Zofenopril-d5
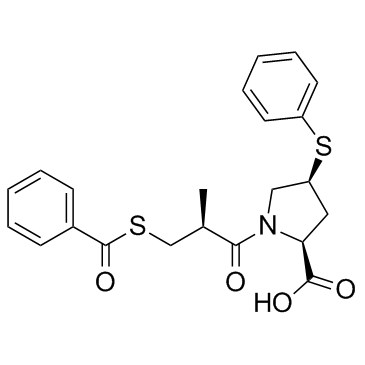
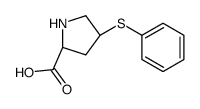
Zofenopril-d5 structure
|
Common Name | Zofenopril-d5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 81872-10-8 | Molecular Weight | 429.552 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 646.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H23NO4S2 | Melting Point | 129-131.5ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 344.7±31.5 °C | |
Use of Zofenopril-d5Zofenopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with an IC50 of 81 μM. |
| Name | zofenopril |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Zofenopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with an IC50 of 81 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 81 μM (ACE)[1] |
| In Vitro | Kinetic analyses demonstrate that enalapril inhibits the uptake of GlySar in a competitive manner (Ki approximately 6 mM). Fosinopril and Zofenopril have the greatest inhibitory potency (IC50 values of 55 and 81μM, respectively) while the other ACE inhibitors exhibit low-affinity interactions with the renal peptide transporter[1]. |
| In Vivo | Zofenopril, a sulphydrylic compound, at doses higher than 70 mg/kg i.p. produces significant protection (i.e. at 70 mg/kg, P=0.044, F=2.17, d.f.=18; at higher concentration P<0.05) against the tonic phase of the audiogenic seizure response. Pretreatment with Zofenopril (15 mg/kg, i.p.) is able to produce a consistent shift to the left of the dose-response curves and a significant reduction of ED50 values against clonus of some AEDs with the exceptions of diazepam, felbamate, phenobarbital and phenytoin compare with concurrent groups, suggesting an increase in anticonvulsant activity[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Studies are performed in rabbit renal brush border membrane vesicles in which the uptake of radiolabeled GlySar is examined in the absence and presence of captopril, enalapril, enalaprilat, fosinopril, lisinopril, quinapril, quinaprilat, ramipril and Zofenopril[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Male and female mice weighing 8 to12 g (22 to 26 days old) or 20 to 28 g (48 to 56 days old) are used. Mice are exposed to auditory stimulation, 45, 60 or 120 min following intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of ACE inhibitors (including Zofenopril) (10 to 100 mg/kg) or vehicle and 45 min following i.p. injection of the AEDs studied. All ACE inhibitors are suspended in a 1% solution of Tween 80 before administration[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 646.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 129-131.5ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C22H23NO4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 429.552 |
| Flash Point | 344.7±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 429.106842 |
| PSA | 125.28000 |
| LogP | 3.78 |
| Appearance of Characters | crystalline | light yellow |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.659 |
| InChIKey | IAIDUHCBNLFXEF-MNEFBYGVSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(CSC(=O)c1ccccc1)C(=O)N1CC(Sc2ccccc2)CC1C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful;Xi: Irritant; |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 23-24/25 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | QJ0875000 |
|
~% 
Zofenopril-d5 CAS#:81872-10-8 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 52, # 13 p. 1493 - 1494 |
|
~% 
Zofenopril-d5 CAS#:81872-10-8 |
| Literature: WO2010/84515 A2, ; Page/Page column 33 ; |
|
~% 
Zofenopril-d5 CAS#:81872-10-8 |
| Literature: WO2010/84515 A2, ; Page/Page column 32 ; |
|
~74% 
Zofenopril-d5 CAS#:81872-10-8 |
| Literature: Krapcho; Turk; Cushman; Powell; DeForrest; Spitzmiller; Karanewsky; Duggan; Rovnvak; Schwartz; Natarajan; Godfrey; Ryono; Neubeck; Atwa; Petrillo Jr. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1988 , vol. 31, # 6 p. 1148 - 1160 |
| L-Proline, 1-[(2S)-3-(benzoylthio)-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl]-4-(phenylthio)-, (4S)- |
| UNII-290ZY759PI |
| (4S)-N-((S)-3-Mercapto-2-methylpropionyl)-4-(phenylthio)-L-proline Benzoate (Ester) |
| Zoprace |
| (1(R*),2a,4a)-1-(3-(Benzoylthio)-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-4-(phenylthio)-L-proline |
| Zofenopril |
| (4S)-1-[(2S)-3-(Benzoylsulfanyl)-2-methylpropanoyl]-4-(phenylsulfanyl)-L-proline |
| Zofenoprilum |
| (2S,4S)-1-[(2S)-3-benzoylsulfanyl-2-methylpropanoyl]-4-phenylsulfanylpyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD00004046 |
| EINECS 201-705-8 |
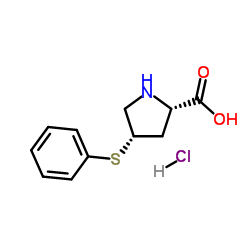
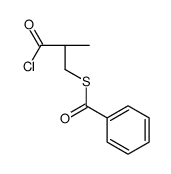
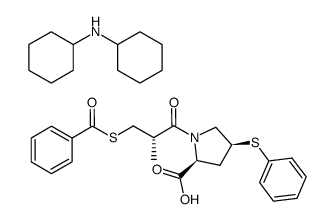

 CAS#:81938-43-4
CAS#:81938-43-4