S-Methylisothiourea sulfate
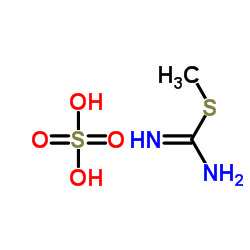
S-Methylisothiourea sulfate structure
|
Common Name | S-Methylisothiourea sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 867-44-7 | Molecular Weight | 188.226 | |
| Density | 1.28 | Boiling Point | 138.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C2H8N2O4S2 | Melting Point | 240-241 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 37.7ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of S-Methylisothiourea sulfateS-Methylisothiourea sulfate is a potent, selective and competitive inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). S-Methylisothiourea sulfate exerts beneficial effects in rodent models of septic shock[1]. |
| Name | 2-Methyl-2-thiopseudourea sulfate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | S-Methylisothiourea sulfate is a potent, selective and competitive inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). S-Methylisothiourea sulfate exerts beneficial effects in rodent models of septic shock[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
iNOS[1] |
| In Vitro | S-Methylisothiourea sulfate is a competitive inhibitor of iNOS activity at the L-arginine site[1]. S-Methylisothiourea sulfate prevents the NO-mediated cytotoxic effect of LPS in cultured macrophages[1]. S-Methylisothiourea sulfate (100 nM-100 μM) exhibits inhibitory effects on LPS (ug/mL)-induced nitrite production in J774.2 macrophages and rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells[1]. S-Methylisothiourea sulfate(up to 1 mM) does not inhibit the activity of xanthine oxidase, diaphorase, lactate dehydrogenase, monoamine oxidase, catalase, cytochrome P450, or superoxide dismutase[1]. |
| In Vivo | S-Methylisothiourea sulfate (0.01-3 mg/kg; i.v.) dose-dependently reverses the hypotension and the vascular hyporeactivity to vasoconstrictor agents caused by endotoxin LPS in anesthetized rats[1]. S-Methylisothiourea sulfate (5 mg/kg; i.p.; given 2 hr after LPS; 10 mg/kg, i.p.) attenuates the rises in plasma alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, bilirubin, and creatinine and also prevents hypocalcaemia when measured 6 hr after administration of LPS[1]. S-Methylisothiourea sulfate (1 mg/kg; i.p.) improves 24-hr survival of mice treated with a high dose of LPS (60 mg/kg; i.p.)[1]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats (260-320 g)[1] Dosage: 0.01 mg/kg, 0.1 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 3 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection Result: Caused a prompt restoration of the blood pressure to pre-LPS levels at 3 mg/kg dose in LPS (10 mg/kg, i.v.)-treated rats; Inhibits iNOS activity measured in homogenates of lung. |
| References |
| Density | 1.28 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 138.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 240-241 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C2H8N2O4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 188.226 |
| Flash Point | 37.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 187.992554 |
| PSA | 158.15000 |
| LogP | 1.47090 |
| InChIKey | NNBBQNFHCVVQHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CSC(=N)N.O=S(=O)(O)O |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 260 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UM9200000 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Lipopolysaccharides Promote S-Nitrosylation and Proteasomal Degradation of Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1) in Macrophages in Vivo.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 19011-7, (2015) LKB1 (liver kinase B1) plays important roles in tumor suppression, energy metabolism, and, recently, in innate immune responses. However, how LKB1 is regulated under physiological or pathological cond... |
|
|
Antioxidant comparative effects of two grape pomace Mexican extracts from vineyards on erythrocytes.
