Berberine hydrochloride
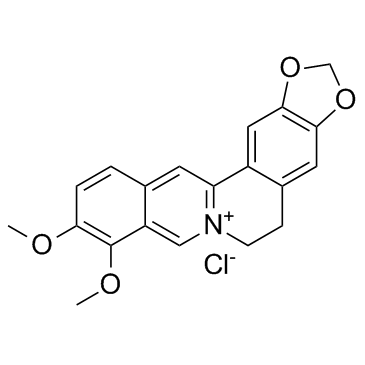
Berberine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Berberine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 633-65-8 | Molecular Weight | 372.822 | |
| Density | 1.654g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18ClNO4 | Melting Point | 200ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Berberine hydrochlorideBerberine has shown to be effective in inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis in various cancerous cells; MAPK and Wnt/β-catenin pathways affected by Berberine.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer agentThe plant-based alkaloid berberine has potential therapeutic applications for breast cancer, although a better understanding of the genes and cellular pathways regulated by this compound is needed to define the mechanism of its action in cancer treatment. In this review, the molecular targets of berberine in various cancers, particularly breast cancer, are discussed. Berberine was shown to be effective in inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis in various cancerous cells. Some signaling pathways affected by berberine, including the MAP (mitogen-activated protein) kinase and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, are critical for reducing cellular migration and sensitivity to various growth factors [1]. Treatment with BBR(Berberine) in rats on the atherogenic diet reduced plasma total cholesterol and nonHDL cholesterol levels by 29%-33% and 31%-41%, respectively, with no significant differences being observed among the three doses [2]. Berberine induced both apoptotic and autophagic death of HepG2 cells, which was associated with a significant activation of AMPK and an increased expression of the inactive form of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) [3]. Berberine did not show major effects on viability of HEK-293 embryonic kidney and HCT116 colon carcinoma cells and was not toxic in concentrations up to 20 μM. Berberine inhibited β-catenin transcriptional activity and attenuated anchorage-independent growth. As a result of berberine treatment, cellular levels of active β-catenin were reduced concomitant with an increase in the expression of E-cadherin [4]. |
| Name | berberine chloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Berberine has shown to be effective in inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis in various cancerous cells; MAPK and Wnt/β-catenin pathways affected by Berberine.IC50 value:Target: Anticancer agentThe plant-based alkaloid berberine has potential therapeutic applications for breast cancer, although a better understanding of the genes and cellular pathways regulated by this compound is needed to define the mechanism of its action in cancer treatment. In this review, the molecular targets of berberine in various cancers, particularly breast cancer, are discussed. Berberine was shown to be effective in inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis in various cancerous cells. Some signaling pathways affected by berberine, including the MAP (mitogen-activated protein) kinase and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, are critical for reducing cellular migration and sensitivity to various growth factors [1]. Treatment with BBR(Berberine) in rats on the atherogenic diet reduced plasma total cholesterol and nonHDL cholesterol levels by 29%-33% and 31%-41%, respectively, with no significant differences being observed among the three doses [2]. Berberine induced both apoptotic and autophagic death of HepG2 cells, which was associated with a significant activation of AMPK and an increased expression of the inactive form of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) [3]. Berberine did not show major effects on viability of HEK-293 embryonic kidney and HCT116 colon carcinoma cells and was not toxic in concentrations up to 20 μM. Berberine inhibited β-catenin transcriptional activity and attenuated anchorage-independent growth. As a result of berberine treatment, cellular levels of active β-catenin were reduced concomitant with an increase in the expression of E-cadherin [4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.654g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 200ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18ClNO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 372.822 |
| Exact Mass | 372.099701 |
| PSA | 40.80000 |
| LogP | 0.10030 |
| InChIKey | VKJGBAJNNALVAV-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | COc1ccc2cc3[n+](cc2c1OC)CCc1cc2c(cc1-3)OCO2.[Cl-] |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE IN COLD WATER |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | DR9866400 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 3003409000 |
|
~7% 
Berberine hydro... CAS#:633-65-8 |
| Literature: Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: Organic and Bio-Organic Chemistry (1972-1999), , p. 911 - 918 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 3003409000 |
|---|
|
Berberine blocks the relapse of Clostridium difficile infection in C57BL/6 mice after standard vancomycin treatment.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59 , 3726-35, (2015) Vancomycin is a preferred antibiotic for treating Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and has been associated with a rate of recurrence of CDI of as high as 20% in treated patients. Recent studies h... |
|
|
Functional cloning and characterization of the multidrug efflux pumps NorM from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and YdhE from Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 3052-60, (2008) Active efflux of antimicrobial agents is one of the most important adapted strategies that bacteria use to defend against antimicrobial factors that are present in their environment. The NorM protein ... |
|
|
Synergistic topical application of salt-processed Phellodendron amurense and Sanguisorba officinalis Linne alleviates atopic dermatitis symptoms by reducing levels of immunoglobulin E and pro-inflammatory cytokines in NC/Nga mice.
Mol. Med. Report. 12 , 7657-64, (2015) Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease, and salt-processed Phellodendron amurense (CPE) and Sanguisorba officinalis Linne (SOE) are widely used as anti-inflammatory agents in Asia. T... |
| 1,3-Benzodioxolo[5,6-a]benzo[g]quinolizinium, 5,6-dihydro-9,10-dimethoxy-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| EINECS 211-195-9 |
| berberine hydrochloride |
| BERBERINE HCL |
| 5,6-dihydro-9,10-dimethoxy-1,3-benzodioxolo[5,6-a]benzo[g]quinolizinium chloride (1:1) |
| MFCD00011939 |
| 9,10-dimethoxy-5,6-dihydro[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ium chloride |
| Berberine (chloride) |

![Pyrimido[4,5-g]quinazoline-4,9-dione,3,8-dihydro-5,10-dihydroxy-2,7-bis(hydroxymethyl)-3,8-dimethyl- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/032/143430-38-0.png) CAS#:143430-38-0
CAS#:143430-38-0 CAS#:485-91-6
CAS#:485-91-6 CAS#:2086-83-1
CAS#:2086-83-1 CAS#:6020-18-4
CAS#:6020-18-4 CAS#:522-97-4
CAS#:522-97-4 CAS#:15401-69-1
CAS#:15401-69-1 CAS#:25459-91-0
CAS#:25459-91-0 CAS#:10134-52-8
CAS#:10134-52-8 CAS#:549-21-3
CAS#:549-21-3
