Sodium theophylline glycinate
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 18:04:12
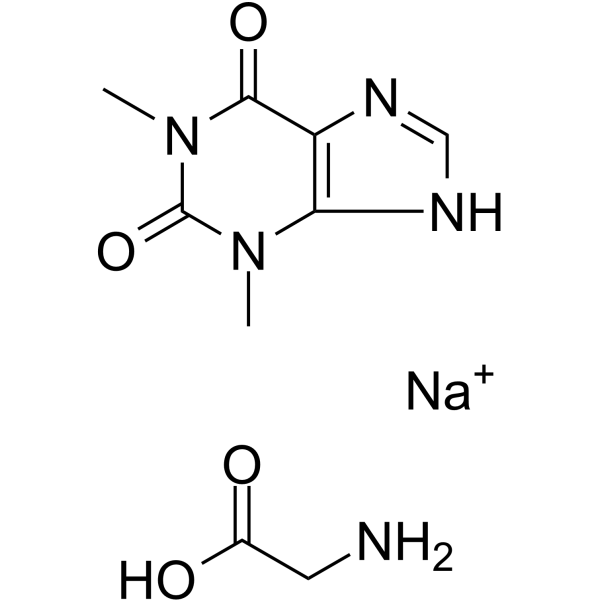
Sodium theophylline glycinate structure
|
Common Name | Sodium theophylline glycinate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8000-10-0 | Molecular Weight | 277.21200 | |
| Density | 1.465 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 454.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12N5NaO4 | Melting Point | 272 - 274ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 228.4ºC | |
Use of Sodium theophylline glycinateTheophylline (1,3-Dimethylxanthine) sodium glycinate is a potent phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor, adenosine receptor antagonist, and histone deacetylase (HDAC) activator. Theophylline sodium glycinate inhibits PDE3 activity to relax airway smooth muscle. Theophylline sodium glycinate has anti-inflammatory activity by increase IL-10 and inhibit NF-κB into the nucleus. Theophylline sodium glycinate induces apoptosis. Theophylline sodium glycinate can be used for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) research[1][2][3][4][5]. |
| Name | Sodium theophylline glycinate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Theophylline (1,3-Dimethylxanthine) sodium glycinate is a potent phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor, adenosine receptor antagonist, and histone deacetylase (HDAC) activator. Theophylline sodium glycinate inhibits PDE3 activity to relax airway smooth muscle. Theophylline sodium glycinate has anti-inflammatory activity by increase IL-10 and inhibit NF-κB into the nucleus. Theophylline sodium glycinate induces apoptosis. Theophylline sodium glycinate can be used for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) research[1][2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Theophylline sodium glycinate (1-1000 µM) inhibits cAMP hydrolysis by PDE in homogenates of bronchial tissue to relax human bronchus and pulmonary arteries[1]. Theophylline sodium glycinate (10 µg/mL; 24 h) induces apoptosis through a reduction in the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 in eosinophils[2]. Theophylline sodium glycinate (0-500 µM; 2 h) inhibits NF-κB activation, I kappa B alpha (I-κBα) degradation and decreases the level of IL-6 in a concentration-dependent manner[3]. Theophylline sodium glycinate (0-1000 µM; 30 min; A549 cells) induces histone deacetylase activity to decrease inflammatory gene expression[4]. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: A549 cells Concentration: 0, 20, 100 and 500 µM Incubation Time: 2 hours Result: Decreased the expression of NF-κB p65 and I-κBα degradation in a dose-dependent manner. |
| In Vivo | Theophylline sodium glycinate (100 mg/kg; i.p.; daily, for 9 d) has anti-inflammatory activity in mice and increases IL-6 and IL-10 levels and inhibits TNF-α and NO in male Swiss mice[1]. Animal Model: Male Swiss mice[1] Dosage: 100 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 9 days Result: Increased IL-6 and IL-10 levels and inhibited TNF-α and NO. |
| References |
[4]. Barnes PJ. Theophylline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Oct 15;188(8):901-6. |
| Density | 1.465 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 454.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 272 - 274ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C9H12N5NaO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 277.21200 |
| Flash Point | 228.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 277.07900 |
| PSA | 138.83000 |
| Sodium 2-aminoacetate 1,3-dimethyl-7H-purine-2,6-dione |