Physostigmine hemisulfate
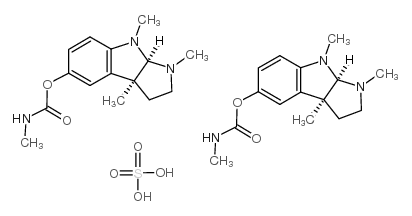
Physostigmine hemisulfate structure
|
Common Name | Physostigmine hemisulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 64-47-1 | Molecular Weight | 648.77100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 557.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21N3O2.1/2H2O4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 291ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Physostigmine hemisulfatePhysostigmine hemisulfate (Eserine hemisulfate) is a potent cholinesterase inhibitor. Physostigmine hemisulfate crosses the blood-brain barrier and stimulates central cholinergic neurotransmission. Physostigmine hemisulfate induces reanimation from isoflurane anesthesia in adult rats[1]. |
| Name | Eserine hemisulfate salt |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Physostigmine hemisulfate (Eserine hemisulfate) is a potent cholinesterase inhibitor. Physostigmine hemisulfate crosses the blood-brain barrier and stimulates central cholinergic neurotransmission. Physostigmine hemisulfate induces reanimation from isoflurane anesthesia in adult rats[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Physostigmine hemisulfate (IV; 0.1, 0.2 mg/kg) delays time to emergence from isoflurane anesthesia at doses ≥0.2 mg/kg in male Sprague-Dawley rats[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 557.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H21N3O2.1/2H2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 648.77100 |
| Flash Point | 291ºC |
| Exact Mass | 648.29400 |
| PSA | 172.60000 |
| LogP | 4.76340 |
| InChIKey | LLIODTIILSCNOH-PBCQUBLHSA-N |
| SMILES | CNC(=O)Oc1ccc2c(c1)C1(C)CCN(C)C1N2C.O=S(=O)(O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 + H330 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P284-P301 + P310-P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Phrases | 26/28 |
| Safety Phrases | S25-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UY8585000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
Cholinergic activation of the murine trachealis muscle via non-vesicular acetylcholine release involving low-affinity choline transporters.
Int. Immunopharmacol. 29 , 173-80, (2015) In addition to quantal, vesicular release of acetylcholine (ACh), there is also non-quantal release at the motor endplate which is insufficient to evoke postsynaptic responses unless acetylcholinester... |
|
|
Determination of high-affinity choline uptake (HACU) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) activity in the same population of cultured cells.
Brain Res. 1297 , 160-8, (2009) Cholinergic neurons are a major constituent of the mammalian central nervous system. Acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter used by cholinergic neurons, is synthesized from choline and acetyl CoA by the ... |
|
|
Comparative studies on acetylcholinesterase characteristics between the aphids, Sitobion avenae and Rhopalosiphum padi.
J. Insect Sci. 13 , 9, (2013) The aphids Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) and Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) (Hemiptera: Aphidiae) are serious pests on grain crops and usually coexist on late period of wheat growth in China. Bioassays s... |
| [(3aR,8bS)-3,4,8b-trimethyl-2,3a-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]indol-7-yl] N-methylcarbamate,sulfuric acid |
| EINECS 200-585-4 |
| MFCD06795853 |
| Eserine Hemisulfate |