Food Chem. 194 , 1081-8, (2015) Maceration and Soxhlet methods were used to obtain methanol extracts from a Mexican grape (Ruby Cabernet) pomace and the biological activity and phenolic profiles were compared. The antioxidant capaci... |
|
|
Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides and metabolites in manure samples by one-step ultrasound/microwave-assisted solid-liquid-solid dispersive extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407(13) , 3545-54, (2015) An in-line matrix cleanup method was used for the simultaneous extraction of 15 sulfonamides and two metabolites from manure samples. The ultrasound/microwave-assisted extraction (UMAE) combined with ... |
| S-Methyl-isothiouronium Hemisulfate |
| S-METHYLTHIOPSEUDOUREA SULPHATE |
| 2-Methyl-2-thiopseudourea sulfate |
| 2-Methyl-2-thiopseudourea hemisulfate |
| S-METHYLISOTHIOHARNSTOFF HEMISULFAT |
| S-methylisothiourea sulfuric acid salt 1:1 |
| S-EIT hemihydrate |
| 2-methyl-2-thiopseudouronium sulfate |
| S-METHYLISOTHIOURONIUM SULPHATE |
| 2-Methyl-2-thiopseudoureasulfate |
| S-METHYL-ISO-THIOUREA SULFATE |
| S-Methylisothiourea Hemisulfate Salt |
| S-METHYLISOTHIOURONIUM SULPHATE/S-METHYLISOTHIOUREA SULPHATE/2-METHYL-2-THIOPSEUDOUREA SULPHATE |
| 2-METHYL-2-THIOPSEUDOUREA SULFATE (S-METHYLISOTHIOUREA SULFATE) |
| MFCD00129752 |
| methyl imidothiocarbamate |
| S-METHYL ISOTHIOUREA SULFATE |
| Carbamimidothioic acid, methyl ester, sulfate (2:1) |
| S-methyl-2-thiopseudourea hydrogen sulfate |
| S-METHYLTHIOURONIUM SULFATE |
| S-methylisothiourea hydrogensulfate |
| S-Methyl-ITU |
| S-MethyliSothourea Sulfate |
| methyl imidothiocarbamate sulfate |
| 2-Methyl-2-thiopseud |
| EINECS 212-759-7 |
| S-methyl isothiourea sultate |
| 2-METHYL-2-THIOPSEUDO UREA 14C SULFATE |
| S-METHYL-ISO-THIOUREA |
| S-methyl Isothiourea (hemisulfate) |
| S-METHYLISOTHIOURONIUM SULFATE |
| 5-METHYLISOTHIOUREA HEMISULFATE |
| Carbamimidothioic acid, methyl ester, sulfate (1:1) |
| (S)-METHYLISOTHIOUREA SULFATE |
| METHYLTHIOURONIUMSULPHATE |
| Methyl carbamimidothioate sulfate (1:1) |
| S-METHYLTHIOUREA |
| S-METHYL-2-ISOTHIOUREA HEMISULPHATE |
| S-methylisothiouronium hydrogensulfate |
| methyl carbamimidothioate |
| S-METHYLISOTHIOUREASULFATE |
| S-METHYLTHIOURONIUM SULFATE FOR SYNTHESIS |
| S-Methylisothiourea hemisulfate |
| S-METHYLISOTHIOUREA HEMISULFATE SALT _X000D_ |
| S-Methylisothiourea sulfate |
| IMINO(METHYLSULFANYL)METHYLAMINE |
| Amino(methylsulfanyl)methaniminium hydrogen sulfate (1:1:1) |
| S-Methyl-ITU . sulfate |
| S-METHYLTHIOURONIUMSULFATE(2:1) |
| METHYLTHIURONIUMSULPHATE |
| 2-METHYL-ISOTHIOUREA |
 CAS#:34840-23-8
CAS#:34840-23-8 CAS#:352-97-6
CAS#:352-97-6 CAS#:14923-17-2
CAS#:14923-17-2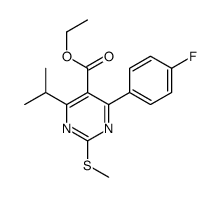 CAS#:147118-27-2
CAS#:147118-27-2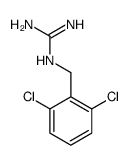 CAS#:14885-07-5
CAS#:14885-07-5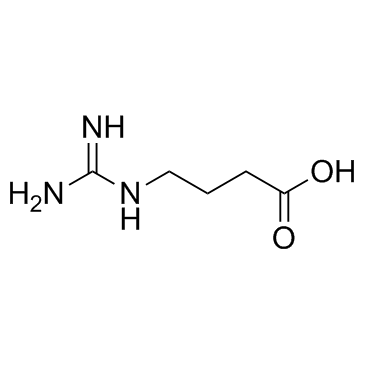 CAS#:463-00-3
CAS#:463-00-3![2-[2-(isoquinolin-5-ylsulfonylamino)ethyl]guanidine,hydrochloride structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/489/92564-34-6.png) CAS#:92564-34-6
CAS#:92564-34-6 CAS#:18240-93-2
CAS#:18240-93-2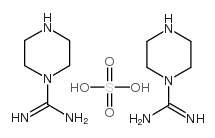 CAS#:22365-47-5
CAS#:22365-47-5 CAS#:21735-15-9
CAS#:21735-15-9
