D-(+)-Malic acid
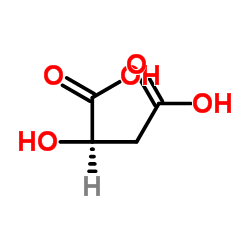
D-(+)-Malic acid structure
|
Common Name | D-(+)-Malic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 636-61-3 | Molecular Weight | 134.087 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 306.4±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O5 | Melting Point | 98-104ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 153.4±20.2 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of D-(+)-Malic acidD-(+)-Malic acid (D-Malic acid), an active enantiomer of Malic acid, is a competitive inhibitor of L(--)malic acid transport[1]. |
| Name | (R)-malic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-(+)-Malic acid (D-Malic acid), an active enantiomer of Malic acid, is a competitive inhibitor of L(--)malic acid transport[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Some bacteria belonging to Arthrobacter, Brevibacterium, Corynebacterium, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, and Acinetobacter produced D-(+)-Malic acid (D-Malic acid) from Maleic acid when the cells grown in a medium containing citraconic acid are reacted aerobically with Maleic acid in the pH 7.0 phosphate buffer containing 0.1% sodium chloride[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 306.4±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 98-104ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C4H6O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 134.087 |
| Flash Point | 153.4±20.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 134.021530 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | -1.26 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.529 |
| InChIKey | BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UWTATZPHSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CC(O)C(=O)O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | ON7260000 |
| HS Code | 29181980 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918199090 other carboxylic acids with alcohol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
GC/TOFMS analysis of metabolites in serum and urine reveals metabolic perturbation of TCA cycle in db/db mice involved in diabetic nephropathy.
Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 304(11) , F1317-24, (2013) Early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy (DN) is difficult although it is of crucial importance to prevent its development. To probe potential markers and the underlying mechanism of DN, an animal mode... |
|
|
