Rottlerin

Rottlerin structure
|
Common Name | Rottlerin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 82-08-6 | Molecular Weight | 516.539 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 800.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H28O8 | Melting Point | 200 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 266.0±27.8 °C | |
Use of RottlerinRottlerin is a specific PKC inhibitor, with IC50 values for PKCδ of 3-6 μM, PKCα,β,γ of 30-42 μM, PKCε,η,ζ of 80-100 μM. |
| Name | rottlerin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Rottlerin is a specific PKC inhibitor, with IC50 values for PKCδ of 3-6 μM, PKCα,β,γ of 30-42 μM, PKCε,η,ζ of 80-100 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PKCδ:3 μM (IC50, Porcine spleen) PKCα:30 μM (IC50, baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) PKCγ:40 μM (IC50, baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) PKCβ:42 μM (IC50, baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) PKCη:82 μM (IC50, baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) PKCζ:100 μM (IC50, baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) PKCε:100 μM (IC50, baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells) CaM kinase III:5.3 μM (IC50, EF-2 kinase activity in cytosol of murine pancreas) CKII:30 μM (IC50, holoenzyme expressed in E.coli) PKA:78 μM (IC50, catalytic subunit from porcine heart) |
| In Vitro | Rottlerin is a powerful inhibitor of the Ca2+-unresponsive PKCδ with an IC50 of 3 μM for the enzyme from porcine spleen and 6 μM for the recombinant enzyme from baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells. Other PKC isoenzymes provestobe at least one order of magnitude less sensitive for Rottlerin. The IC50 values for the different PKC isoenzymes increased in the following order: δ<α, β, γ<η, ζ, ε[1]. Rottlerin inhibits cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. The combination of both inhibitors (Sorafenib and Rottlerin) is substantially more effective than either single agent and produces a significant decrease in glioma cell survival. The cytotoxic effect of Rottlerin and Sorafenib is further confirmed using a clonogenic assay. There is a dose-dependent decrease in colony forming ability due to Rottlerin and Sorafenib, when administered independently, with the latter having activity at concentrations above 5 μM. In addition, there is striking potentiation of efficacy when the two agents are administered in combination[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells (5×103/well) are plated in 96-well microtiter plates in 100 μL of growth medium, and after overnight attachment, are exposed for 3 days to a range of concentrations of sorafenib and Rottlerin (0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.5, 3, 6, 12, 25, 50 μM), alone and in combination. Control cells receive vehicle alone (DMSO). After the treatment, cells are washed, and the number of viable cells is determined using a colorimetric cell proliferation assay. To perform the assay, 20 μL of MTS/phenazine methosulfate solution is added to each well, and after 1 h of incubation at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere, absorbance is measured at 490 nm in a microplate reader. To directly assess cellular toxicity, 2.5×105 cells are seeded in 60-mm Petri dishes and treated with selected concentrations of inhibitors or vehicle[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 800.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 200 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C30H28O8 |
| Molecular Weight | 516.539 |
| Flash Point | 266.0±27.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 516.178406 |
| PSA | 144.52000 |
| LogP | 8.66 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.682 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Low Level Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Decrease Connexin36 Gap Junction Coupling in Mouse and Human Islets through Nitric Oxide-mediated Protein Kinase Cδ.
J. Biol. Chem. 291 , 3184-96, (2016) Pro-inflammatory cytokines contribute to the decline in islet function during the development of diabetes. Cytokines can disrupt insulin secretion and calcium dynamics; however, the mechanisms underly... |
|
|
PKC theta and p38 MAPK activate the EBV lytic cycle through autophagy induction.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853 , 1586-95, (2015) PKC activation by combining TPA with sodium butyrate (T/B) represents the most effective and widely used strategy to induce the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic cycle. The results obtained in this study... |
|
|
Two types of overcontraction are involved in intrarenal artery dysfunction in type II diabetic mouse.
J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 351(1) , 77-86, (2014) Contractile responses in small intrarenal arteries are associated with diabetic nephropathy. However, the mechanisms that induce and maintain altered small vessel contraction are not clearly understoo... |
| Kamalin |
| 2-Propen-1-one, 1-[6-[(3-acetyl-2,4,6-trihydroxy-5-methylphenyl)methyl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-8-yl]-3-phenyl-, (2E)- |
| Mallotoxin |
| (E)-1-[6-[(3-acetyl-2,4,6-trihydroxy-5-methylphenyl)methyl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethylchromen-8-yl]-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one |
| (2E)-1-[6-(3-Acetyl-2,4,6-trihydroxy-5-methylbenzyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2H-chromen-8-yl]-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one |
| 5,7-Dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-6-(2,4,6-trihydroxy-3-methyl-5-acetylbenzyl)-8-cinnamoyl-1,2-chromene |
| EINECS 201-395-4 |
| MFCD00017361 |
| Rottlerin |
| (2E)-1-[6-(3-Acetyl-2,4,6-trihydroxy-5-methylbenzyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2H-chromen-8-yl]-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-one |
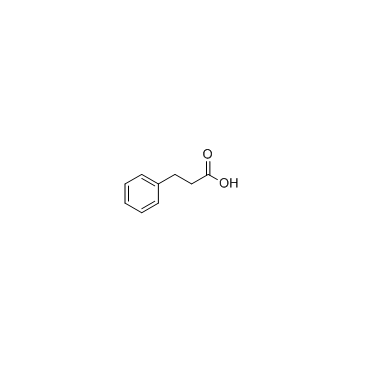 CAS#:501-52-0
CAS#:501-52-0 CAS#:619-89-6
CAS#:619-89-6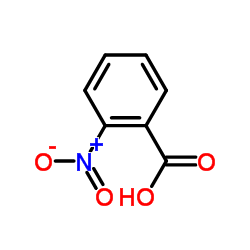 CAS#:552-16-9
CAS#:552-16-9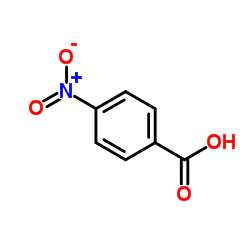 CAS#:62-23-7
CAS#:62-23-7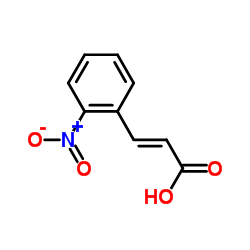 CAS#:612-41-9
CAS#:612-41-9 CAS#:88-03-9
CAS#:88-03-9 CAS#:108-73-6
CAS#:108-73-6 CAS#:621-82-9
CAS#:621-82-9 CAS#:64-19-7
CAS#:64-19-7 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0