Alizarin

Alizarin structure
|
Common Name | Alizarin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 72-48-0 | Molecular Weight | 240.211 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 430.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8O4 | Melting Point | 287 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 228.0±23.8 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of AlizarinAlizarin is a natural dye extracted from the roots of madder plant and has been widely used as a pigment in textile fabrics and paintings[1]. |
| Name | alizarin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Alizarin is a natural dye extracted from the roots of madder plant and has been widely used as a pigment in textile fabrics and paintings[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 430.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 287 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 240.211 |
| Flash Point | 228.0±23.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 240.042252 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | 4.09 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.733 |
| InChIKey | RGCKGOZRHPZPFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C1c2ccccc2C(=O)c2c1ccc(O)c2O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25-S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YO8300000 |
| HS Code | 2914700090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2914690090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2914690090 other quinones。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Alveolar bone dynamics in osteoporotic rats treated with raloxifene or alendronate: confocal microscopy analysis.
J. Biomed. Opt. 20(3) , 38003, (2015) In this study, the characteristics of the alveolar bone of rats with induced osteoporosis were examined. Thirty-two rats were divided into four groups according to the induction of osteoporosis and dr... |
|
|
Differentially circulating miRNAs after recent osteoporotic fractures can influence osteogenic differentiation.
Bone 79 , 43-51, (2015) Osteoporosis is the consequence of altered bone metabolism resulting in the systemic reduction of bone strength and increased risk of fragility fractures. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression o... |
|
|
Donor-matched mesenchymal stem cells from knee infrapatellar and subcutaneous adipose tissue of osteoarthritic donors display differential chondrogenic and osteogenic commitment.
Eur. Cell. Mater. 27 , 298-311, (2014) Cell-based therapies have recently been proposed for the treatment of degenerative articular pathologies, such as early osteoarthritis, with an emphasis on autologous mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), as... |
| Red 83 |
| Pincoffin |
| Acid Mordant Red B |
| 1,2-Dihydroxy-9,10-anthracenedione |
| 1,2-Anthraquinonediol |
| Alizarina |
| Aliazrin |
| S NO 1141 |
| EINECS 200-782-5 |
| Alizarin |
| Acid Metachrome Red B |
| dihydroxyanthraquinone |
| 1,2-Dihydroxy anthraquinone |
| 9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,2-dihydroxy- |
| 1,2-Dihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone |
| C Ext. Red 62 |
| Alizarine |
| D & C Orange No. 15 |
| mordant red 11 |
| MFCD00132540 |
 CAS#:85-44-9
CAS#:85-44-9 CAS#:120-80-9
CAS#:120-80-9 CAS#:88-95-9
CAS#:88-95-9 CAS#:82-34-8
CAS#:82-34-8 CAS#:84-65-1
CAS#:84-65-1 CAS#:117-79-3
CAS#:117-79-3 CAS#:84-45-7
CAS#:84-45-7 CAS#:95-57-8
CAS#:95-57-8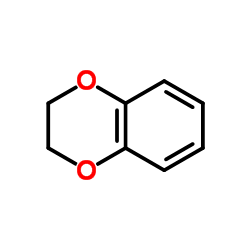 CAS#:493-09-4
CAS#:493-09-4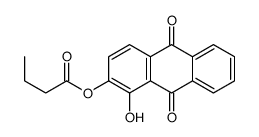 CAS#:110349-96-7
CAS#:110349-96-7 CAS#:3952-78-1
CAS#:3952-78-1 CAS#:22516-90-1
CAS#:22516-90-1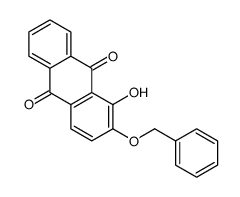 CAS#:22516-62-7
CAS#:22516-62-7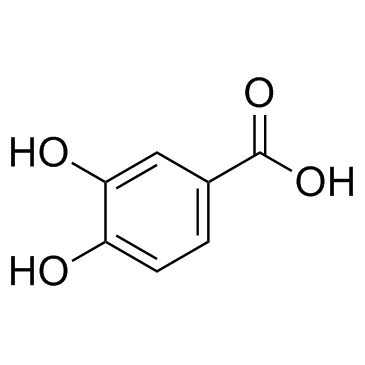 CAS#:99-50-3
CAS#:99-50-3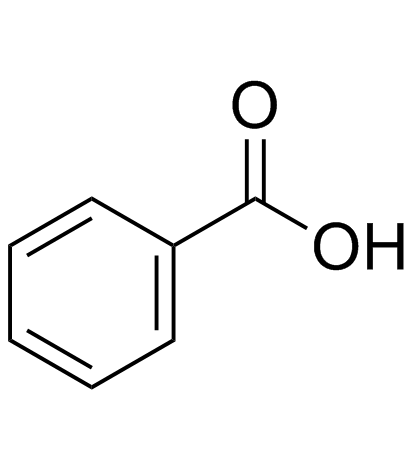 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0 CAS#:613-31-0
CAS#:613-31-0 CAS#:6596-35-6
CAS#:6596-35-6 CAS#:129-43-1
CAS#:129-43-1 CAS#:81-54-9
CAS#:81-54-9
