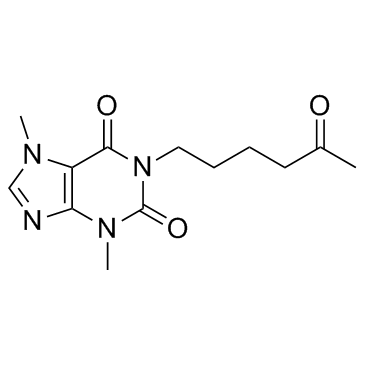
Lisofylline
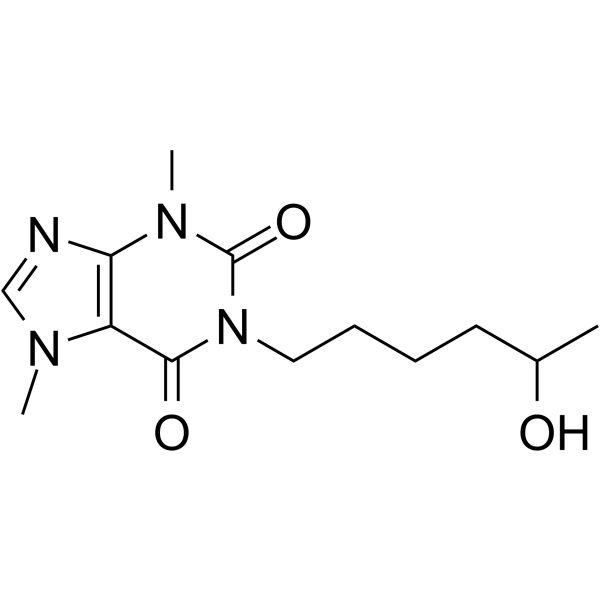
Lisofylline structure
|
Common Name | Lisofylline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 6493-06-7 | Molecular Weight | 280.323 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 511.2±56.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H20N4O3 | Melting Point | 123-125ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 263.0±31.8 °C | |
Use of Lisofylline(±)-Lisofylline ((±)-Lisophylline) is the racemate of Lisofylline. Lisofylline inhibits the generation of phosphatidic acid and free fatty acids. Lisofylline also blocks the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in oxidative tissue injury, in response to cancer chemotherapy and in experimental sepsis. Lisofylline can be used for Type 1 diabetes research[1]. |
| Name | (±)-Lisofylline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (±)-Lisofylline ((±)-Lisophylline) is the racemate of Lisofylline. Lisofylline inhibits the generation of phosphatidic acid and free fatty acids. Lisofylline also blocks the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in oxidative tissue injury, in response to cancer chemotherapy and in experimental sepsis. Lisofylline can be used for Type 1 diabetes research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 511.2±56.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 123-125ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C13H20N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 280.323 |
| Flash Point | 263.0±31.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 280.153534 |
| PSA | 82.05000 |
| LogP | 0.34 |
| Appearance of Characters | solid | white |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.621 |
| InChIKey | NSMXQKNUPPXBRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(O)CCCCn1c(=O)c2c(ncn2C)n(C)c1=O |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~91% 
Lisofylline CAS#:6493-06-7 |
| Literature: Kala, Elzbieta P.; Wojcik, Tomasz Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica - Drug Research, 2007 , vol. 64, # 2 p. 109 - 113 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits human immunodeficiency type 1 transmission by Langerhans cells via an autocrine/paracrine feedback mechanism.
Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 213(2) , 432-41, (2015) Peripheral neurones innervating mucosal epithelia are in direct contact with resident immune cells, including Langerhans cells (LCs). Such neurones secrete the neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related pep... |
| R-1-(5-Hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine |
| (R)-3,7-Dihydro-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| 1-[(5R)-5-Hydroxyhexyl]-3,7-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| Penthydroxifillyne |
| HYDROXY PENTOXIFYLLINE |
| Lisofylline |
| 1-(5-Hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1-[(5R)-5-hydroxyhexyl]-3,7-dimethyl- |
| UNII:R99EE080JS |
| 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethyl- |
| ProTec |
| 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 3,7-dihydro-1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethyl-, (R)- |
| 1-[(R)-5-Hydroxyhexyl]theobromine |
| CT 1501R |