2,6-Xylenol
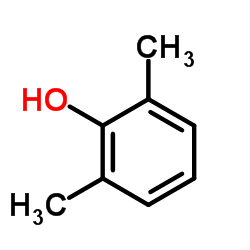
2,6-Xylenol structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-Xylenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 576-26-1 | Molecular Weight | 122.164 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 201.1±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O | Melting Point | 43-45 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 78.3±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 2,6-Dimethylphenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 201.1±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 43-45 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H10O |
| Molecular Weight | 122.164 |
| Flash Point | 78.3±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 122.073166 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 2.40 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.540 |
| InChIKey | NXXYKOUNUYWIHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1cccc(C)c1O |
| Stability | Stable. Very flammable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, steel, copper, copper alloys, bases, acid chlorides. |
| Water Solubility | 10 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311-H314-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R24/25;R34;R51/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2261 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | ZE6125000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29071400 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2907199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2907199090 other monophenols VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Increased tolerance to salt stress in OPDA-deficient rice ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE mutants is linked to an increased ROS-scavenging activity.
J. Exp. Bot. 66 , 3339-52, (2015) Salinity stress represents a global constraint for rice, the most important staple food worldwide. Therefore the role of the central stress signal jasmonate for the salt response was analysed in rice ... |
|
|
Calculating virtual log P in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and its derived parameters deltalog P(N)(oct-alk) and log D(pH)(alk).
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 3269-79, (2005) Growing interest in the use of both the logarithm of the partition coefficient of the neutral species in the alkane/water system (log P(N)(alk)) and the difference between log P(N)(oct) (the logarithm... |
|
|
Cellular apoptosis and cytotoxicity of phenolic compounds: a quantitative structure-activity relationship study.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 7234-42, (2005) In this comprehensive study on the caspase-mediated apoptosis-inducing effect of 51 substituted phenols in a murine leukemia cell line (L1210), we determined the concentrations needed to induce caspas... |
| Phenol, 2,6-dimethyl- |
| 2,6-Dimethylphenol |
| 2,6-dimethylphenethyl chloride |
| 2,6-Xylenol |
| 2,6-di-methyl phenol |
| MFCD00002240 |
| 2,6-DIMETHYL PHENOL |
| 2-hydroxy-1,3-dimethylbenzene |
| 2,6-Dimethylphenethylchlorid |
| 2,6-Dimethyl-phenol |
| 2,6-Me2C6H3OH |
| 2,3-Xylenol |
| 2,6-Me-PhOH |
| EINECS 209-400-1 |
 CAS#:576-22-7
CAS#:576-22-7 CAS#:6781-98-2
CAS#:6781-98-2 CAS#:100379-00-8
CAS#:100379-00-8 CAS#:1004-66-6
CAS#:1004-66-6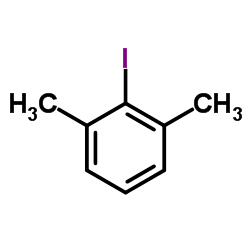 CAS#:608-28-6
CAS#:608-28-6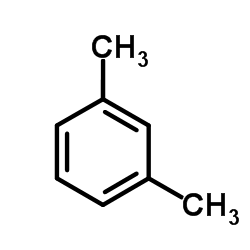 CAS#:108-38-3
CAS#:108-38-3 CAS#:845786-38-1
CAS#:845786-38-1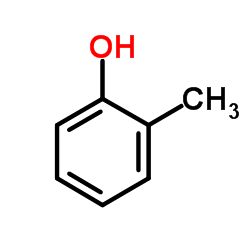 CAS#:95-48-7
CAS#:95-48-7 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1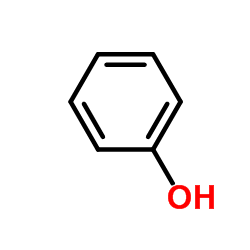 CAS#:108-95-2
CAS#:108-95-2![[3-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)-2-hydroxypropyl]-dimethyl-propan-2-ylazanium,iodide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/309/105996-40-5.png) CAS#:105996-40-5
CAS#:105996-40-5 CAS#:100311-41-9
CAS#:100311-41-9![4-[[4-hydroxy-3,5-bis[(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)methyl]phenyl]methyl]-2,6-dimethylphenol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/309/105052-80-0.png) CAS#:105052-80-0
CAS#:105052-80-0 CAS#:654-42-2
CAS#:654-42-2 CAS#:527-61-7
CAS#:527-61-7 CAS#:2913-40-8
CAS#:2913-40-8 CAS#:4906-22-3
CAS#:4906-22-3 CAS#:5520-77-4
CAS#:5520-77-4 CAS#:718-36-5
CAS#:718-36-5 CAS#:555-16-8
CAS#:555-16-8