In vitro reactive oxygen species production by mitochondria from the rabbitfish Siganus fuscessens livers and the effects of Irgarol-1051.
Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 35(2) , 154-60, (2013) In this study, the mitochondria from the livers of Siganus fuscessens were exposed to the Irgarol-1051with or without respiratory chain inhibitors using succinate or malate as the substrate, and the e... |
|
|
Changes in pH and organic acids in mucilage of Eriophorum angustifolium roots after exposure to elevated concentrations of toxic elements.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 20(3) , 1876-80, (2013) The presence of Eriophorum angustifolium in mine tailings of pyrite maintains a neutral pH, despite weathering, thus lowering the release of toxic elements into acid mine drainage water. We investigat... |
| Malic acid, D- |
| (R)-Hydroxybutanedioic acid |
| Butanedioic acid, 2-hydroxy-, (2R)- |
| EINECS 211-262-2 |
| (R)-(+)-HYDROXYSUCCINIC ACID |
| Malic acid,D |
| R-Malic acid |
| D-malate |
| D-Malic Acid |
| (R)-2-Hydroxysuccinic acid |
| (R)-2-Hydroxy-succinic acid |
| (2R)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid |
| 2(R)-hydroxybutanedioic acid |
| (2R)-2-Hydroxysuccinic acid |
| L-malic acid |
| (R)-malic acid |
| D-(+)-Malic Acid |
| D-Hydroxybutanedioic acid |
| MFCD00004245 |
| D(+)-Malic acid |
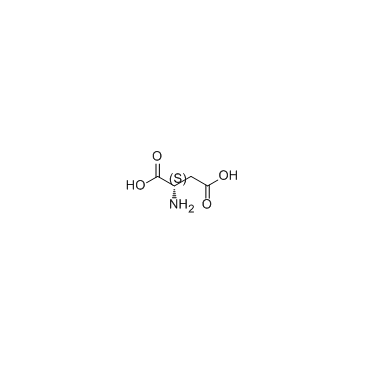 CAS#:56-84-8
CAS#:56-84-8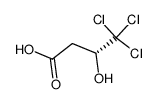 CAS#:80513-23-1
CAS#:80513-23-1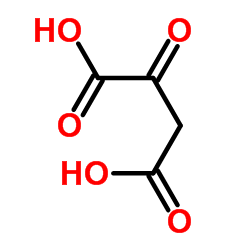 CAS#:328-42-7
CAS#:328-42-7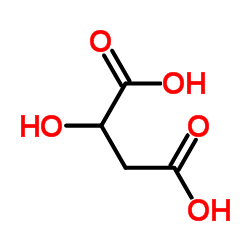 CAS#:617-48-1
CAS#:617-48-1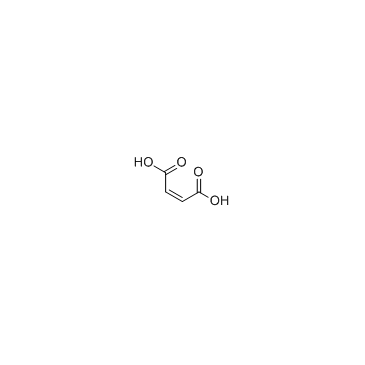 CAS#:110-16-7
CAS#:110-16-7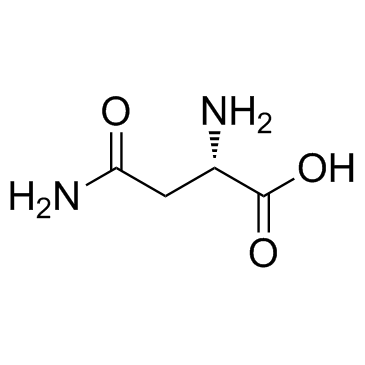 CAS#:70-47-3
CAS#:70-47-3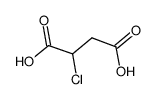 CAS#:16045-92-4
CAS#:16045-92-4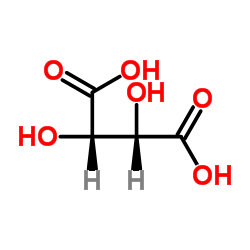 CAS#:87-69-4
CAS#:87-69-4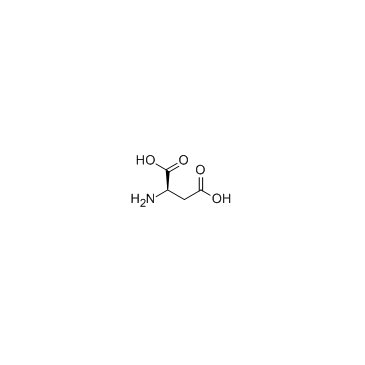 CAS#:1783-96-6
CAS#:1783-96-6 CAS#:923-06-8
CAS#:923-06-8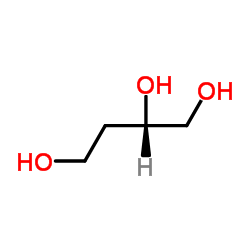 CAS#:42890-76-6
CAS#:42890-76-6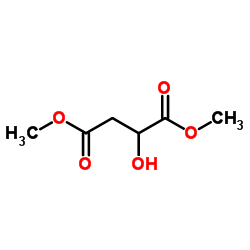 CAS#:38115-87-6
CAS#:38115-87-6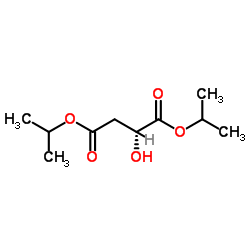 CAS#:83540-97-0
CAS#:83540-97-0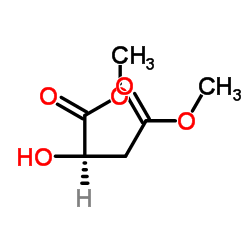 CAS#:70681-41-3
CAS#:70681-41-3 CAS#:7554-28-1
CAS#:7554-28-1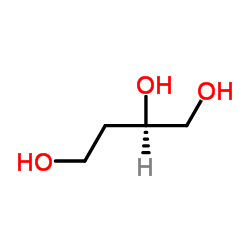 CAS#:70005-88-8
CAS#:70005-88-8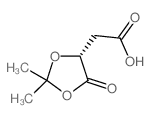 CAS#:73991-95-4
CAS#:73991-95-4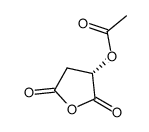 CAS#:59025-03-5
CAS#:59025-03-5
