Thiamine hydrochloride
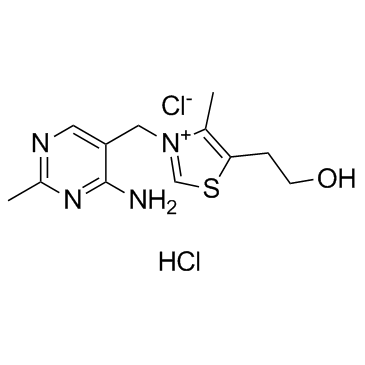
Thiamine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Thiamine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67-03-8 | Molecular Weight | 337.268 | |
| Density | 1.401 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18Cl2N4OS | Melting Point | 246-254ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Thiamine hydrochlorideThiamine hydrochloride is an essential micronutrient needed as a cofactor for many central metabolic enzymes. |
| Name | thiamine(2+) dichloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Thiamine hydrochloride is an essential micronutrient needed as a cofactor for many central metabolic enzymes. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.401 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 246-254ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18Cl2N4OS |
| Molecular Weight | 337.268 |
| Flash Point | 100ºC |
| Exact Mass | 336.057831 |
| PSA | 104.15000 |
| InChIKey | DPJRMOMPQZCRJU-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | Cc1ncc(C[n+]2csc(CCO)c2C)c(N)n1.Cl.[Cl-] |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents. |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 0.1 g/mL at 20 °C, clear, colorless | 1 g/mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H301 + H311 + H331-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P301 + P310-P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN1230 - class 3 - PG 2 - Methanol, solution |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | XI7350000 |
| HS Code | 2934100090 |
|
~% 
Thiamine hydroc... CAS#:67-03-8 |
| Literature: Litvak Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 1999 , vol. 33, # 2 p. 101 - 103 |
|
~% 
Thiamine hydroc... CAS#:67-03-8 |
| Literature: Contant; Forzy; Hengartner; Moine Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1990 , vol. 73, # 5 p. 1300 - 1305 |
|
~% 
Thiamine hydroc... CAS#:67-03-8 |
| Literature: Contant; Forzy; Hengartner; Moine Helvetica Chimica Acta, 1990 , vol. 73, # 5 p. 1300 - 1305 |
|
~% 
Thiamine hydroc... CAS#:67-03-8 |
| Literature: Bergel; Todd Journal of the Chemical Society, 1938 , p. 26 Full Text Show Details Andersag; Westphal Chemische Berichte, 1937 , vol. 70, p. 2035,2044 Full Text Show Details Todd; Bergel Journal of the Chemical Society, 1937 , p. 367 Journal of the Chemical Society, 1938 , p. 28 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Hoffmann-La Roche Patent: US2127446 , 1938 ; Full Text Show Details Hoffmann-La Roche Patent: DE676980 , 1937 ; DRP/DRBP Org.Chem. |
|
~% 
Thiamine hydroc... CAS#:67-03-8 |
| Literature: Matsukawa; Yurugi Yakugaku Zasshi, 1951 , vol. 71, p. 1423,1427 Chem.Abstr., 1952 , p. 8127 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Koenig et al. Patent: US2393109 , 1941 ; |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2934100090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934100090 other compounds containing an unfused thiazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:20.0% |
|
Protein enrichment of an Opuntia ficus-indica cladode hydrolysate by cultivation of Candida utilis and Kluyveromyces marxianus.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95(5) , 1094-102, (2015) The cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica (prickly pear cactus) have a low protein content; for use as a balanced feed, supplementation with other protein sources is therefore desirable. We investigated pr... |
|
|
Effects of N source concentration and NH4(+)/NO3(-) ratio on phenylethanoid glycoside pattern in tissue cultures of Plantago lanceolata L.: a metabolomics driven full-factorial experiment with LC-ESI-MS(3.).
