ph is reported to inhibit TNF-alpha secretion. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
TNF-alpha[1] |
| In Vitro | Binding of N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe to its specific cell surface receptor, N-formyl peptide receptor (FPR), triggers different cascades of biochemical events, eventually leading to cellular activation. FPR is a chemoattractant receptor belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor family. N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe promotes osteoblastic commitment and suppresses adipogenic commitment under osteoblastic differentiation conditions. N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe stimulates osteogenesis is associated with increased expression of osteogenic markers and mineralization. N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe inhibits expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ1. N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-stimulated osteogenic differentiation is mediated via FPR1-phospholipase C/phospholipase D-Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent kinase II-ERK-CREB signaling pathways[1]. N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe, a bacterial-derived peptide, induced proinflammatory cytokine gene expression in human peripheral blood monocytes. Bacterial products LPS and N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe synergistically induce inflammatory response via multiple signaling pathways. TLR4, IKKβ-IκBα, and NF-κB signaling pathways are involved in the synergistic induction of TNF-α via p65 nuclear translocation-dependent mechanisms[2]. |
| In Vivo | N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe promotes bone formation in zebrafish and rabbits. Extensive skeletal development is evident at 5 dpf in over 80% of N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-treated zebrafish. Treatment with N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe results in increased expression of Runx2. Bone marrow spaces are widely formed, and connective tissue covering bone is dense, like periosteum, in N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-treated calvaria[1]. N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe mediate release of calprotectin from PMN in vitro. It induces release of calprotectin from PMN in a dose dependent manner. A minimum of 10% of total PMN calprotectin is retained at concentrations of 0.1-10.0 nM of N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are cotransfected with either a dominant negative form of IκBα or a dominant negative form of IKKβ together with the NF-κB-dependent luciferase reporter plasmid. The plasmid pCMVβ is used as a control for transfection efficiency and this is monitored via the expression of β-galactosidase. Cells are transiently transfected with plasmids using DEAE-dextran. The transfected cells are cultivated for 48 h before a 6-h incubation in medium ±N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe, LPS, or N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe/LPS. Luciferase activity is determined by using the luciferase assay kit and a Monolight 3010 luminometer[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe is prepared in sterile PBS. Under the anesthesia, mice are intranasally treated with LPS (0.3 mg/kg) or N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (0.5 mg/kg) or N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe and LPS in 50 μL of sterile PBS (control), BAL is performed by cannulating the trachea with sterilized PBS, and cells from BAL fluid are stained with Wright-Giemsa stain after cytocentrifuge. For TNF-α protein release, BAL fluid is collected and secreted TNF-α is measured by ELISA as described above[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 783.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 271-274 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C21H31N3O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 437.553 |
| Flash Point | 427.6±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 437.198456 |
| PSA | 149.90000 |
| LogP | 3.13 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.551 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | DMF: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | SJ6050000 |
| HS Code | 2922299090 |
| HS Code | 2922299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922299090. other amino-naphthols and other amino-phenols, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, their ethers and esters; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Real-time tracking of hydrogen peroxide secreted by live cells using MnO2 nanoparticles intercalated layered doubled hydroxide nanohybrids.
Anal. Chim. Acta 898 , 34-41, (2015) We report a facile and green method for the fabrication of new type of electrocatalysts based on MnO2 nanoparticles incorporated on MgAl LDH P-type semiconductive channel and explore its practical app... |
|
|
Antiallergic and antiasthmatic effects of a novel enhydrazinone ester (CEE-1): inhibition of activation of both mast cells and eosinophils.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 350(2) , 444-54, (2014) Activation of mast cells and eosinophils is a fundamental process in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases. We have previously reported that the novel enhydrazinone ester CEE-1 (ethyl 4-phenylhydra... |
|
|
TLR4 accessory molecule RP105 (CD180) regulates monocyte-driven arteriogenesis in a murine hind limb ischemia model.
PLoS ONE 9(6) , e99882, (2014) We investigated the role of the TLR4-accessory molecule RP105 (CD180) in post-ischemic neovascularization, i.e. arteriogenesis and angiogenesis. TLR4-mediated activation of pro-inflammatory Ly6Chi mon... |
| N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe |
| formyl-Met-Leu-Phe |
| N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine |
| L-Phenylalanine, N-(N-(N-formyl-L-methionyl)-L-leucyl)- |
| Chemotactic peptide |
| formyl-MLF |
| MFCD00012901 |
| N-Formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine |
| N-Formylmethionine leucyl-phenylalanine |
| EINECS 200-462-5 |
| L-Phenylalanine, N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl- |
| N-formyl-L-methyonyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine |
| NformylLmethionylLleucylLphenylalaninol |
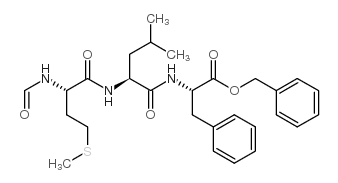 CAS#:70637-32-0
CAS#:70637-32-0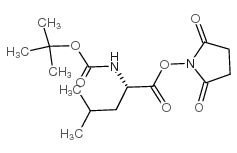 CAS#:3392-09-4
CAS#:3392-09-4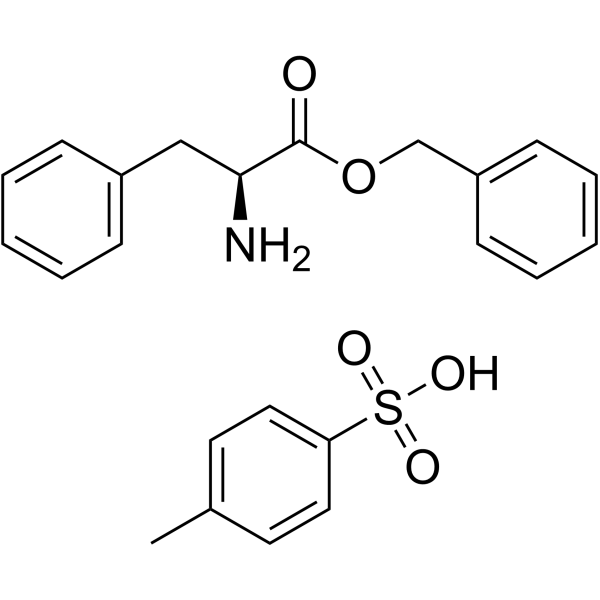 CAS#:1738-78-9
CAS#:1738-78-9 CAS#:70637-27-3
CAS#:70637-27-3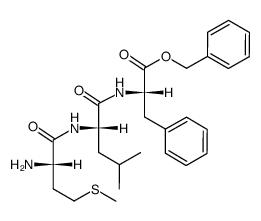 CAS#:70637-30-8
CAS#:70637-30-8
