2,6-Dibromophenol

2,6-Dibromophenol structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-Dibromophenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 608-33-3 | Molecular Weight | 251.903 | |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 256.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Br2O | Melting Point | 53-56 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 82.5±21.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2,6-Dibromophenol2,6-Dibromophenol is an endogenous metabolite. |
| Name | 2,6-dibromophenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,6-Dibromophenol is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 256.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 53-56 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H4Br2O |
| Molecular Weight | 251.903 |
| Flash Point | 82.5±21.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 249.862869 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 3.41 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.644 |
| Storage condition | Room temperature. |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 29081000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2908199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2908199090. derivatives of polyphenols or phenol-alcohols containing only halogen substituents and their salts. VAT:17.0%. tax rebate rate:9.0%. supervision conditions:None. MFN tariff:5.5%. general tariff:30.0% |
|
cIEF for rapid pKa determination of small molecules: a proof of concept.
Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 63 , 14-21, (2014) A capillary isoelectric focusing (cIEF) method was developed for the determination of the ionization constants (pKa) of small molecules. Two approaches used to decrease the electroosmotic flow (EOF) w... |
|
|
Reductive dehalogenase structure suggests a mechanism for B12-dependent dehalogenation.
Nature 517(7535) , 513-6, (2015) Organohalide chemistry underpins many industrial and agricultural processes, and a large proportion of environmental pollutants are organohalides. Nevertheless, organohalide chemistry is not exclusive... |
|
|
Biodegradation of brominated aromatics by cultures and laccase of Trametes versicolor.
Chemosphere 76(6) , 826-32, (2009) 2-Bromophenol (1), 4-bromophenol (2), 2,4-dibromophenol (3), 2,6-dibromophenol (4), 2,4,6-tribromophenol (5) and tetrabromobisphenol A (6) (1 mM each) added to growing submerged cultures of Trametes v... |
| Phenol, 2,6-dibromo- |
| 2,6-bromophenol |
| 2.6-Dibrom-1-hydroxy-benzol |
| MFCD00002152 |
| 2,6-Dibromo-phenol |
| 2,5-DEOXYFRUCTOSAZINE-13C4 |
| Phenol,2,6-dibromo |
| 2,6-dibromo-pheno |
| 2,6-Dibrom-phenol |
| 2,6-Dibromophenol |
| EINECS 210-161-0 |
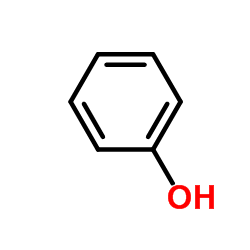 CAS#:108-95-2
CAS#:108-95-2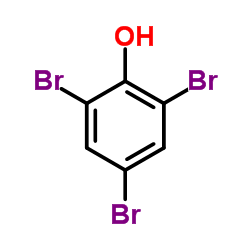 CAS#:118-79-6
CAS#:118-79-6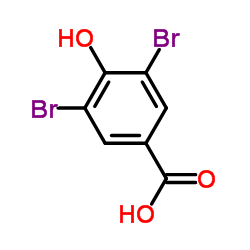 CAS#:3337-62-0
CAS#:3337-62-0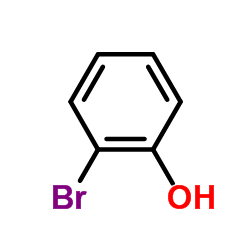 CAS#:95-56-7
CAS#:95-56-7 CAS#:100477-81-4
CAS#:100477-81-4 CAS#:91-22-5
CAS#:91-22-5 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:609-21-2
CAS#:609-21-2 CAS#:3883-95-2
CAS#:3883-95-2 CAS#:38603-09-7
CAS#:38603-09-7 CAS#:33491-30-4
CAS#:33491-30-4 CAS#:142273-81-2
CAS#:142273-81-2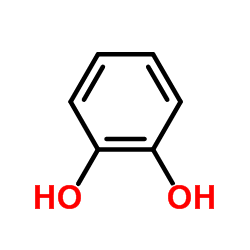 CAS#:120-80-9
CAS#:120-80-9 CAS#:87-66-1
CAS#:87-66-1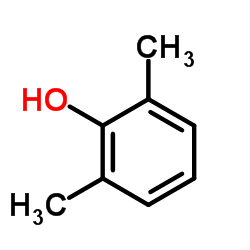 CAS#:576-26-1
CAS#:576-26-1 CAS#:13319-71-6
CAS#:13319-71-6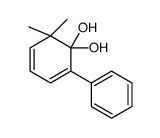 CAS#:32750-14-4
CAS#:32750-14-4