Phytochemistry 106 , 44-54, (2014) Tissue cultures of a medicinal plant, Plantago lanceolata L. were screened for phenylethanoid glycosides (PGs) and other natural products (NPs) with LC-ESI-MS(3). The effects of N source concentration... |
|
|
Capillary electromigration techniques as tools for assessing the status of vitamins A, C and E in patients with cystic fibrosis.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 102 , 45-53, (2014) The purpose of this work is the evaluation of the nutritional status of patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), based on the level of vitamin C in urine and vitamins A and E in serum, using the fast, sele... |
| Thiamine Hydrochloride |
| Aneurine hydrochloride |
| Vitamin B1 hydrochloride |
| EINECS 200-641-8 |
| MFCD00012780 |
| Thiazolium,3-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methyl-chloride (1:1), hydrochloride (1:1) |

![Pyrimido[4,5-D]pyrimidine, 1,5-dihydro-2-methyl- (6ci,8ci,9ci) structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/367/31375-19-6.png)
![N-[(4-amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidyl)methyl]thioformamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/012/31375-20-9.png)


 CAS#:490-82-4
CAS#:490-82-4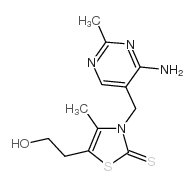 CAS#:299-35-4
CAS#:299-35-4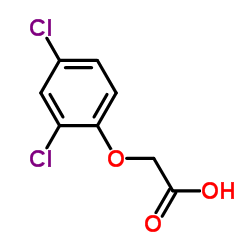 CAS#:94-75-7
CAS#:94-75-7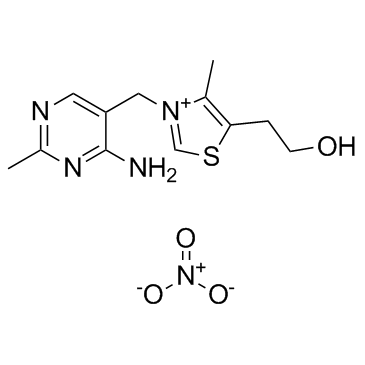 CAS#:532-43-4
CAS#:532-43-4 CAS#:59-58-5
CAS#:59-58-5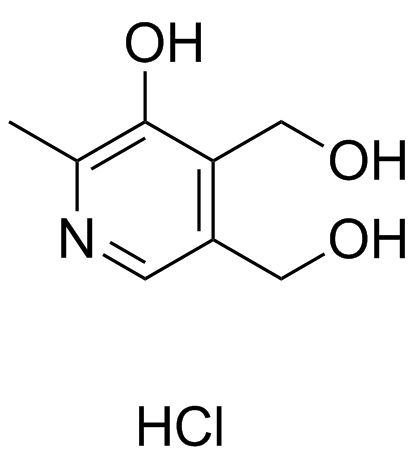 CAS#:58-56-0
CAS#:58-56-0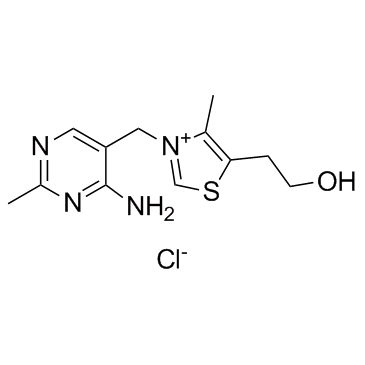 CAS#:59-43-8
CAS#:59-43-8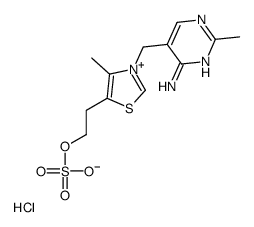 CAS#:15743-04-1
CAS#:15743-04-1![3-[(4-Amino-2-methyl-5-pyrimidinyl)methyl]-5-{2-[(hydroxy{[hydrox y(phosphonooxy)phosphoryl]oxy}phosphoryl)oxy]ethyl}-4-methyl-1,3- thiazol-3-ium structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/432/15666-52-1.png) CAS#:15666-52-1
CAS#:15666-52-1
